|
Pkg-config
pkg-config is a computer program that defines and supports a unified interface for querying installed libraries for the purpose of compiling software that depends on them. It allows programmers and installation scripts to work without explicit knowledge of detailed library path information. pkg-config was originally designed for Linux, but it is now also available for BSD, Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Solaris. It outputs various information about installed libraries. This information may include: * Parameters (flags) for C or C++ compiler * Parameters (flags) for linker * Version of the package in question The first implementation was written in shell. Later, it was rewritten in C using the GLib library. Synopsis When a library is installed (automatically through the use of an RPM, deb, or other binary packaging system or by compiling from the source), a .pc file should be included and placed into a directory with other .pc files (the exact directory is dependent upon the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedesktop
freedesktop.org (fd.o) is a project to work on interoperability and shared base technology for free-software desktop environments for the X Window System (X11) and Wayland on Linux and other Unix-like operating systems. It was founded by Havoc Pennington, a GNOME developer working for Red Hat in March 2000. The project's servers are hosted by Portland State University, sponsored by Hewlett-Packard, Intel, and Google. Widely used open-source X-based desktop projects, such as GNOME, KDE's Plasma Desktop, and Xfce, are collaborating with the freedesktop.org project. In 2006, the project released Portland 1.0 (xdg-utils), a set of common interfaces for desktop environments. However, freedesktop.org is a "collaboration zone" for standards and specifications where users can freely discuss ideas, and not a formal standards organization. freedesktop.org was formerly known as the X Desktop Group, and the abbreviation "XDG" remains common in their work. freedesktop.org joined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Libtool
In computer programming, GNU Libtool is a software development tool, part of the GNU build system, consisting of a shell script created to address the software portability problem when compiling shared libraries from source code. It hides the differences between computing platforms for the commands which compile shared libraries. It provides a commandline interface that is identical across platforms and it executes the platform's native commands. Rationale Different operating systems handle shared libraries differently. Some platforms do not use shared libraries at all. It can be difficult to make a software program portable: the C compiler differs from system to system; certain library functions are missing on some systems; header files may have different names. One way to handle this is to write conditional code, with code blocks selected by means of preprocessor directives (#ifdef); but because of the wide variety of build environments this approach quickly becomes u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RPM Package Manager
RPM Package Manager (RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager, now a recursive acronym) is a free and open-source package management system. The name RPM refers to the file format and the package manager program itself. RPM was intended primarily for Linux distributions; the file format is the baseline package format of the Linux Standard Base. Although it was created for use in Red Hat Linux, RPM is now used in many Linux distributions such as PCLinuxOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, CentOS, openSUSE, OpenMandriva and Oracle Linux. It has also been ported to some other operating systems, such as Novell NetWare (as of version 6.5 SP3), IBM's AIX (as of version 4), IBM i, and ArcaOS. An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files. Most RPM files are “binary RPMs” (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also “source RPMs” (or SRPMs) containing the source code used to build a binary package. These have an appropriate tag in the file header tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havoc Pennington
Robert Sanford Havoc Pennington (born c. 1976) is an American computer engineer and entrepreneur. He is known in the free software movement due to his work on HAL, GNOME, Metacity, GConf, and D-Bus. History Havoc Pennington graduated from the University of Chicago in 1998. After graduation, he worked at Red Hat as a Desktop manager/engineer for nine years, ending in 2008. He also founded the project freedesktop.org in 2000. He promoted the idea of the Gnome Online Desktop in 2007. For a time, he led the development of the 2006–2009 Mugshot project. From 2008 until June 2011, he worked on a consumer product for the startup company Litl (hardware, and proprietary software and services). From 2011 to 2015 he worked for Typesafe (now Lightbend). In 2017 he cofounded Tidelift, which seeks to improve the ecosystem around open source software by providing support for professional teams using open source and helping maintainers build sustainable businesses around their projects. Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
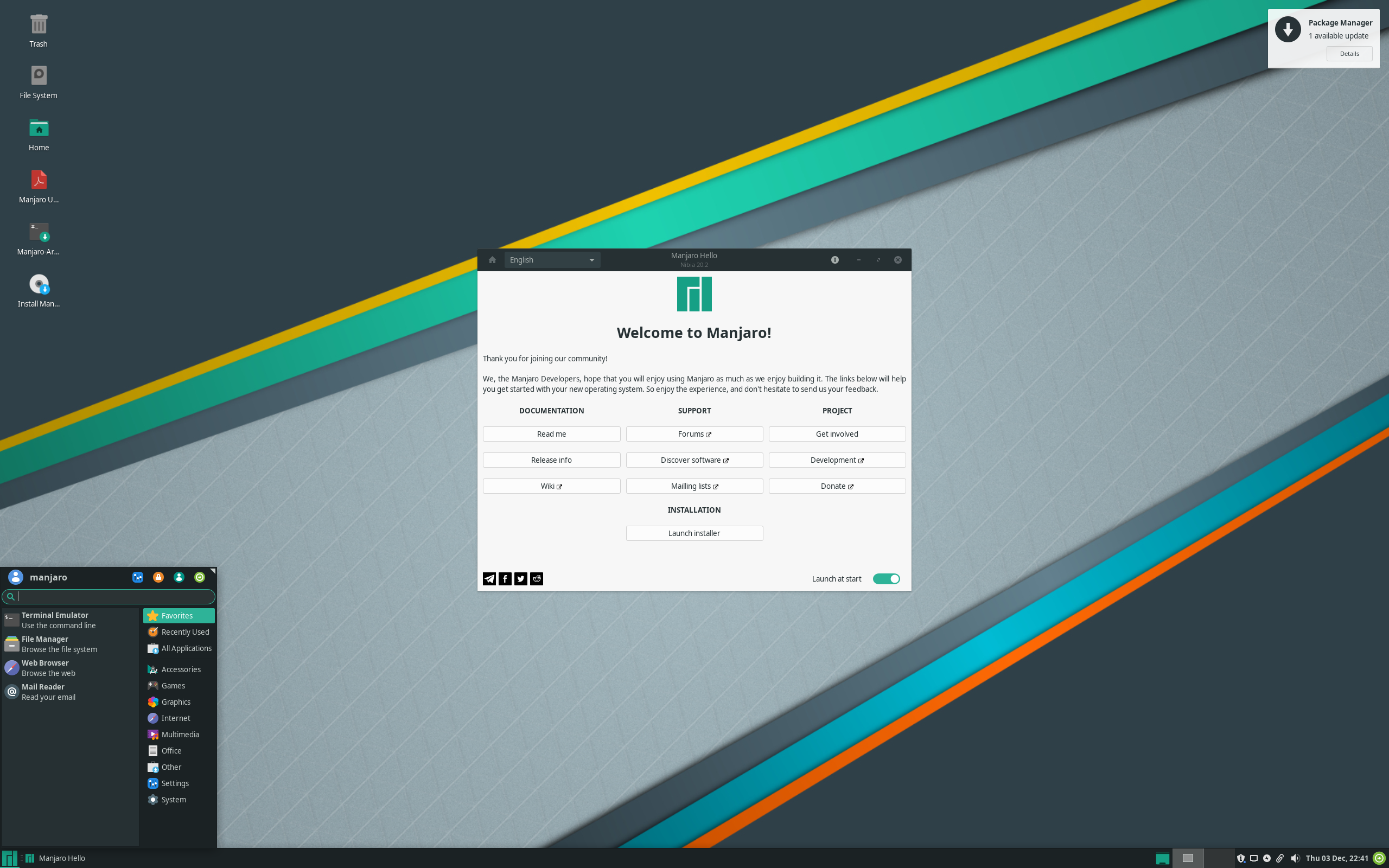
Manjaro
Manjaro ( ) is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on the Arch Linux operating system that has a focus on user-friendliness and accessibility. It uses a rolling release update model and Pacman as its package manager. It is developed mainly in Austria, France and Germany. History Manjaro was first released on July 10, 2011. By mid 2013, Manjaro was in the beta stage, though key elements of the final system had all been implemented such as: a GUI installer (then an Antergos installer fork); a package manager (Pacman) with its choice of frontends; Pamac (GTK) for Xfce desktop and Octopi ( Qt) for its Openbox edition; MHWD (Manjaro Hardware Detection, for detection of free & proprietary video drivers); and Manjaro Settings Manager (for system-wide settings, user management, and graphics driver installation and management). GNOME Shell support was dropped with the release of version 0.8.3 in 2012. However, efforts within Arch Linux made it possible to restart the Cinn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mageia
Mageia is a Linux-based operating system, distributed as free and open source software. It was forked from the Mandriva Linux distribution. The Greek term () means enchantment, fascination, glamour, wizardry. The first release of the software distribution, Mageia 1, took place in June 2011. History Mageia was created in 2010 as a fork of Mandriva Linux, by a group of former employees of Mandriva S.A. and several other members of the Mandriva community. On September 2, 2010, Edge IT, one of the subsidiaries of Mandriva, was placed under liquidation process by the Tribunal de commerce in Paris; effective September 17, all assets were liquidated and employees were let go. The next day, on September 18, 2010, some of these former employees, who were mostly responsible for the development and maintenance of the Mandriva Linux distribution, and several community members announced the creation of Mageia, with the support of many members of the community of developers, users and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular open-source BSD operating system, accounting for more than three-quarters of all installed and permissively licensed BSD systems. FreeBSD has similarities with Linux, with two major differences in scope and licensing: FreeBSD maintains a complete system, i.e. the project delivers a kernel, device drivers, userland utilities, and documentation, as opposed to Linux only delivering a kernel and drivers, and relying on third-parties for system software; FreeBSD source code is generally released under a permissive BSD license, as opposed to the copyleft GPL used by Linux. The FreeBSD project includes a security team overseeing all software shipped in the base distribution. A wide range of additional third-party applications may be installe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fedora (operating System)
Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. Fedora is the upstream (software development), upstream source for Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Since the release of Fedora 35, six different editions are made available tailored to personal computer, server (computing), server, cloud computing, Container (computing), container and Internet of Things installations. A new version of Fedora Linux is released every six months. , Fedora Linux has an estimated 1.2 million users, including Linus Torvalds (), creator of the Linux kernel. Features Fedora has a reputation for focusing on innovation, integrating new technologies early on and working closely with Upstream (software development), upstream Linux communities. Making changes upstream instead of specifically for Fedora Linux ensures that the changes are available t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CentOS
CentOS (, from Community Enterprise Operating System; also known as CentOS Linux) is a Linux distribution that provides a free and open-source community-supported computing platform, functionally compatible with its upstream source, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). In January 2014, CentOS announced the official joining with Red Hat while staying independent from RHEL, under a new CentOS governing board. The first CentOS release in May 2004, numbered as CentOS version 2, was forked from RHEL version 2.1AS. Since version 8, CentOS officially supports the x86-64, ARM64, and POWER8 architectures, and releases up to version 6 also supported the IA-32 architecture. , AltArch releases of CentOS 7 are available for the IA-32 architecture, Power ISA, and for the ARMv7hl and AArch64 variants of the ARM architecture. CentOS 8 was released on 24 September 2019. In December 2020, Red Hat unilaterally terminated CentOS development. In response, CentOS founder Gregory Kurtzer created the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a Rolling release, rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required. #Pacman, Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update Package (package management system), software packages. Arch Linux uses a Rolling release, rolling release model, meaning there are no "major releases" of completely new versions of the system; a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest Arch software; the installation images released every month by the Arch team are simply up-to-date snapshots of the main system components. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation, consisting of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Linux
Alpine Linux is a Linux distribution designed to be small, simple and secure. Alpine Linux uses musl, BusyBox and OpenRC instead of the more commonly used glibc, GNU Core Utilities and systemd respectively.Security-Oriented Alpine Linux 3.7 Has UEFI Support, GRUB Support in Installer ''Softpedia News''10 Most Secure Linux Distros For Complete Privacy & Anonymity , 2017 Edition ''FossBytes'' For security, Alpine compiles all |
CMake
In software development, CMake is cross-platform free and open-source software for build automation, testing, packaging and installation of software by using a compiler-independent method. CMake is not a build system itself; it generates another system's build files. It supports directory hierarchies and applications that depend on multiple libraries. It is used in conjunction with native build environments such as Make, Qt Creator, Ninja, Android Studio, Apple's Xcode, and Microsoft Visual Studio. It has minimal dependencies, requiring only a C++ compiler on its own build system. CMake is distributed as open-source software under a permissive BSD-3-Clause license. History CMake development began in 1999 in response to the need for a cross-platform build environment for the Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit. The project is funded by the United States National Library of Medicine as part of the Visible Human Project. It was partially inspired by pcmaker, which was m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |