|
Peptidyl-tRNA
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria. Initiation Initiation of translation in bacteria involves the assembly of the components of the translation system, which are: the two ribosomal subunits (50S and 30S subunits); the mature mRNA to be translated; the tRNA charged with N-formylmethionine (the first amino acid in the nascent peptide); guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as a source of energy, and the three prokaryotic initiation factors IF1, IF2, and IF3, which help the assembly of the initiation complex. Variations in the mechanism can be anticipated. The ribosome has three active sites: the A site, the P site, and the E site. The ''A site'' is the point of entry for the aminoacyl tRNA (except for the first aminoacyl tRNA, which enters at the P site). The ''P site'' is where the peptidyl tRNA is formed in the ribosome. And the ''E site'' which is the exit site of the now uncharged tRNA after it gives its amino acid to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Release Factor
A release factor is a protein that allows for the termination of translation by recognizing the termination codon or stop codon in an mRNA sequence. They are named so because they release new peptides from the ribosome. Background During translation of mRNA, most codons are recognized by "charged" tRNA molecules, called aminoacyl-tRNAs because they are adhered to specific amino acids corresponding to each tRNA's anticodon. In the standard genetic code, there are three mRNA stop codons: UAG ("amber"), UAA ("ochre"), and UGA ("opal" or "umber"). Although these stop codons are triplets just like ordinary codons, they are not decoded by tRNAs. It was discovered by Mario Capecchi in 1967 that, instead, tRNAs do not ordinarily recognize stop codons at all, and that what he named "release factor" was not a tRNA molecule but a protein. Later, it was demonstrated that different release factors recognize different stop codons. Classification There are two classes of release factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23S Ribosomal RNA
The 23S rRNA is a 2,904 nucleotide long (in '' E. coli'') component of the large subunit ( 50S) of the bacterial/archean ribosome and makes up the peptidyl transferase center (PTC). The 23S rRNA is divided into six secondary structural domains titled I-VI, with the corresponding 5S rRNA being considered domain VII. The ribosomal peptidyl transferase activity resides in domain V of this rRNA, which is also the most common binding site for antibiotics that inhibit translation, making it a target for ribosomal engineering. A well-known member of this antibiotic class, chloramphenicol, acts by inhibiting peptide bond formation, with recent 3D-structural studies showing two different binding sites depending on the species of ribosome. Numerous mutations in domains of the 23S rRNA with Peptidyl transferase activity have resulted in antibiotic resistance. 23S rRNA genes typically have higher sequence variations, including insertions and/or deletions, compared to other rRNAs. The euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
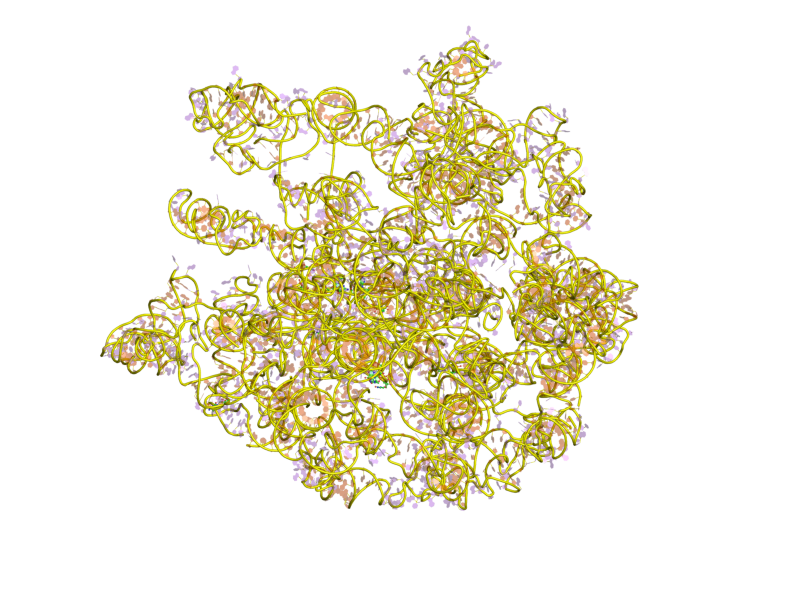
Ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and many ribosomal proteins (RPs or r-proteins). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA chain. Ribosomes bind to messenger RNAs and use their sequences for determining the correct sequence of amino acids to generate a given protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain via an anti-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, genetic inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GTPase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases. Functions GTPases function as molecular switches or timers in many fundamental cellular processes. Examples of these roles include: * Signal transduction in response to activation of cell surface receptors, including transmembrane receptors such as those mediating taste, smell and vision. * Protein biosynthesis (a.k.a. translation) at the ribosome. * Regulation of cell differentiation, proliferation, division and movement. * Translocation of proteins through membranes. * Transport of vesicles within the cell, and vesicle-mediated secretion and uptake, through GTPase control of vesicle coat assembly. GTPases are active when bound to GTP and inactive when bound to GDP. In the generalized recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Growth
250px, Growth is shown as ''L'' = log(numbers) where numbers is the number of colony forming units per ml, versus ''T'' (time.) Bacterial growth is proliferation of bacterium into two daughter cells, in a process called binary fission. Providing no event occurs, the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Hence, bacterial growth occurs. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. However, if the surviving number exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists; the basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony counting), or indirect and bulk (most probable number, turbidity, nutrient uptake) methods. Models reconcile theory with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysome
A polyribosome (or polysome or ergosome) is a group of ribosomes bound to an mRNA molecule like “beads” on a “thread”. It consists of a complex of an mRNA molecule and two or more ribosomes that act to translate mRNA instructions into polypeptides. Originally coined "ergosomes" in 1963, they were further characterized by Jonathan Warner, Paul M. Knopf, and Alex Rich Alexander Rich (15 November 1924 – 27 April 2015) was an American biologist and biophysicist. He was the William Thompson Sedgwick Professor of Biophysics at MIT (since 1958) and Harvard Medical School. Rich earned an A.B. ('' magna cum lau .... Polysomes are formed during the elongation phase when ribosomes and elongation factors synthesize the encoded polypeptide. Multiple ribosomes move along the coding region of mRNA, creating a polysome. The ability of multiple ribosomes to function on an mRNA molecule explains the limited abundance of mRNA in the cell. Polyribosome structure differs between pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome Recycling Factor
Ribosome recycling factor or ribosome release factor (RRF) is a protein found in bacterial cells as well as eukaryotic organelles, specifically mitochondria and chloroplasts. It functions to recycle ribosomes after completion of protein synthesis (bacterial translation). In humans, the mitochrondrial version is coded by the MRRF gene. Discovery The ribosome recycling factor was discovered in the early 1970s by the work of Akira Kaji and Akikazu Hiroshima at the University of Pennsylvania. Their work described the requirement for two protein factors to release ribosomes from mRNA. These two factors were identified as RRF, an unknown protein until then, and Elongation Factor G (EF-G), a protein already identified and known to function in protein synthesis. RRF was originally called Ribosome ''Releasing'' Factor but is now called Ribosome ''Recycling'' Factor. Function RRF accomplishes the recycling of ribosomes by splitting ribosomes into subunits, thereby releasing the bound m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol; they are important in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters typically have a pleasant smell; those of low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and are found in essential oils and pheromones. They perform as high-grade solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers, and are one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market. Polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties. '' Nomenclature Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)