|
Parallactic Angle
In spherical astronomy, the parallactic angle is the angle between the great circle through a celestial object and the zenith, and the hour circle of the object. It is usually denoted ''q''. In the triangle zenith—object—celestial pole, the parallactic angle will be the position angle of the zenith at the celestial object. Despite its name, this angle is unrelated with parallax. The parallactic angle is zero or 180° when the object crosses the meridian. Uses For ground-based observatories, the Earth atmosphere acts like a prism which disperses light of different wavelengths such that a star generates a rainbow along the direction that points to the zenith. So given an astronomical picture with a coordinate system with a known direction to the Celestial pole, the parallactic angle represents the direction of that prismatic effect relative to that reference direction. Knowledge of that angle is needed to align Atmospheric Dispersion Correctors with the beam axis of the teles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Astronomy
Spherical astronomy, or positional astronomy, is a branch of observational astronomy used to locate astronomical objects on the celestial sphere, as seen at a particular date, time, and location on Earth. It relies on the mathematical methods of spherical geometry and the measurements of astrometry. This is the oldest branch of astronomy and dates back to antiquity. Observations of celestial objects have been, and continue to be, important for religious and astrological purposes, as well as for timekeeping and navigation. The science of actually measuring positions of celestial objects in the sky is known as astrometry. The primary elements of spherical astronomy are celestial coordinate systems and time. The coordinates of objects on the sky are listed using the equatorial coordinate system, which is based on the projection of Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere. The position of an object in this system is given in terms of right ascension (α) and declination (δ). The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnal Motion
Diurnal motion (, ) is an astronomical term referring to the apparent motion of celestial objects (e.g. the Sun and stars) around Earth, or more precisely around the two celestial poles, over the course of one day. It is caused by Earth's rotation around its axis, so almost every star appears to follow a circular arc path, called the diurnal circle, often depicted in star trail photography. The time for one complete rotation is 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds – one sidereal day. The first experimental demonstration of this motion was conducted by Léon Foucault. Because Earth orbits the Sun once a year, the sidereal time at any given place and time will gain about four minutes against local civil time, every 24 hours, until, after a year has passed, one additional sidereal "day" has elapsed compared to the number of solar days that have gone by. Relative direction The relative direction of diurnal motion in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere are as follows: * Facing nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altazimuth Mount
An altazimuth mount or alt-azimuth mount is a simple two-axis mount for supporting and rotating an instrument about two perpendicular axes – one vertical and the other horizontal. Rotation about the vertical axis varies the azimuth (compass bearing) of the pointing direction of the instrument. Rotation about the horizontal axis varies the altitude angle (angle of elevation) of the pointing direction. These mounts are used, for example, with telescopes, cameras, radio antennas, heliostat mirrors, solar panels, and guns and similar weapons. Several names are given to this kind of mount, including altitude-azimuth, azimuth-elevation and various abbreviations thereof. A gun turret is essentially an alt-azimuth mount for a gun, and a standard camera tripod is an alt-azimuth mount as well. Astronomical telescope altazimuth mounts When used as an astronomical telescope mount, the biggest advantage of an alt-azimuth mount is the simplicity of its mechanical design. The primary disadv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Mount
An equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that compensates for Earth's rotation by having one rotational axis, the polar axis, parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. This type of mount is used for astronomical telescopes and cameras. The advantage of an equatorial mount lies in its ability to allow the instrument attached to it to stay fixed on any celestial object with diurnal motion by driving one axis at a constant speed. Such an arrangement is called a sidereal or clock drive. Equatorial mounts achieve this by aligning their rotational axis with the Earth, a process known as polar alignment. Astronomical telescope mounts In astronomical telescope mounts, the equatorial axis (the '' right ascension'') is paired with a second perpendicular axis of motion (known as the '' declination''). The equatorial axis of the mount is often equipped with a motorized "''clock drive''", that rotates that axis one revolution every 23 hours and 56 minutes in exact sync with the appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libration
In lunar astronomy, libration is the wagging or wavering of the Moon perceived by Earth-bound observers and caused by changes in their perspective. It permits an observer to see slightly different hemispheres of the surface at different times. It is similar in both cause and effect to the changes in the Moon's apparent size due to changes in distance. It is caused by three mechanisms detailed below, two of which cause a relatively tiny physical libration via tidal forces exerted by the Earth. Such true librations are known as well for other moons with locked rotation. The quite different phenomenon of a trojan asteroid's movement has been called ''Trojan libration''; and ''Trojan libration point'' means Lagrangian point. Lunar libration The Moon keeps one hemisphere of itself facing the Earth, due to tidal locking. Therefore, the first view of the far side of the Moon was not possible until the Soviet probe Luna 3 reached the Moon on October 7, 1959, and further lunar exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereal Time
Sidereal time (as a unit also sidereal day or sidereal rotation period) (sidereal ) is a timekeeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time, it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coordinates in the night sky. In short, sidereal time is a "time scale that is based on Earth's rate of rotation measured relative to the fixed stars", or more correctly, relative to the March equinox. Viewed from the same location, a star seen at one position in the sky will be seen at the same position on another night at the same sidereal time. This is similar to how the time kept by a sundial (Solar time) can be used to find the location of the Sun. Just as the Sun and Moon appear to rise in the east and set in the west due to the rotation of Earth, so do the stars. Both Solar time and sidereal time make use of the regularity of Earth's rotation about its polar axis: solar time following the Sun while, roughly speaking, sidereal time follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
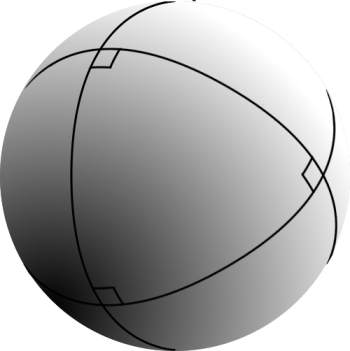
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
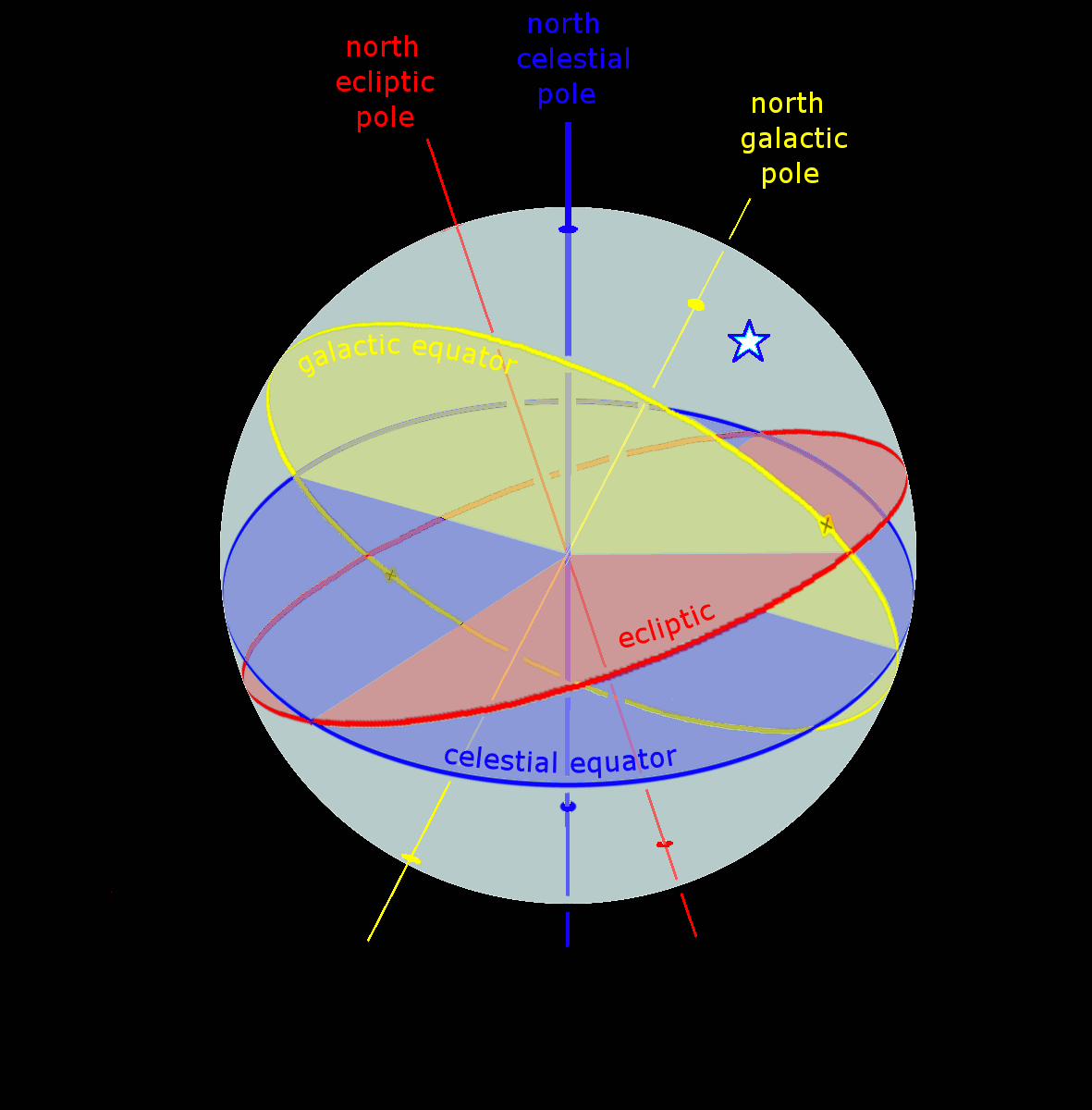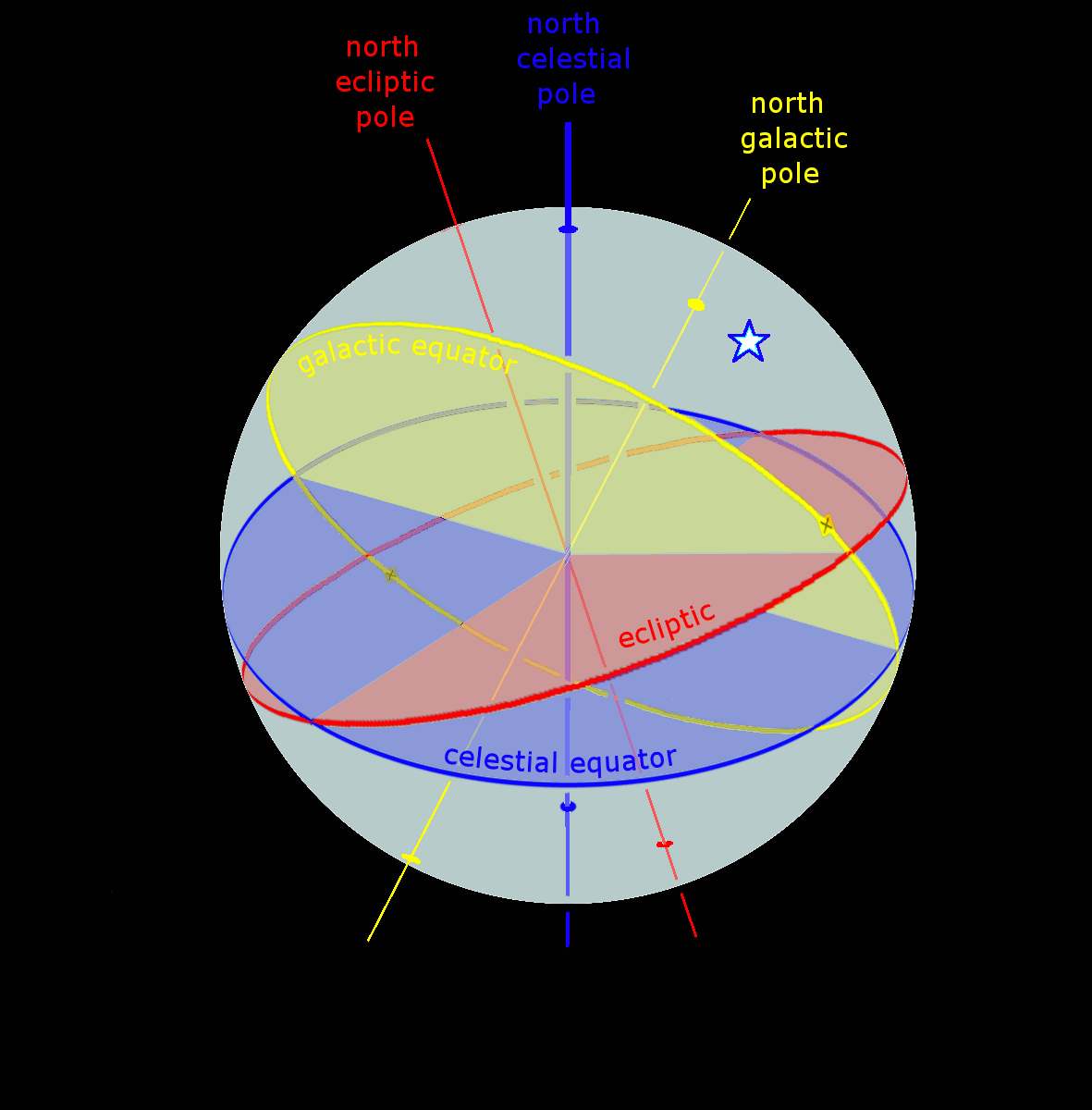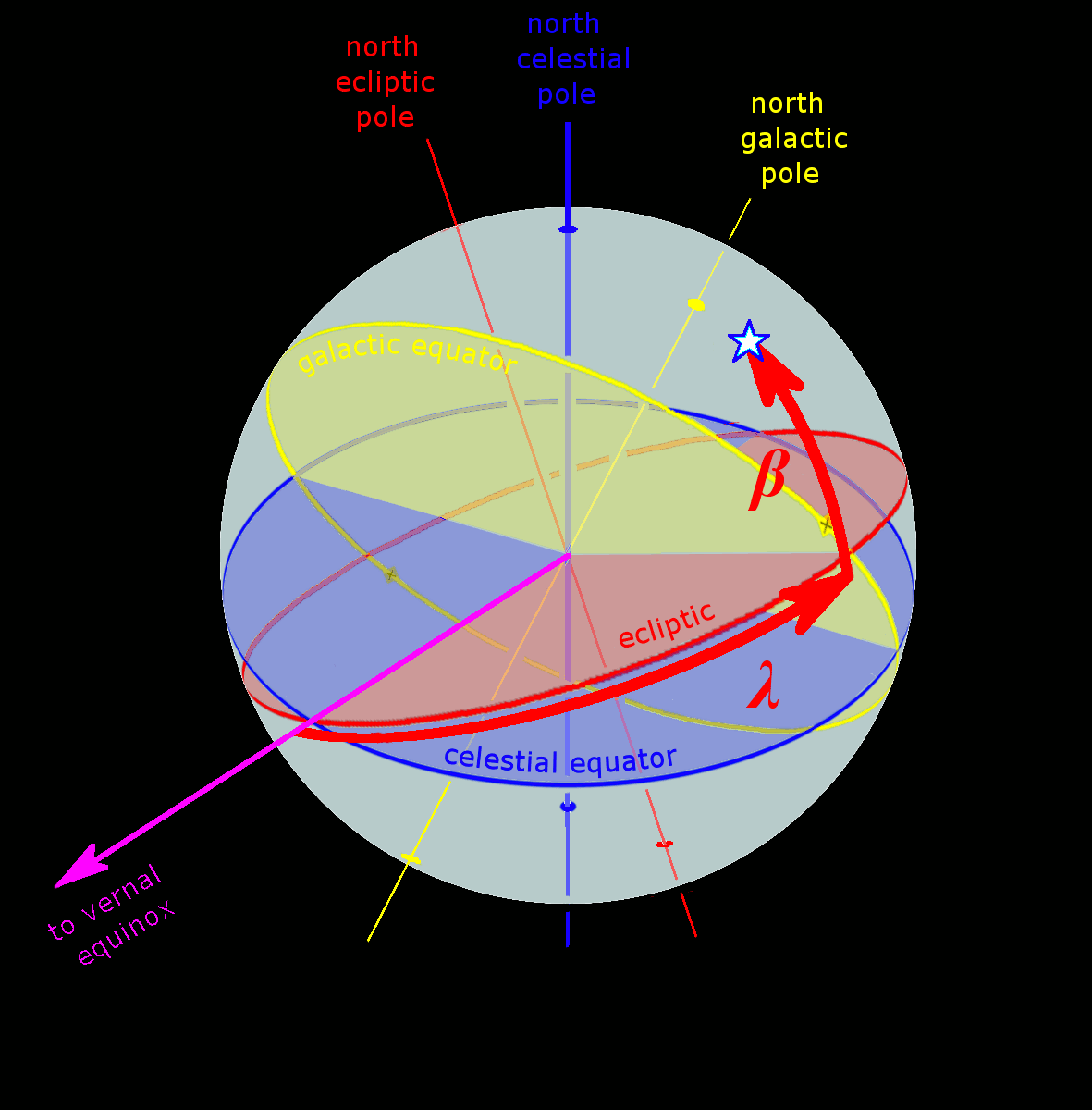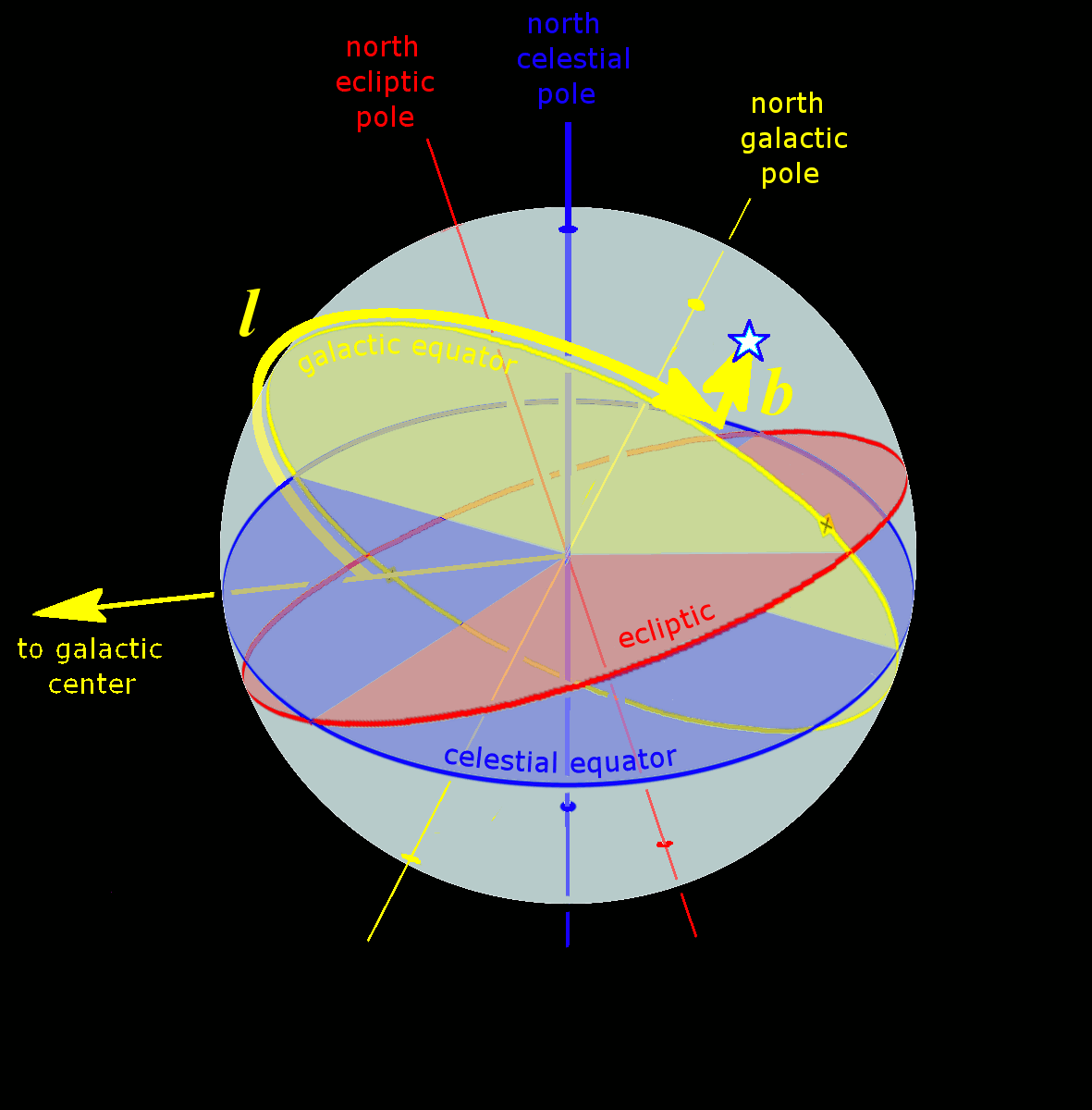
Celestial Coordinate System
Astronomical coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated observer (e.g. the true horizon and north cardinal direction to an observer situated on the Earth's surface). Coordinate systems in astronomy can specify an object's position in three-dimensional space or plot merely its direction on a celestial sphere, if the object's distance is unknown or trivial. Spherical coordinates, projected on the celestial sphere, are analogous to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of Earth. These differ in their choice of fundamental plane, which divides the celestial sphere into two equal hemispheres along a great circle. Rectangular coordinates, in appropriate units, have the same fundamental () plane and primary (-axis) direction, such as a rotation axis. Each coordinate system is named after its choice of fundamental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clockwise
Two-dimensional rotation can occur in two possible directions. Clockwise motion (abbreviated CW) proceeds in the same direction as a clock's hands: from the top to the right, then down and then to the left, and back up to the top. The opposite sense of rotation or revolution is (in Commonwealth English) anticlockwise (ACW) or (in North American English) counterclockwise (CCW). Terminology Before clocks were commonplace, the terms " sunwise" and "deasil", "deiseil" and even "deocil" from the Scottish Gaelic language and from the same root as the Latin "dexter" ("right") were used for clockwise. "Widdershins" or "withershins" (from Middle Low German "weddersinnes", "opposite course") was used for counterclockwise. The terms clockwise and counterclockwise can only be applied to a rotational motion once a side of the rotational plane is specified, from which the rotation is observed. For example, the daily rotation of the Earth is clockwise when viewed from above the South Pole, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Position Angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial pole (NCP), turning positive into the direction of the right ascension. In the standard (non-flipped) images, this is a counterclockwise measure relative to the axis into the direction of positive declination. In the case of observed visual binary stars, it is defined as the angular offset of the secondary star from the primary relative to the north celestial pole. As the example illustrates, if one were observing a hypothetical binary star with a PA of 135°, that means an imaginary line in the eyepiece drawn from the north celestial pole to the primary (P) would be offset from the secondary (S) such that the angle would be 135°. When graphing visual binaries, the NCP is, as in the illustration, normally drawn from the center point (origin) that is the Primary downward&nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsolar Point
The subsolar point on a planet is the point at which its sun is perceived to be directly overhead (at the zenith); that is, where the sun's rays strike the planet exactly perpendicular to its surface. It can also mean the point closest to the sun on an astronomical object, even though the sun might not be visible. To an observer on a planet with an orientation and rotation similar to those of Earth, the subsolar point will appear to move westward, completing one circuit around the globe each day, approximately moving along the equator. However, it will also move north and south between the tropics over the course of a year, so it is spiraling like a helix. The subsolar point contacts the Tropic of Cancer on the June solstice and the Tropic of Capricorn on the December solstice. The subsolar point crosses the Equator on the March and September equinoxes. Coordinates of the subsolar point The subsolar point moves constantly on the surface of the Earth, but for any given time, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |