|
Pea Aphid
''Acyrthosiphon pisum'', commonly known as the pea aphid (and colloquially known as the green dolphin, pea louse, and clover louse), is a sap-sucking insect in the family Aphididae. It feeds on several species of legumes (plant family Fabaceae) worldwide, including forage crops, such as pea, clover, alfalfa, and broad bean, and ranks among the aphid species of major agronomical importance. The pea aphid is a model organism for biological study whose genome has been sequenced and annotated. Generalities and life cycle In the autumn, female pea aphids lay fertilized eggs overwinter that hatch the following spring. The nymphs that hatch from these eggs are all females, which undergo four moults before reaching sexual maturity. They will then begin to reproduce by viviparous parthenogenesis, like most aphids. Each adult female gives birth to four to 12 female nymphs per day, around a hundred in her lifetime. These develop into mature females in about seven to ten days. The life sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
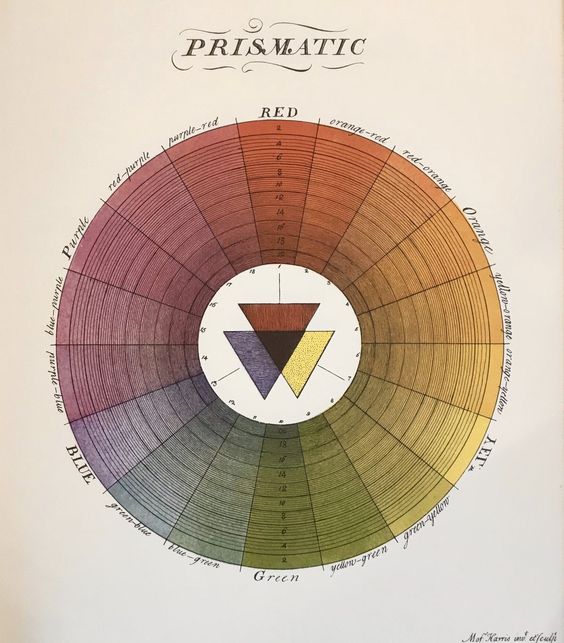
Moses Harris
Moses Harris (15 April 1730 – 1787) was an English entomologist and engraver. Life and work Harris was encouraged in entomology from a young age by his uncle, a member of the Society of the Aurelians. In 1762 he became secretary of a second Society of Aurelians. He was a skilled artist, displaying some of his insect drawings at the Royal Academy in 1785. He drew and engraved illustrations for books including Dru Drury's ''Illustrations of Natural History'' (3 volumes, 1770–1782) and John Coakley Lettsom's ''The Naturalist's and Traveller's Companion'' (1772). Colour theory In "The Natural System of Colours" published in 1766, Harris discussed the multitude of colours that can be created using three "grand or principle" colours: red, yellow and blue. As a naturalist and an engraver, Harris focussed on the relationships between colours and how they are coded and created. He explained how three colours can be íntermixed, tinted and shaded to create 660 colours "materially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylet (anatomy)
A stylet is a hard, sharp, anatomical structure found in some invertebrates. For example, the word ''stylet'' or stomatostyle is used for the primitive piercing mouthparts of some nematodes and some nemerteans. In these groups the stylet is a hardened protrusible opening to the stomach. These stylets are adapted for the piercing of cell walls and usually function by providing the operative organism with access to the nutrients contained within the prey cell. The mouthparts of tardigrades, diptera and aphid Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A t ...s are also called stylets. In octopodes, the stylets are internal, needle-like bent rods within the mantle, the vestigial remnants of an external shell. References Nematode anatomy {{Animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Sap
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separate substance, separately produced, and with different components and functions. Insect honeydew is called sap, particularly when it falls from trees, but is only the remains of eaten sap and other plant parts. Types of sap Saps may be broadly divided into two types: xylem sap and phloem sap. Xylem sap Xylem sap (pronounced ) consists primarily of a watery solution of hormones, mineral elements and other nutrients. Transport of sap in xylem is characterized by movement from the roots toward the leaves. Over the past century, there has been some controversy regarding the mechanism of xylem sap transport; today, most plant scientists agree that the cohesion-tension theory best explains this process, but multiforce theories that hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seedpod
This page provides a glossary of plant morphology. Botanists and other biologists who study plant morphology use a number of different terms to classify and identify plant organs and parts that can be observed using no more than a handheld magnifying lens. This page provides help in understanding the numerous other pages describing plants by their various taxa. The accompanying page—Plant morphology—provides an overview of the science of the external form of plants. There is also an alphabetical list: Glossary of botanical terms. In contrast, this page deals with botanical terms in a systematic manner, with some illustrations, and organized by plant anatomy and function in plant physiology. This glossary primarily includes terms that deal with vascular plants (ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms), particularly flowering plants (angiosperms). Non-vascular plants (bryophytes), with their different evolutionary background, tend to have separate terminology. Although plant morphol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics. Overview In humans, eye color is an example of an inherited characteristic: an individual might inherit the "brown-eye trait" from one of the parents. Inherited traits are controlled by genes and the complete set of genes within an organism's genome is called its genotype. The complete set of observable traits of the structure and behavior of an organism is called its phenotype. These traits arise from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. As a result, many aspects of an organism's phenotype are not inherited. For example, suntanned skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morph (zoology)
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Ford E.B. 1965. ''Genetic polymorphism''. Faber & Faber, London. Put simply, polymorphism is when there are two or more possibilities of a trait on a gene. For example, there is more than one possible trait in terms of a jaguar's skin colouring; they can be light morph or dark morph. Due to having more than one possible variation for this gene, it is termed 'polymorphism'. However, if the jaguar has only one possible trait for that gene, it would be termed "monomorphic". For example, if there was only one possible skin colour that a jaguar could have, it would be termed monomorphic. The term polyphenism can be used to clarify that the different forms arise from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapause
In animal dormancy, diapause is the delay in development in response to regular and recurring periods of adverse environmental conditions.Tauber, M.J., Tauber, C.A., Masaki, S. (1986) ''Seasonal Adaptations of Insects''. Oxford University Press It is a physiological state with very specific initiating and inhibiting conditions. The mechanism is a means of surviving predictable, unfavorable environmental conditions, such as temperature extremes, drought, or reduced food availability. Diapause is observed in all the life stages of arthropods, especially insects. Embryonic diapause, a somewhat similar phenomenon, occurs in over 130 species of mammals, possibly even in humans, and in the embryos of many of the oviparous species of fish in the order Cyprinodontiformes. Activity levels of diapausing stages can vary considerably among species. Diapause may occur in a completely immobile stage, such as the pupae and eggs, or it may occur in very active stages that undergo extensive migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea and eubacteria, bacteria. Many Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms including plants, animals, and Fungus, fungi can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Komodo dragons and some monitor lizards can also reproduce asexually. While all prokaryotes reproduce without the formation and fusion of gametes, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods such as insects, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother. At and up to , the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overwintering
Overwintering is the process by which some organisms pass through or wait out the winter season, or pass through that period of the year when "winter" conditions (cold or sub-zero temperatures, ice, snow, limited food supplies) make normal activity or even survival difficult or near impossible. In some cases "winter" is characterized not necessarily by cold but by dry conditions; passing through such periods could likewise be called overwintering. Hibernation and migration are the two major ways in which overwintering is accomplished. Animals may also go into a state of reduced physiological activity known as torpor. Overwintering occurs in several classes of lifeform. Insects In entomology, overwintering is how an insect passes the winter season. Many insects overwinter as adults, pupae, or eggs. This can be done inside buildings, under tree bark, or beneath fallen leaves or other plant matter on the ground, among other places. All such overwintering sites shield the insect fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_with_its_prey.jpg)







