|
Pralaya
Pralaya ( sa, प्रलय, , Apocalypse or the Annihilation of the Universe, translit=Pralaya) is a concept in Hindu eschatology. Generally referring to four different phenomena, it is most commonly used to indicate the event of the dissolution of the entire universe that follows a ''kalpa'' (a period of 4.32 billion years) called the ''Brahmapralaya''. Pralaya also refers to ''Nityapralaya'', the continuous destruction of all animate and inanimate beings that occurs on a daily basis, ''Prakritapralaya'', the great flood produced by Prakriti (Nature) that ends all of creation after the completion of the Chaturyuga (four-age) cycle, and ''Atyantikapralaya'', the dissolution of one's Atman (Self) due to its union with Brahman (Ultimate Reality). A concept that has been referenced in literature since the Upanishads, the concept of pralaya has been widely discussed in Hindu cosmology as well as philosophy. Description Hindu cosmology posits an endless cycle of the periodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Cosmology
Hindu cosmology is the description of the universe and its states of matter, cycles within time, physical structure, and effects on living entities according to Hindu texts. Hindu cosmology is also intertwined with the idea of a creator who allows the world to exist and take shape. Matter All matter is based on three inert '' gunas'' (qualities or tendencies):James G. Lochtefeld, Guna, in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism: A-M, Vol. 1, Rosen Publishing, , pages 224, 265, 520Theos Bernard (1999), ''Hindu Philosophy'', Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 74–76 * ''sattva'' (goodness) * ''rajas'' (passion) * '' tamas'' (darkness) There are three states of the ''gunas'' that make up all matter in the universe: * ''pradhana'' (root matter): ''gunas'' in an unmixed and unmanifested state (equilibrium). * '' prakriti'' (primal matter): ''gunas'' in a mixed and unmanifested state (agitated). * '' mahat-tattva'' (matter or universal womb): ''gunas'' in a mixed and manifested state. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
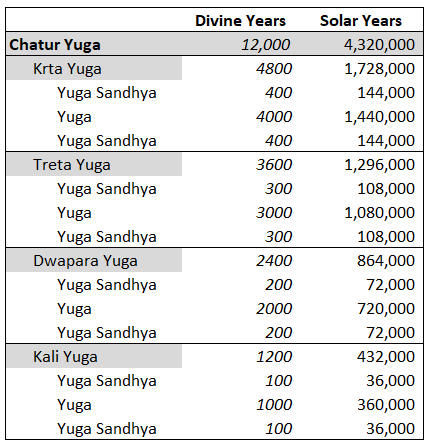
Yuga Cycle
A ''Yuga'' Cycle ( ''chatur yuga'', ''maha yuga'', etc.) is a cyclic age (epoch) in Hindu cosmology. Each cycle lasts for 4,320,000 years (12,000 divine years) and repeats four ''yugas'' (world ages): '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'', ''Treta Yuga'', '' Dvapara Yuga'', and '' Kali Yuga''. As a ''Yuga'' Cycle progresses through the four ''yugas'', each '' yuga's'' length and humanity's general moral and physical state within each ''yuga'' decrease by one-fourth. ''Kali Yuga'', which lasts for 432,000 years, is believed to have started in 3102 BCE. Near the end of ''Kali Yuga'', when virtues are at their worst, a cataclysm and a re-establishment of '' dharma'' occur to usher in the next cycle's ''Satya Yuga'', prophesied to occur by Kalki. There are 71 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''manvantara'' (age of Manu) and 1,000 ''Yuga'' Cycles in a ''kalpa'' (day of Brahma). Lexicology A ''Yuga'' Cycle has several names. Age or ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग, , an age of the gods): : "Age" and "''Yuga''", some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalpa (time)
A ''kalpa'' is a long period of time (aeon) in Hindu and Buddhist cosmology, generally between the creation and recreation of a world or universe. Etymology ''Kalpa'' ( sa, कल्प, , a formation or creation) in this context, means "a long period of time (aeon) related to the lifetime of the universe (creation)." It is derived from ''कॢप्'' (kḷp) + -अ (-a, nominalizing suffix) ( sa, कॢप्, kḷp, to create, prepare, form, produce, compose, invent). Hinduism In Hinduism, a ''kalpa'' is equal to 4.32 billion years, a "day of Brahma" (12-hour day proper) or one thousand '' mahayugas'', measuring the duration of the world. Each ''kalpa'' is divided into 14 ''manvantara'' periods, each lasting 71 ''Yuga Cycles'' (306,720,000 years). Preceding the first and following each ''manvantara'' period is a juncture (''sandhya'') equal to the length of a ''Satya Yuga'' (1,728,000 years). A ''kalpa'' is followed by a ''pralaya'' (dissolution) of equal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treta Yuga
''Treta Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the second and second best of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Krita (Satya) Yuga'' and followed by '' Dvapara Yuga''. ''Treta Yuga'' lasts for 1,296,000 years (3,600 divine years). ''Treta'' means 'a collection of three things' in Sanskrit, and is so called because during the ''Treta Yuga'', there were three Avatars of Vishnu that were seen, the fifth, sixth and seventh incarnations as Vamana, Parashurama and Rama, respectively. The bull of Dharma symbolizes that morality stood on three legs during this period. It had all four legs in the ''Satya Yuga'' and two in the succeeding ''Dvapara Yuga''. Currently, in the immoral age of ''Kali'', it stands on one leg. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived from ' (Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kali Yuga
''Kali Yuga'', in Hinduism, is the fourth and worst of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by '' Dvapara Yuga'' and followed by the next cycle's '' Krita (Satya) Yuga''. It is believed to be the present age, which is full of conflict and sin. The "Kali" of ''Kali Yuga'' means "strife", "discord", "quarrel", or "contention" and ''Kali Yuga'' is associated with the demon Kali (not to be confused with the goddess Kālī). According to Puranic sources, Krishna's death marked the end of '' Dvapara Yuga'' and the start of ''Kali Yuga'', which is dated to 17/18 February 3102 BCE. Lasting for 432,000 years (1,200 divine years), ''Kali Yuga'' began years ago and has years left as of CE. ''Kali Yuga'' will end in the year 428,899 CE. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvapara Yuga
''Dvapara Yuga'' ( Dwapara Yuga), in Hinduism, is the third and third best of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Treta Yuga'' and followed by ''Kali Yuga''. ''Dvapara Yuga'' lasts for 864,000 years (2,400 divine years). According to the Puranas, this ''yuga'' ended when Krishna returned to his eternal abode of Vaikuntha. There are only two pillars of religion during the ''Dvapara Yuga'': compassion and truthfulness. Vishnu assumes the colour yellow and the Vedas are categorized into four parts: ''Rig Veda'', ''Sama Veda'', ''Yajur Veda'' and ''Atharva Veda''. During these times, the Brahmins are knowledgeable of two or three of these but rarely have studied all the four Vedas thoroughly. Accordingly, because of this categorization, different actions and activities come into existence. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satya Yuga
''Satya Yuga'' ( ''Krita Yuga''), in Hinduism, is the first and best of the four ''yugas'' (world ages) in a ''Yuga Cycle'', preceded by ''Kali Yuga'' of the previous cycle and followed by ''Treta Yuga''. ''Satya Yuga'' lasts for 1,728,000 years (4,800 divine years). ''Satya Yuga'' is known as the age of truth, when humanity is governed by gods, and every manifestation or work is close to the purest ideal and humanity will allow intrinsic goodness to rule supreme. It is sometimes referred to as the "Golden Age". The god ''Dharma'' (depicted in the form of a bull), which symbolizes morality, stood on all four legs during this period. The legs of ''Dharma'' reduce by one in each ''yuga'' that follows. Etymology ''Yuga'' ( sa, युग), in this context, means "an age of the world", where its archaic spelling is ''yug'', with other forms of ''yugam'', , and ''yuge'', derived from ''yuj'' ( sa, युज्, , to join or yoke), believed derived from ' (Proto-Indo-European: 'to j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu Purana
The Vishnu Purana (IAST:, sa, विष्णुपुराण) is one of the eighteen Puranas#Mahapuranas, Mahapuranas, a genre of ancient and medieval texts of Hinduism. It is an important Pancharatra text in the Vaishnavism literature corpus. The manuscripts of ''Vishnu Purana'' have survived into the modern era in many versions. More than any other major Purana, the ''Vishnu Purana'' presents its contents in ''Pancalaksana'' format – ''Sarga'' (cosmogony), ''Pratisarga'' (cosmology), ''Vamśa'' (genealogy of the gods, sages and kings), ''Manvantara'' (cosmic cycles), and ''Vamśānucaritam'' (legends during the times of various kings). Some manuscripts of the text are notable for not including sections found in other major Puranas, such as those on ''Mahatmyas'' and tour guides on pilgrimage, but some versions include chapters on temples and travel guides to sacred pilgrimage sites. The text is also notable as the earliest Purana to have been translated and published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Literature
Hindu texts are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. A few of these texts are shared across these traditions and they are broadly considered Hindu scriptures. These include the Puranas, Itihasa and Vedas. Scholars hesitate in defining the term "Hindu scriptures" given the diverse nature of Hinduism,Dominic Goodall (1996), Hindu Scriptures, University of California Press, , page ix-xliii but many list the Bhagavad Gita and the Agamas as Hindu scriptures,Klaus Klostermaier (2007), A Survey of Hinduism: Third Edition, State University of New York Press, , pages 46–52, 76–77 and Dominic Goodall includes Bhagavata Purana and Yajnavalkya Smriti in the list of Hindu scriptures as well. History There are two historic classifications of Hindu texts: ''Śruti'' – that which is heard, and ''Smriti'' – that which is remembered. The ''Shruti'' refers to the body of most authoritative, ancient religious tex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narayana
Narayana (Sanskrit: नारायण, IAST: ''Nārāyaṇa'') is one of the forms and names of Vishnu, who is in yogic slumber under the celestial waters, referring to the masculine principle. He is also known as Purushottama, and is considered the Supreme Being in Vaishnavism. Etymology L. B. Keny proposes that Narayana was associated with the Dravidian, and ultimately, the Indus Valley Civilisation, prior to his syncretism with Vishnu. To this end, he states that the etymology of the deity is associated with the Dravidian ''nara'', meaning water, ''ay'', which in Tamil means "to lie in a place", and ''an'', which is the masculine termination in Dravidian languages. He asserts that this is also the reason why Narayana is represented as lying on a serpent in the sea. He quotes, "This Nārāyana of the Āryan pantheon seems to be the supreme being of the Mohenjo-Darians, a god who was probably styled Ān, a name still kept in Tamil literature as Āndivanam, the prototype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satya-loka
Brahmaloka (Sanskrit: ब्रह्मालोक, IAST: Brahmāloka) or Satyaloka (Sanskrit: सत्यलोक) is the abode of Brahma, the creator god, a member of the Trimurti along with Vishnu and Shiva, along with his consort Saraswati. It is also referred to as Brahmapura, in the Puranas. Brahmaloka, described to be 60,000,000 miles above the Prajapati loka, is considered to be of great soteriological significance, the sphere where its inhabitants never again know death, dwelling perpetually in the company of yogins, and drinking the excellent nectar of yoga. Location In the center of Brahmaloka is Brahmapura, a huge palace where Brahma resides. Description Brahmaloka is a realm composed entirely of Brahman, considered superior to the Svarga loka and is full of immortal energy, knowledge and bliss. It is also known as the planet of the Bhagavān. The above statement shows that Brahmaloka is an eternal Vaikuntha that is neither created nor located within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loka
Loka () is a concept in Hinduism and other Indian religions, that may be translated as a planet, the universe, a plane, or a realm of existence. In some philosophies, it may also be interpreted as a mental state that one can experience. A primary concept in several Indian religions is the idea that different lokas are home to various divine beings, and one takes birth in such realms based on their karma. Hinduism Three lokas The most common classification of lokas in Hinduism is the Trailokya, or the three worlds. The concept of the three worlds has a number of different interpretations in Hindu cosmology. In Hindu literature, the three worlds refer to either the earth (Bhuloka), heaven (Svarga), and hell (Naraka), or the earth (Bhuloka), heaven (Svarga), and the netherworld (Patala) Bhuloka In the Narada Purana, Bhuloka is identified with the planet Earth, the world of human beings. It is described to be split up into seven regions, referred to as dvipas (islands). These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |