|
Proximal 18q-
Proximal 18q- is a rare genetic condition caused by a deletion of genetic material within one of the two copies of chromosome 18. This deletion involves the proximal (near the centromere) section of the long arm of chromosome 18 somewhere between 18q11.2 (18.9 Mb) to 18q21.1 (43.8 Mb).Cody JD, Sebold C, Malik A, Heard P, Carter E, Crandall A, Soileau B, Semrud-Clikeman M, Cody CM, Hardies LJ, Li J, Lancaster J, Fox PT, Stratton RF, Perry B, Hale DE (2007). Am J Med Genet 143A(11):1181-90. Exact breakpoints vary. Signs and symptoms Proximal 18q- causes a range of medical and developmental concerns. There is significant variation in severity due to the variation in breakpoints reported. Current research is focused on establishing genotype-phenotype correlations to enable predictive genotyping. A group of individuals with similar deletions within this region have been described (Cody et al., 2007): The medical and developmental problems are described below. Congenital anomalies C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch tics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specialty, predictive medicine. Scope Medical genetics encompasses many different areas, including clinical practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or neural oscillation, synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness (tonic-clonic seizure), to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness (focal seizure), to a subtle momentary loss of awareness (absence seizure). Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Urinary incontinence, Loss of bladder control may occur. Seizures may be provoked and unprovoked. Provoked seizures are due to a temporary event such as low blood sugar, alcohol withdrawal, abusing alcohol together with prescription medication, low blood sodium, fever, brain infection, or concussion. Unprovoked seizures occur without a known or fixable cause such that ongoing seizures are likely. Unprovoked seizur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus (placental tissue) and testing it for chromosomal abnormalities, usually with FISH or PCR. CVS usually takes place at 10–12 weeks' gestation, earlier than amniocentesis or percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling. It is the preferred technique before 15 weeks. CVS was performed for the first time in Milan by Italian biologist Giuseppe Simoni, scientific director of Biocell Center, in 1983. Use as early as eight weeks in special circumstances has been described. It can be performed in a transcervical or transabdominal manner. Although this procedure is mostly associated with testing for Down syndrome, overall, CVS can detect more than 200 disorders. Indications Poss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
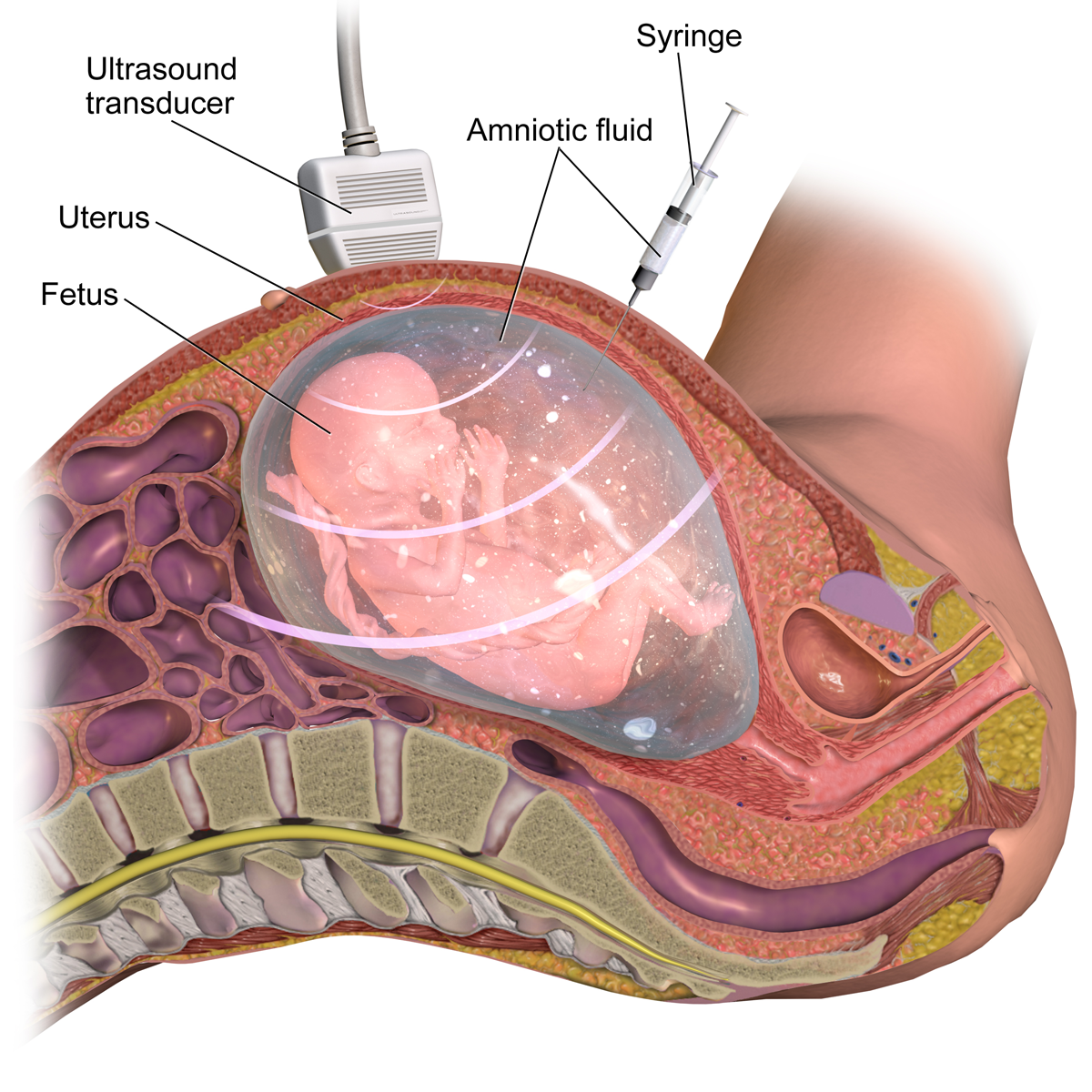
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is necessary to conclusively diagnose the majority of genetic disorders, with amniocentesis being the gold-standard procedure after 15 weeks' gestation. In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the abdomen of the pregnant woman. The needle punctures the amnion, which is the membrane that surrounds the developing fetus. The fluid within the amnion is called amniotic fluid, and because this fluid surrounds the developing fetus, it contains fetal cells. The amniotic fluid is sampled and analyzed via methods such as karyotyping and DNA analysis technology for genetic abnormalities. An amniocentesis is typically performed in the second trimester between the 15th and 20th week of gestation. Women who choose to have this test are prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problems with the pregnancy as early as possible. These may be anatomic and physiologic problems with the health of the zygote, embryo, or fetus, either before gestation even starts (as in preimplantation genetic diagnosis) or as early in gestation as practicable. Screening can detect problems such as neural tube defects, chromosome abnormalities, and gene mutations that would lead to genetic disorders and birth defects, such as spina bifida, cleft palate, Down syndrome, Tay–Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and fragile X syndrome. Some tests are designed to discover problems which primarily affect the health of the mother, such as PAPP-A to detect pre-eclampsia or glucose tolerance tests to diagnose gestational diabetes. Screening can also detect anatomical defects such as hydrocephalus, anencephal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome Analysis
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include karyotyping, analysis of G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescent ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated that the set of chromosomes (the karyotype) was the carrier of the genes. Levitsky seems to have been t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or human growth hormone deficiency, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density. GHD can be present at birth or develop later in life. Causes may include genetics, trauma, infections, tumors, or radiation therapy. Genes that may be involved include GH1, GHRHR, or BTK. In a third of cases no cause is apparent. The underlying mechanism generally involves problems with the pituitary gland. Some cases are associated with a lack of other pituitary hormones, in which case it is known as combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure growth hormone levels. Treatment is by growth hormone replacement using synthetic human growth hormone. The frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which a person's spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually "S"- or "C"-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to another condition such as muscle spasms, cerebral palsy, Marfan syndrome, and tumors such as neurofibromatosis. Diagnosis is confirmed with X-rays. Scoliosis is typically classified as either structural in which the curve is fixed, or functional in which the underlying spine is normal. Treatment depends on the degree of curve, location, and cause. Minor curves may simply be watched periodically. Treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pes Planus
Flat feet (also called pes planus or fallen arches) is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Sometimes children are born with flat feet (congenital). There is a functional relationship between the structure of the arch of the foot and the biomechanics of the lower leg. The arch provides an elastic, springy connection between the forefoot and the hind foot so that a majority of the forces incurred during weight bearing on the foot can be dissipated before the force reaches the long bones of the leg and thigh. In pes planus, the head of the talus bone is displaced medially and distal from the navicular bone. As a result, the Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (spring ligament) and the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle are stretched to the extent that the individual with pes planus loses the function of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA). If the MLA is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve tracts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Hypotonia is a lack of resistance to passive movement, whereas muscle weakness results in impaired active movement. Central hypotonia originates from the central nervous system, while peripheral hypotonia is related to problems within the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and/or skeletal muscles. Severe hypotonia in infancy is commonly known as floppy baby syndrome. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Condition
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |