|
Peptidylarginine Deiminases
In enzymology, a protein-arginine deiminase () is an enzyme that catalyzes a form of post translational modification called arginine de-imination or citrullination: :protein L-arginine + H2O \rightleftharpoons protein L-citrulline + NH3 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are protein L-arginine (arginine residue inside a protein) and H2O, whereas its two products are protein L-citrulline and NH3: : This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in linear amidines. The systematic name of this enzyme class is protein-L-arginine iminohydrolase. This enzyme is also called peptidylarginine deiminase. Structural studies As of late 2007, seven structures have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes , , , , , , and . Mammalian proteins Mammals have 5 protein-arginine deiminases, with symbols *PADI1, PADI2, PADI3, PADI4, PADI6 except for rodent Rodents (from Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzymology
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
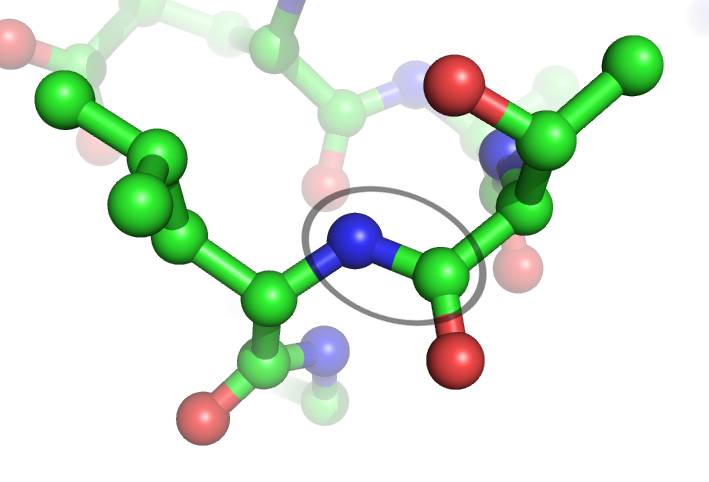
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for New Zealand, Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/richochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Rabbits, hares, and pikas, whose i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PADI4
Protein-arginine deiminase type-4, is a human protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PADI4'' gene. The protein as an enzyme, specifically protein-arginine deiminase, a type of hydrolase. Molecular biology The human gene is found on the short arm of Chromosome 1 near the telomere (1p36.13). It is located on the Watson (plus) strand and is 55,806 bases long. The protein is 663 amino acids long with a molecular weight of 74,095 Da. Function This gene is a member of a gene family which encodes enzymes responsible for the conversion of arginine to citrulline residues ( citrullination). This gene may play a role in granulocyte and macrophage development leading to inflammation and immune response. PADI4 plays a role in the epigenetics, the deimination of arginines on histones H3 and H4 can act antagonistically to arginine methylation. The protein may be found in oligomers and binds 5 calcium ions per subunit. It catalyses the reaction: * Protein L-arginine + H2O = protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PADI3
Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type III, also known as PADI3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PADI3'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family of enzymes, which catalyze the post-translational deimination of proteins by converting arginine residues into citrullines in the presence of calcium ions. The family members have distinct substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression patterns. The type III enzyme modulates hair structural proteins, such as filaggrin in the hair follicle and trichohyalin in the inner root sheath, during hair follicle formation. Together with the type I enzyme, this enzyme may also play a role in terminal differentiation of the epidermis. This gene exists in a cluster with four other paralogous genes. See also *Protein-arginine deiminase In enzymology, a protein-arginine deiminase () is an enzyme that catalyzes a form of post translational modification called arginine de-imination or citrullina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PADI2
Protein-arginine deiminase type-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PADI2'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family of enzymes, which catalyze the post- translational deimination of proteins by converting arginine residues into citrullines in the presence of calcium ions. The family members have distinct substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression patterns. The type II enzyme is the most widely expressed family member. Known substrates for this enzyme include myelin basic protein in the central nervous system and vimentin in skeletal muscle and macrophages. This enzyme is thought to play a role in the onset and progression of neurodegenerative human disorders, including Alzheimer disease and multiple sclerosis, and it has also been implicated in glaucoma pathogenesis. This gene exists in a cluster with four other paralogous Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PADI1
Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type I, also known as PADI1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PADI1'' gene. This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl arginine deiminase family of enzymes, which catalyze the post-translational deimination of proteins by converting arginine residues into citrullines in the presence of calcium ions. The family members have distinct substrate specificities and tissue-specific expression patterns. The type I enzyme is involved in the late stages of epidermal differentiation, where it deiminates filaggrin and keratin K1, which maintains hydration of the stratum corneum, and hence the cutaneous barrier function. This enzyme may also play a role in hair follicle formation. This gene exists in a cluster with four other paralogous Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB. The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology. History Two force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure.Branden C. and Tooze J. "Introduction to Protein Structure" Garland Publishing, New York. 1990 and 1991. A number of tertiary structures may fold into a quaternary structure.Kyte, J. "Structure in Protein Chemistry." Garland Publishing, New York. 1995. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
This article lists enzymes by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. * List of EC numbers (EC 5) * List of EC numbers (EC 6) :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) (Oxidoreductase) *Dehydrogenase * Luciferase *DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) **Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase **Diacetyl reductase **Glycerol dehydrogenase **Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase **L-xylulose reductase **Lactate dehydrogenase **Malate dehydrogenase **Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) **Glucose oxidase **L-gulonolactone oxidase **Thiamine oxidase **Xanthine oxidase * :EC 1.1.4 (with a disul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amidine
Amidines are organic compounds with the functional group RC(NR)NR2, where the R groups can be the same or different. They are the imine derivatives of amides (RC(O)NR2). The simplest amidine is formamidine, HC(=NH)NH2. Examples of amidines include: * DBU * diminazene * benzamidine * Pentamidine * Paranyline Preparation A common route to primary amidines is the Pinner reaction. Reaction of the nitrile with alcohol in the presence of acid gives an iminoether. Treatment of the resulting compound with ammonia then completes the conversion to the amidine. Instead of using a Bronsted acid, Lewis acids such as aluminium trichloride promote the direct amination of nitriles. They are also generated by amination of an imidoyl chloride. They are also prepared by the addition of organolithium reagents to diimines, followed by protonation or alkylation. Dimethylformamide acetal reacts with primary amines to give amidines: :Me2NC(H)(OMe)2 + RNH2 → Me2NC=NHR + 2 MeOH Properties and appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |