|
Polyphenols
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some of which have been used historically as dyes and for tanning garments. Etymology The name derives from the Ancient Greek word (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and the word phenol which refers to a chemical structure formed by attaching to an aromatic benzenoid (phenyl) ring to a hydroxyl (-OH) group as is found in alcohols (hence the ''-ol'' suffix). The term polyphenol has been in use at least since 1894. Definition The term polyphenol is not well-defined, but is generally agreed that they are natural products "having a polyphenol structure (i.e., several hydroxyl groups on aromatic rings)" including four principal classes: "phenolic acids, flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans". *Flavonoids include flavones, flavonols, flavanols, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proanthocyanidin
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in many plants, such as cranberry, blueberry, and grape seeds. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More complex polyphenols, having the same polymeric building block, form the group of tannins. Proanthocyanidins were discovered in 1947 by Jacques Masquelier, who developed and patented techniques for the extraction of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from pine bark and grape seeds. Often associated with prevention of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by consuming cranberries, grape seeds or red wine, proanthocyanidins have not been conclusively shown as effective for preventing or treating UTIs. Distribution in plants Proanthocyanidins, including the lesser bioactive and bioavailable polymers (four or more catechins), represent a group of condensed flavan-3-ols, such as procyanidins, prodelphinidins and propelargonidins. They can be found in many plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods. Occurrence Quercetin is a flavonoid widely distributed in nature. The name has been used since 1857, and is derived from ''quercetum'' (oak forest), after the oak genus ''Quercus''. It is a naturally occurring polar auxin transport inhibitor. Quercetin is one of the most abundant dietary flavonoids, with an average daily consumption of 25–50 milligrams. In red onions, higher concentrations of quercetin occur in the outermost rings and in the part closest to the root, the latter being the part of the plant with the highest concentration. One study found that organically grown tomatoes had 79% more quercetin than non-organically grown fruit. Quercetin is presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate. This latter compound aromatizes. Reactions Oxidation and oxidative coupling Alkaline solutions of gallic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellagic Acid
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid. Name The name comes from the French term ''acide ellagique'', from the word ''galle'' spelled backwards because it can be obtained from ''noix de galle'' ( galls), and to distinguish it from ''acide gallique'' (gallic acid). The molecule structure resembles to that of two gallic acid molecules being assembled "head to tail" and bound together by a C–C bond (as in biphenyl, or in diphenic acid) and two lactone links (cyclic carboxylic esters). Metabolism Biosynthesis Plants produce ellagic acid from hydrolysis of tannins such as ellagitannin and geraniin. Biodegradation Urolithins are gut flora human metabolites of dietary ellagic acid derivatives. Ellagic acid has low bioavailability, with 90% remaining unabsorbed from the intestines until metabolized by microflora to the more bioavailable urolintins. History Ellagic acid was first discovered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechin
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids. The name of the catechin chemical family derives from ''catechu'', which is the tannic juice or boiled extract of ''Mimosa catechu'' (''Acacia catechu'' L.f). Chemistry Catechin possesses two benzene ring Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atom ...s (called the A- and B-rings) and a dihydropyran heterocycle (the C-ring) with a hydroxyl group on carbon 3. The A-ring is similar to a resorcinol moiety while the B-ring is similar to a catechol moiety. There are two chirality (chemistry), chiral centers on the molecule on carbons 2 and 3. Therefore, it has four diastereoisomers. Two of the isomers are in trans configura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignan
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores. Biosynthesis and metabolism Lignans and lignin differ in their molecular weight, the former being small and soluble in water, the latter being high polymers that are undigestable. Both are polyphenolic substances derived by oxidative coupling of monolignols. Thus, most lignans feature a C18 cores, resulting from the dimerization of C9 precursors. The coupling of the lignols occurs at C8. Eight classes of lignans are: "furofuran, furan, dibenzylbutane, dibenzylbutyrolactone, aryltetralin, arylnaphthalene, dibenzocyclooctadiene, and dibenzylbutyrolactol." Many lignans are metabolized by mammalian gut microflora, producing so-called enterolignans. Food sources Flax s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soybeans contain significant amounts of phytic acid, dietary minerals and B vitamins. Soy vegetable oil, used in food and industrial applications, is another product of processing the soybean crop. Soybean is the most important protein source for feed farm animals (that in turn yields animal protein for human consumption). Etymology The word "soy" originated as a corruption of the Cantonese or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanidin
Cyanidin is a natural organic compound. It is a particular type of anthocyanidin (glycoside version called anthocyanins). It is a pigment found in many red berries including grapes, bilberry, blackberry, blueberry, cherry, chokeberry, cranberry, elderberry, hawthorn, loganberry, açai berry and raspberry. It can also be found in other fruits such as apples and plums, and in red cabbage and red onion. It has a characteristic reddish-purple color, though this can change with pH; solutions of the compound are red at pH 11. In certain fruits, the highest concentrations of cyanidin are found in the seeds and skin. Cyanidin has been found to be a potent sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) activator. List of cyanidin derivatives * Antirrhinin (cyanidin-3-rutinoside or 3-C-R), found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3-xylosylrutinoside, found in black raspberry * Cyanidin-3,4′-di-''O''-β-glucopyranoside, found in red onion * Cyanidin-4′-''O''-β-glucoside, found in red onion * Chrysanthemin ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperetin
Hesperetin is the 4'-methoxy derivative of eriodictyol, a flavanone. Hesperetin's 7-O-glycoside, hesperidin, is a naturally occurring flavanon-glycoside, the main flavonoid in lemons and sweet oranges. Hesperetin (and naringenin, the parent flavanone of naringin) are not found to a significant extent in ''Citrus'' spp. Glycosides A variety of glycosides of hesperetin are known, including: * Hesperidin (hesperetin-7-''O''-rutinoside) is a water-insoluble flavonoid glycoside whose solubility is below 5 μg/ml in water. Hesperidin is found in citrus fruits and upon ingestion it releases its aglycone, hesperetin. * Neohesperidin is the 7-''O''-neohesperidoside of hesperetin. * Hesperetin-7-''O''-α-L-Rhamnopyranoside (CAS 66513-83-5) is found in the roots of clammy cherry (''Cordia obliqua'' a.k.a. ''Cordia obliqua'' var. ''wallichii''). Metabolism Hesperidin 6-''O''-α-L-rhamnosyl-β-D-glucosidase is an enzyme that uses hesperidin and H2O to produce hesperetin and rutinose. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
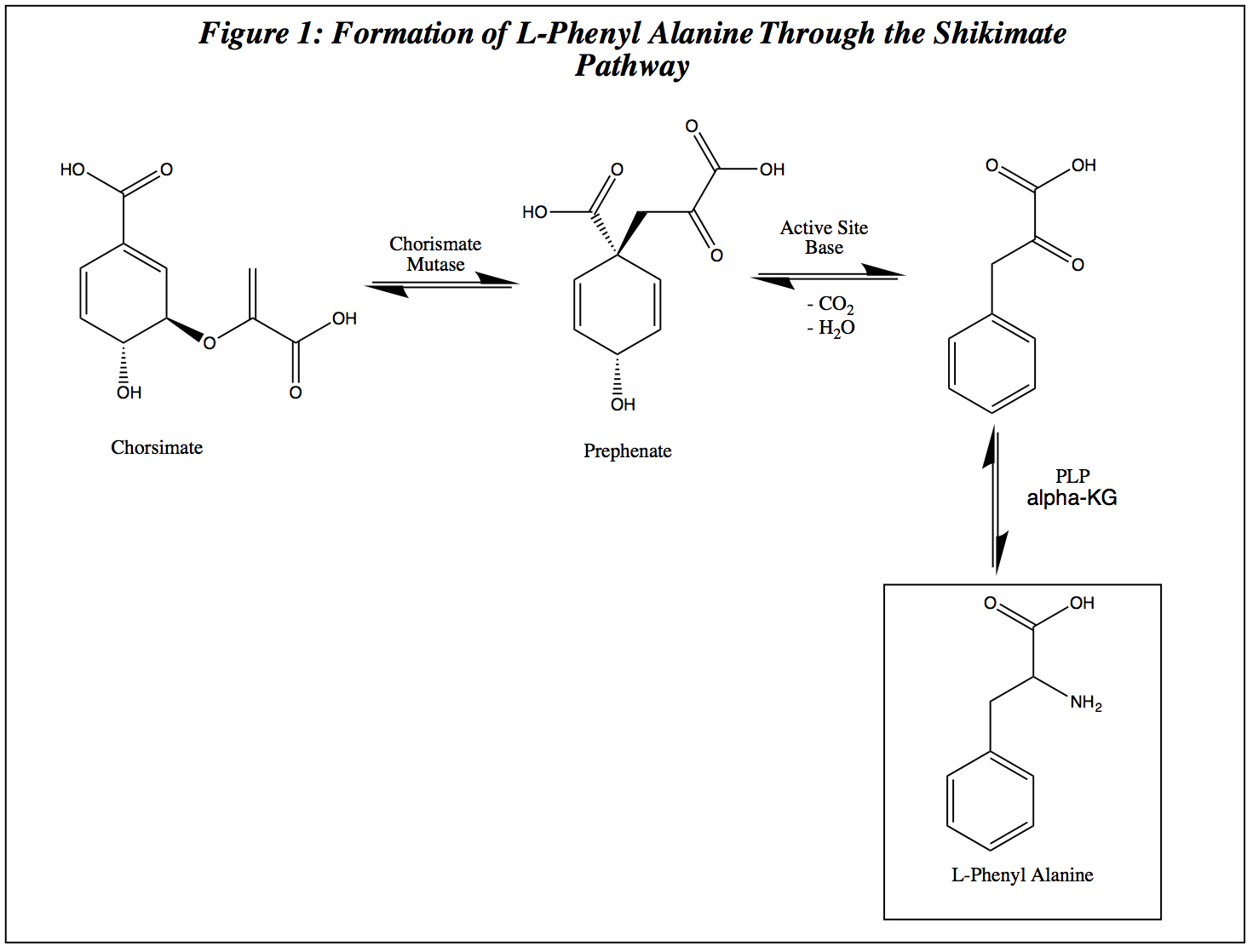
Shikimate
Shikimic acid, more commonly known as its anionic form shikimate, is a cyclohexene, a cyclitol and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is an important biochemical metabolite in plants and microorganisms. Its name comes from the Japanese flower ''shikimi'' (, the Japanese star anise, ''Illicium anisatum''), from which it was first isolated in 1885 by Johan Fredrik Eykman. The elucidation of its structure was made nearly 50 years later. Biosynthesis Phosphoenolpyruvate and erythrose-4-phosphate condense to form 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP), in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme DAHP synthase. DAHP is then transformed to 3-dehydroquinate (DHQ), in a reaction catalyzed by DHQ synthase. Although this reaction requires nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as a cofactor, the enzymic mechanism regenerates it, resulting in the net use of no NAD. : DHQ is dehydrated to 3-dehydroshikimic acid by the enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase, which is reduced to shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be " miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanning (leather)
Tanning is the process of treating Skinning, skins and Hide (skin), hides of animals to produce leather. A tannery is the place where the skins are processed. Tanning hide into leather involves a process which permanently alters the protein structure of skin, making it more durable and less susceptible to decomposition and coloring. Before tanning, the skins are dehaired, degreased, desalted and soaked in water over a period of six hours to two days. Historically this process was considered a noxious or "odoriferous trade" and relegated to the outskirts of town. Historically, tanning used tannin, an acidic chemical compound from which the tanning process draws its name, derived from the bark of certain trees. An alternative method, developed in the 1800s, is chrome tanning, where chromium salts are used instead of natural tannins. History The English word for tanning is from medieval Latin , derivative of (oak bark), from French (tanbark), from old-Cornish (red oak). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |