|
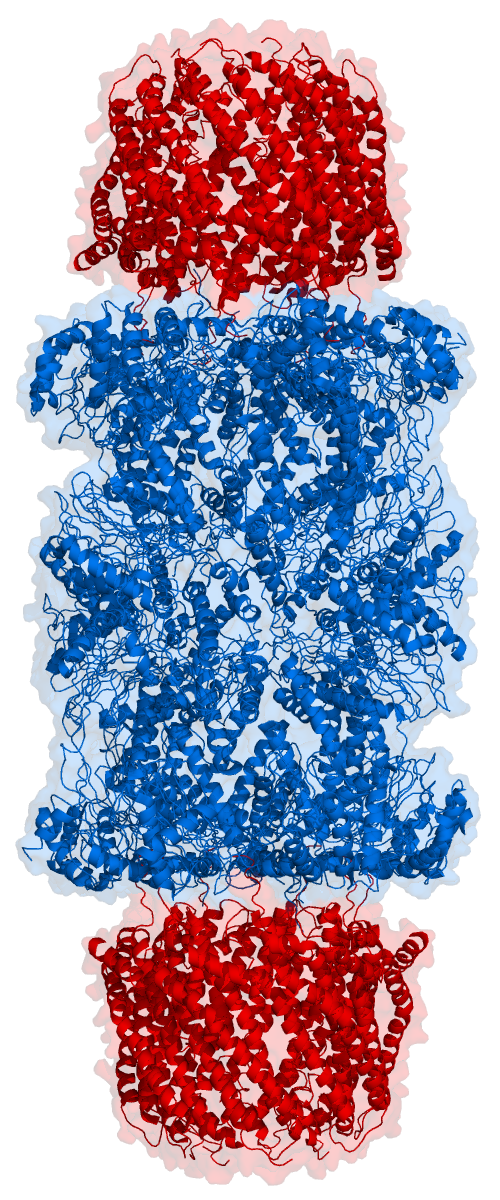
Proteasomes
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A. The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitylation (or, alternatively, ubiquitination or ubiquitinylation). Ubiquitylation affects proteins in many ways: it can mark them for degradation via the proteasome, alter their cellular location, affect their activity, and promote or prevent protein interactions. Ubiquitylation involves three main steps: activation, conjugation, and ligation, performed by ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s), and ubiquitin ligases (E3s), respectively. The result of this sequential cascade is to bind ubiquitin to lysine residues on the protein substrate via an isopeptide bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irwin Rose
Irwin Allan Rose (July 16, 1926 – June 2, 2015) was an American biologist. Along with Aaron Ciechanover and Avram Hershko, he was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. Education and early life Rose was born in Brooklyn, New York, into a secular Jewish family, the son of Ella (Greenwald) and Harry Royze, who owned a flooring store. including the Nobel Lecture on December 8, 2004 ''Ubiquitin at Fox Chase'' Rose attended Washington State University for one year prior to serving in the Navy during World War II. Upon returning from the war he received his Bachelor of Science degree in 1948 and his PhD in biochemistry in 1952, both from the University of Chicago. He did his post-doctoral studies at NYU. Career and research Rose served on the faculty of Yale School of Medicine's department of biochemistry from 1954 to 1963. He then joined the Fox Chase Cancer Center in 1963 and stayed there until he retired in 1995. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avram Hershko
Avram Hershko ( he, אברהם הרשקו, Avraham Hershko, hu, Herskó Ferenc Ábrahám; born December 31, 1937) is a Hungarian-Israeli biochemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2004. Biography He was born Herskó Ferenc in Karcag, Hungary, the son of Shoshana/Margit 'Manci' (née Wulc) and Moshe Hershko, both teachers. including the Nobel Lecture ''The Ubiquitin System for Protein Degradation and some of its Roles in the Control of the Cell Division Cycle'' During the Second World War, his father was forced into labor service in the Hungarian army and then taken as a prisoner by the Soviet Army. For years, Avram's family didn't known anything about what had happened to his father. Avram, his mother and older brother were put in a ghetto in Szolnok. During the final days of the ghetto, most Jews were sent to be murdered in Auschwitz concentration camp, Auschwitz, but Avram and his family managed to board trains that took them to a Nazi concentration camps, concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaron Ciechanover
Aaron Ciechanover ( ; he, אהרן צ'חנובר; born October 1, 1947) is an Israeli biologist who won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for characterizing the method that cells use to degrade and recycle proteins using ubiquitin. Biography Early life Ciechanover was born in Haifa, British Mandate of Palestine on 1 October 1947. He is the son of Bluma (Lubashevsky), a teacher of English, and Yitzhak Ciechanover, an office worker. His mother and father supported the Zionist movement and immigrated to Israel from Poland in the 1920s. Education He earned a master's degree in science in 1971 and graduated from Hadassah Medical School in Jerusalem in 1974. He received his doctorate in biochemistry in 1981 from the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa before conducting postdoctoral research in the laboratory of Harvey Lodish at the Whitehead Institute at MIT from 1981 to 1984. Recent Ciechanover is currently a Technion Distinguished Research Professor in the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "MDCCCXXXIII" above, followed by (smaller) "OB•" then "MDCCCXCVI" below. , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in chemistry , presenter = Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences , location = Stockholm, Sweden , reward = 9 million SEK (2017) , year = 1901 , holder = Carolyn R. Bertozzi, Morten P. Meldal and Karl Barry Sharpless (2022) , most_awards = Frederick Sanger and Karl Barry Sharpless (2) , website nobelprize.org, previous = 2021 , year2=2022, main=2022, next=2023 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal redox state of cells can cause toxic effects through the production of peroxides and free radicals that damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids, and DNA. Oxidative stress from oxidative metabolism causes base damage, as well as strand breaks in DNA. Base damage is mostly indirect and caused by the reactive oxygen species generated, e.g., O2− ( superoxide radical), OH (hydroxyl radical) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide). Further, some reactive oxidative species act as cellular messengers in redox signaling. Thus, oxidative stress can cause disruptions in normal mechanisms of cellular signaling. In humans, oxidative stress is thought to be involved in the development of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life— eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei ( eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate ( binding site) and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate (catalytic site). Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes. Each active site is evolved to be optimised to bind a particular substrate and catalyse a particular reaction, resulting in high specificity. This specificity is determined by the arrangement of amino acids within the active site and the structure of the substrates. Sometimes enzymes also need to bind with some cofactors to fulfil their function. The activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |