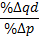|
Parameterized Family
In mathematics and its applications, a parametric family or a parameterized family is a indexed family, family of objects (a set of related objects) whose differences depend only on the chosen values for a set of parameters. Common examples are parametrized (families of) Function (mathematics), functions, probability distributions, curves, shapes, etc. In probability and its applications For example, the probability density function of a random variable may depend on a parameter . In that case, the function may be denoted f_X( \cdot \, ; \theta) to indicate the dependence on the parameter . is not a formal argument of the function as it is considered to be fixed. However, each different value of the parameter gives a different probability density function. Then the ''parametric family'' of densities is the set of functions \ , where denotes the parameter space, the set of all possible values that the parameter can take. As an example, the normal distribution is a family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobb Douglas
Cobb may refer to: People * Cobb (surname), a list of people and fictional characters with the surname Cobb * Cobb Rooney (1900–1973), American professional football running back Places New Zealand * Cobb River * Cobb Reservoir * Cobb Power Station United Kingdom * The Cobb, the harbour wall in Lyme Regis, England United States * Cobb, California, a census designated place * Cobb, former name of Pine Grove, Lake County, California * Cobb Mountain, California * Cobb County, Georgia * Cobb, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Cobb, Indiana, an unincorporated town * Cobb, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * Cobb, Oklahoma, an unincorporated community * Cobb Peak (Idaho) * Cobb Peak, Tooele County, Utah * Cobb River (Minnesota) * Cobb, St. Clair County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Cobb, Stoddard County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Cobb, Texas, an unincorporated community * Mount Cobb, Washington County, Vermont, Vermont * Cobb Town, Wiscon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indexed Family
In mathematics, a family, or indexed family, is informally a collection of objects, each associated with an index from some index set. For example, a ''family of real numbers, indexed by the set of integers'' is a collection of real numbers, where a given function selects one real number for each integer (possibly the same). More formally, an indexed family is a mathematical function together with its domain I and image X. (that is, indexed families and mathematical functions are technically identical, just point of views are different.) Often the elements of the set X are referred to as making up the family. In this view, indexed families are interpreted as collections of indexed elements instead of functions. The set I is called the ''index set'' of the family, and X is the ''indexed set''. Sequences are one type of families indexed by natural numbers. In general, the index set I is not restricted to be countable. For example, one could consider an uncountable family of sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Term
In mathematics, a constant term is a term in an algebraic expression that does not contain any variables and therefore is constant. For example, in the quadratic polynomial :x^2 + 2x + 3,\ the 3 is a constant term. After like terms are combined, an algebraic expression will have at most one constant term. Thus, it is common to speak of the quadratic polynomial :ax^2+bx+c,\ where x is the variable, as having a constant term of c. If the constant term is 0, then it will conventionally be omitted when the quadratic is written out. Any polynomial written in standard form has a unique constant term, which can be considered a coefficient of x^0. In particular, the constant term will always be the lowest degree term of the polynomial. This also applies to multivariate polynomials. For example, the polynomial :x^2+2xy+y^2-2x+2y-4\ has a constant term of −4, which can be considered to be the coefficient of x^0y^0, where the variables are eliminated by being exponentiated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves variables, they may also be called parameters. For example, the polynomial 2x^2-x+3 has coefficients 2, −1, and 3, and the powers of the variable x in the polynomial ax^2+bx+c have coefficient parameters a, b, and c. The constant coefficient is the coefficient not attached to variables in an expression. For example, the constant coefficients of the expressions above are the number 3 and the parameter ''c'', respectively. The coefficient attached to the highest degree of the variable in a polynomial is referred to as the leading coefficient. For example, in the expressions above, the leading coefficients are 2 and ''a'', respectively. Terminology and definition In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Equation
In algebra, a quadratic equation () is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,, where represents an unknown (mathematics), unknown value, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and then the equation is linear equation, linear, not quadratic.) The numbers , , and are the ''coefficients'' of the equation and may be distinguished by respectively calling them, the ''quadratic coefficient'', the ''linear coefficient'' and the ''constant'' or ''free term''. The values of that satisfy the equation are called ''solution (mathematics), solutions'' of the equation, and ''zero of a function, roots'' or ''zero of a function, zeros'' of the Expression (mathematics), expression on its left-hand side. A quadratic equation has at most two solutions. If there is only one solution, one says that it is a double root. If all the coefficients are real numbers, there are either two real solutions, or a single real double root, or two complex number, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Elementary algebra deals with the manipulation of variables (commonly represented by Roman letters) as if they were numbers and is therefore essential in all applications of mathematics. Abstract algebra is the name given, mostly in education, to the study of algebraic structures such as groups, rings, and fields (the term is no more in common use outside educational context). Linear algebra, which deals with linear equations and linear mappings, is used for modern presentations of geometry, and has many practical applications (in weather forecasting, for example). There are many areas of mathematics that belong to algebra, some having "algebra" in their name, such as commutative algebra, and some not, such as Galois theory. The word ''algebra'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Equation Coefficients
In mathematics, the term quadratic describes something that pertains to squares, to the operation of squaring, to terms of the second degree, or equations or formulas that involve such terms. ''Quadratus'' is Latin for ''square''. Mathematics Algebra (elementary and abstract) * Quadratic function (or quadratic polynomial), a polynomial function that contains terms of at most second degree ** Complex quadratic polynomials, are particularly interesting for their sometimes chaotic properties under iteration * Quadratic equation, a polynomial equation of degree 2 (reducible to 0 = ''ax''2 + ''bx'' + ''c'') * Quadratic formula, calculation to solve a quadratic equation for the independent variable (''x'') * Quadratic field, an algebraic number field of degree two over the field of rational numbers * Quadratic irrational or "quadratic surd", an irrational number that is a root of a quadratic polynomial Calculus * Quadratic integral, the integral of the reciprocal of a second-d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Factors Of Production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output—that is, goods and services. The utilized amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the relationship called the production function. There are four ''basic'' resources or factors of production: land, labour, capital and entrepreneur (or enterprise). The factors are also frequently labeled "producer goods or services" to distinguish them from the goods or services purchased by consumers, which are frequently labeled "consumer goods". There are two types of factors: ''primary'' and ''secondary''. The previously mentioned primary factors are land, labour and capital. Materials and energy are considered secondary factors in classical economics because they are obtained from land, labour, and capital. The primary factors facilitate production but neither becomes part of the product (as with raw materials) nor becomes significantly tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (economics)
In economics, elasticity measures the percentage change of one economic variable in response to a percentage change in another. If the price elasticity of the demand of something is -2, a 10% increase in price causes the demand quantity to fall by 20%. Introduction Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in the understanding of various economic concepts, such as the incidence of indirect taxation, marginal concepts relating to the theory of the firm, distribution of wealth, and different types of goods relating to the theory of consumer choice. An understanding of elasticity is also important when discussing welfare distribution, in particular consumer surplus, producer surplus, or government surplus. Elasticity is present throughout many economic theories, with the concept of elasticity appearing in several main indicators. These include price elasticity of demand, price elasticity of supply, income elasticity of demand, elastici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production Function
In economics, a production function gives the technological relation between quantities of physical inputs and quantities of output of goods. The production function is one of the key concepts of mainstream neoclassical theories, used to define marginal product and to distinguish allocative efficiency, a key focus of economics. One important purpose of the production function is to address allocative efficiency in the use of factor inputs in production and the resulting distribution of income to those factors, while abstracting away from the technological problems of achieving technical efficiency, as an engineer or professional manager might understand it. For modelling the case of many outputs and many inputs, researchers often use the so-called Shephard's distance functions or, alternatively, directional distance functions, which are generalizations of the simple production function in economics. In macroeconomics, aggregate production functions are estimated to create a fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
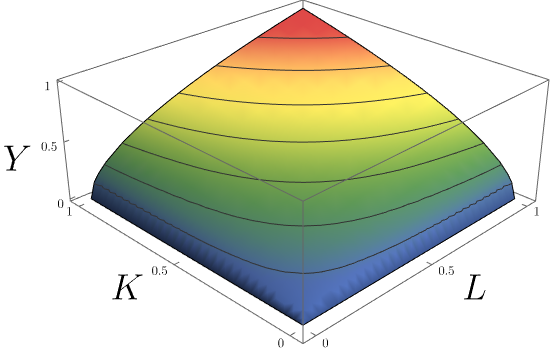
Cobb–Douglas Production Function
In economics and econometrics, the Cobb–Douglas production function is a particular functional form of the production function, widely used to represent the technological relationship between the amounts of two or more inputs (particularly physical capital and labor) and the amount of output that can be produced by those inputs. The Cobb–Douglas form was developed and tested against statistical evidence by Charles Cobb and Paul Douglas between 1927 and 1947; according to Douglas, the functional form itself was developed earlier by Philip Wicksteed. Formulation In its most standard form for production of a single good with two factors, the function is : Y=AL^\beta K^\alpha where: * ''Y'' = total production (the real value of all goods produced in a year or 365.25 days) * ''L'' = labour input (person-hours worked in a year or 365.25 days) * ''K'' = capital input (a measure of all machinery, equipment, and buildings; the value of capital input divided by the price of capi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |