|
Peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
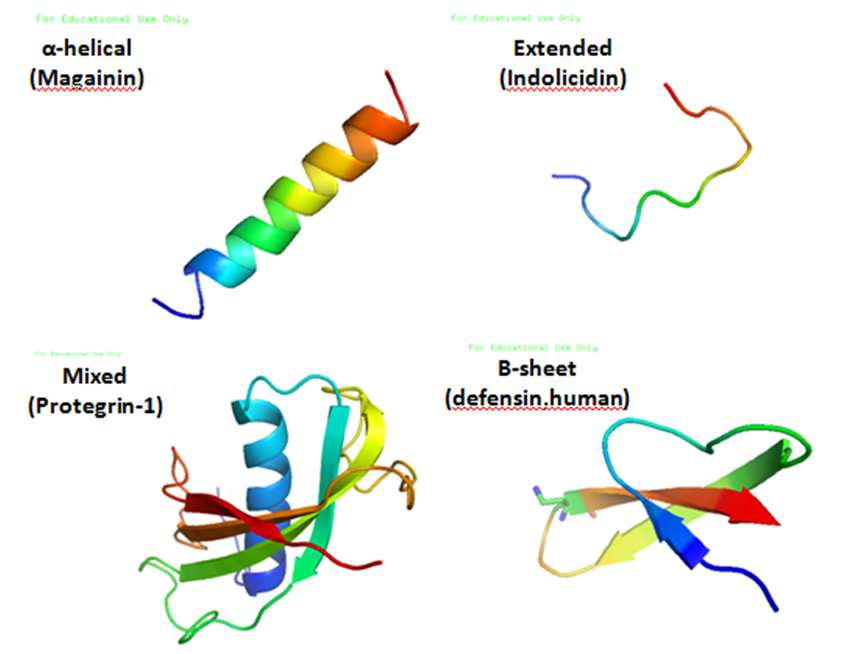
Antimicrobial Peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides are g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipeptide
A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener. Dipeptides are white solids. Many are far more water-soluble than the parent amino acids. For example, the dipeptide Ala-Gln has the solubility of 586 g/L more than 10x the solubility of Gln (35 g/L). Dipeptides also can exhibit different stabilities, e.g. with respect to hydrolysis. Gln does not withstand sterilization procedures, whereas this dipeptide does. Because dipeptides are prone to hydrolysis, the high solubility is exploited in infusions, i.e. to provide nutrition. Examples Commercial value About six dipeptides are of commercial interest. *Aspartame (''N''-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Peptide
Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass. Classification Cyclic peptides can be classified according to the types of bonds that comprise the ring. *Homodetic cyclic peptides, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes including apoptosis, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or misfolded proteins in cells. Consequently, abnormality in the regulation of proteolysis can cause disease. Proteolysis can also be used as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, and it may also be used in industry, for example in food proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligopeptide
An oligopeptide, often just called peptide ('' oligo-'', "a few"), consists of two to twenty amino acids and can include dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and pentapeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides include aeruginosins, cyanopeptolins, microcystins, microviridins, microginins, anabaenopeptins, and cyclamides. Microcystins are best studied, because of their potential toxicity impact in drinking water. A review of some oligopeptides found that the largest class are the cyanopeptolins (40.1%), followed by microcystins (13.4%). Production Oligopeptide classes are produced by nonribosomal peptides synthases (NRPS), except cyclamides and microviridins are synthesized through ribosomic pathways. Examples Examples of oligopeptides include: * Amanitins - Cyclic peptides taken from carpophores of several different mushroom species. They are potent inhibitors of RNA polymerases in most eukaryotic species, the prevent the production of mRNA a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapeptide Structural Formulae V
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides (CTPs), the latter of which mimics protein reverse turns which are often present on the surface of proteins and druggable targets. Tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds. Examples of tetrapeptides are: * Tuftsin (L-threonyl-L-lysyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a peptide related primarily to the immune system function. * Rigin (glycyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a tetrapeptide with functions similar to those of tuftsin. * Postin (Lys-Pro-Pro-Arg) is the N-terminal tetrapeptide of cystatin C and an antagonist of tuftsin. * Endomorphin-1 (H-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) and endomorphin-2 (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) are pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapeptide
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides (CTPs), the latter of which mimics protein reverse turns which are often present on the surface of proteins and druggable targets. Tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds. Examples of tetrapeptides are: * Tuftsin (L-threonyl-L-lysyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a peptide related primarily to the immune system function. * Rigin (glycyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a tetrapeptide with functions similar to those of tuftsin. * Postin (Lys-Pro-Pro-Arg) is the N-terminal tetrapeptide of cystatin C and an antagonist of tuftsin. * Endomorphin-1 (H-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) and endomorphin-2 (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) are pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopolymer
Biopolymers are natural polymers produced by the cells of living organisms. Like other polymers, biopolymers consist of monomeric units that are covalently bonded in chains to form larger molecules. There are three main classes of biopolymers, classified according to the monomers used and the structure of the biopolymer formed: polynucleotides, polypeptides, and polysaccharides. The Polynucleotides, RNA and DNA, are long polymers of nucleotides. Polypeptides include proteins and shorter polymers of amino acids; some major examples include collagen, actin, and fibrin. Polysaccharides are linear or branched chains of sugar carbohydrates; examples include starch, cellulose and alginate. Other examples of biopolymers include natural rubbers (polymers of isoprene), suberin and lignin (complex polyphenolic polymers), cutin and cutan (complex polymers of long-chain fatty acids) and melanin. In addition to their many essential roles in living organisms, biopolymers have applications in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripeptide
A tripeptide is a peptide derived from three amino acids joined by two or sometimes three peptide bonds. As for proteins, the function of peptides is determined by the constituent amino acids and their sequence. The simplest tripeptide is glycine. In terms of scientific investigations, the dominant tripeptide is glutathione (γ-L-Glutamyl-L-cysteinylglycine), which serves many roles in many forms of life. Examples * Eisenin (pGlu-Gln-Ala-OH) is a peptide with immunological activity that is isolated from the Japanese marine alga, ''Eisenia bicyclis'', which more commonly is known as Arame * GHK-Cu (glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) is a human copper binding peptide with wound healing and skin remodeling activity, which is used in anti-aging cosmetics and more commonly referred to as copper peptide *Lactotripeptides (Ile-Pro-Pro and Val-Pro-Pro) found in milk products, act as ACE inhibitors *Leupeptin (''N''-acetyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-argininal) is a protease inhibitor that also acts as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |