|
Pneumocytic Hyperplasia
Pneumocytic hyperplasia is an hyperplasia of pneumocytes lining pulmonary alveoli. Types *Pulmonary atypical adenomatous hyperplasia Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia in the lung. It can be a precursor lesion of in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma). In prostate tissue biopsy, it can be confused for adenocarci ... * Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia References Pulmonary lesion {{med-sign-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumocyte
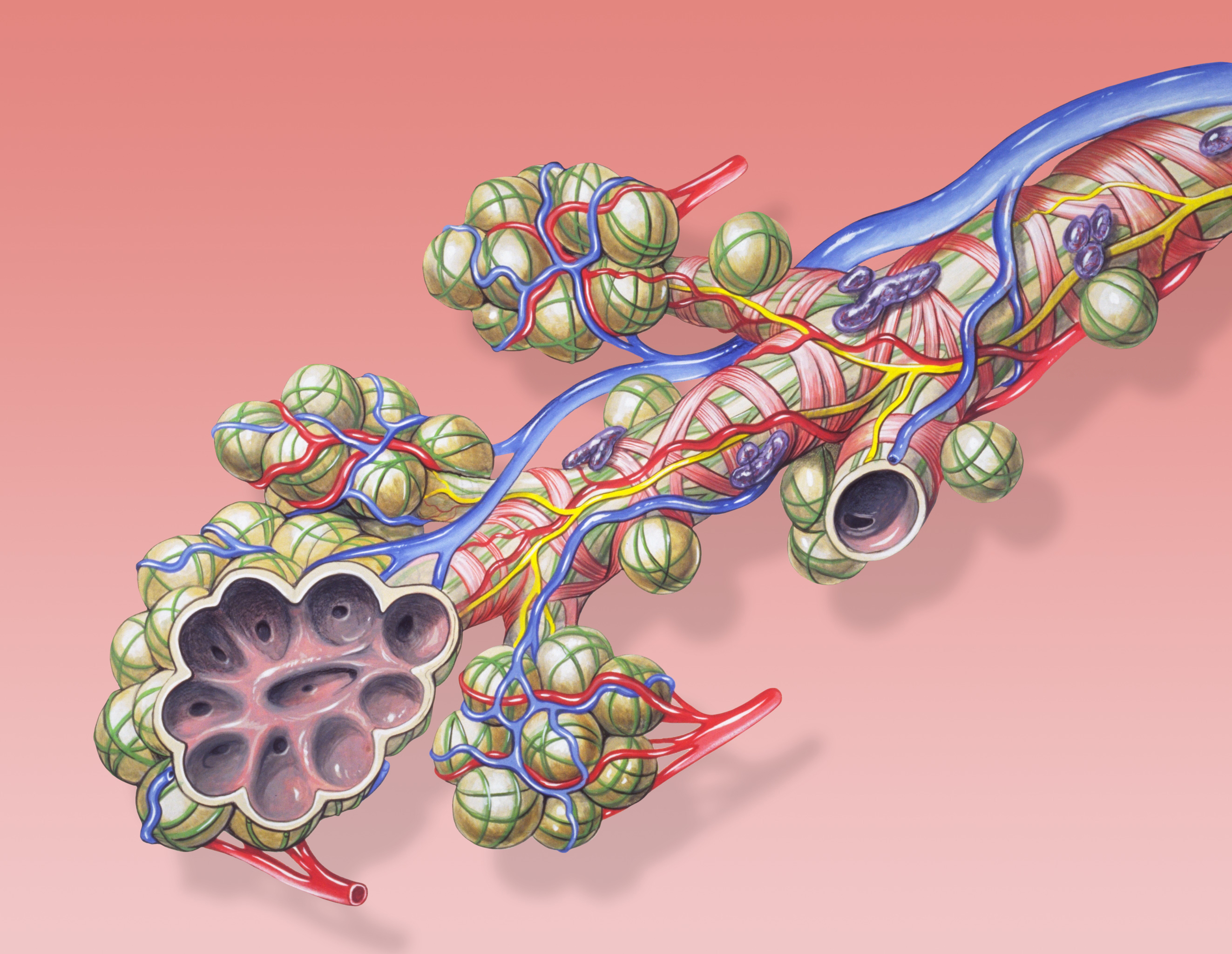
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Alveoli
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia in the lung. It can be a precursor lesion of in situ adenocarcinoma of the lung (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma). In prostate tissue biopsy, it can be confused for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. The needle biopsy rate is less than 1%. Pathology Morphological differential diagnosis * Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) * in situ pulmonary adenocarcinoma (bronchioloalveolar carcinoma – BAC) Variants * multiple atypical adenomatous hyperplasia * disseminated AAH Histopathological images Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(1)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (2) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary adeocaricnoma (3) localized noninvasive type.jpg Image:Pulmonary_adeocaricnoma_(4)_localized_noninvasive_type.jpg See also * EGFR * KRAS ''KRAS'' ( Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called K-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multifocal Micronodular Pneumocyte Hyperplasia
Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia (hyperplasia of pneumocytes lining pulmonary alveoli). Several synonymous terms have been done for this entity: adenomatoid proliferation of alveolar epithelium, papillary alveolar hamartoma, multifocal alveolar hyperplasia, multinodular pneumocyte hyperplasia. These multifocal lesions are observed in tuberous sclerosis, and can be associated with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and perivascular epithelioid cell tumour (PEComa or clear cell " sugar tumor")). It can be diagnosed through lung biopsy using thoracoscopy. Microscopy * Well-demarcated, nodular lesions ranging 2–5 mm in pulmonary parenchyma. * Type II pneumocytes without nuclear atypia lined thickened alveolar septa and proliferated papillary structures. * Enlarged cuboidal cells lining mildly thickened alveolar septa. * Enlarged cuboidal cells have abundant, eosinophilic cytoplasm and large, round nuclei. * Papillary patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |