|
Protoproedros
''Proedros'' ( el, πρόεδρος, "president") was a senior Byzantine court and ecclesiastic title in the 10th to mid-12th centuries. The female form of the title is ''proedrissa'' (προέδρισσα). Court dignity The title was created in the 960s by Nikephoros II Phokas and was first awarded to Basil Lekapenos, the eunuch '' parakoimōmenos''. It was placed very high in the court hierarchy, coming immediately below the position of the '' zostē patrikia'' and before the ''magistros'', meaning that it was the most senior non-imperial title open to males. The title apparently continued to be restricted to eunuchs until the mid-11th century, when it was opened up to the wider aristocracy and extensively awarded. The holder of this dignity was also the president of the Senate (), and the term ''proedros'' was often used to denote precedence in other offices, e.g. ''proedros'' of the ''notarioi'' for the '' prōtonotarios''. The title was widely awarded in the 11th century, aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Aristocracy And Bureaucracy
Through the 5th century Hellenistic political systems, philosophies and theocratic Christian-Eastern concepts had gained power in the eastern Greek-speaking Mediterranean due to the intervention of Important religious figures there such as Eusebius of Caesarea and Origen of Alexandria who had been key to the constant Christianized world of late antiquity. By the 6th century they had already influenced the definitive power of the monarch as the representative of God on earth and his kingdom as an imitation of God's holy realm. The Byzantine empire was a monarchic theocracy, adopting, following and applying the Hellenistic political systems and philosophies. The monarch was the incarnation of the law ''nomos empsychos'', and his power was immeasurable and divine in origin. He was the ultimate benefactor, carer and saviour of his people, '' Evergétis'', '' Philanthrōpía'' and ''Sōtēr''. They in turn were his ''paroikoi'' (subjects). He was the sole administrator and lawg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Chrysostome Homélies Btv1b8470047d
Jean may refer to: People * Jean (female given name) * Jean (male given name) * Jean (surname) Fictional characters * Jean Grey, a Marvel Comics character * Jean Valjean, fictional character in novel ''Les Misérables'' and its adaptations * Jean Pierre Polnareff, a fictional character from ''JoJo's Bizarre Adventure'' Places * Jean, Nevada, USA; a town * Jean, Oregon, USA Entertainment * Jean (dog), a female collie in silent films * "Jean" (song) (1969), by Rod McKuen, also recorded by Oliver * ''Jean Seberg'' (musical), a 1983 musical by Marvin Hamlisch Other uses * JEAN (programming language) * USS ''Jean'' (ID-1308), American cargo ship c. 1918 * Sternwheeler Jean, a 1938 paddleboat of the Willamette River See also *Jehan * * Gene (other) * Jeanne (other) * Jehanne (other) * Jeans (other) * John (other) John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
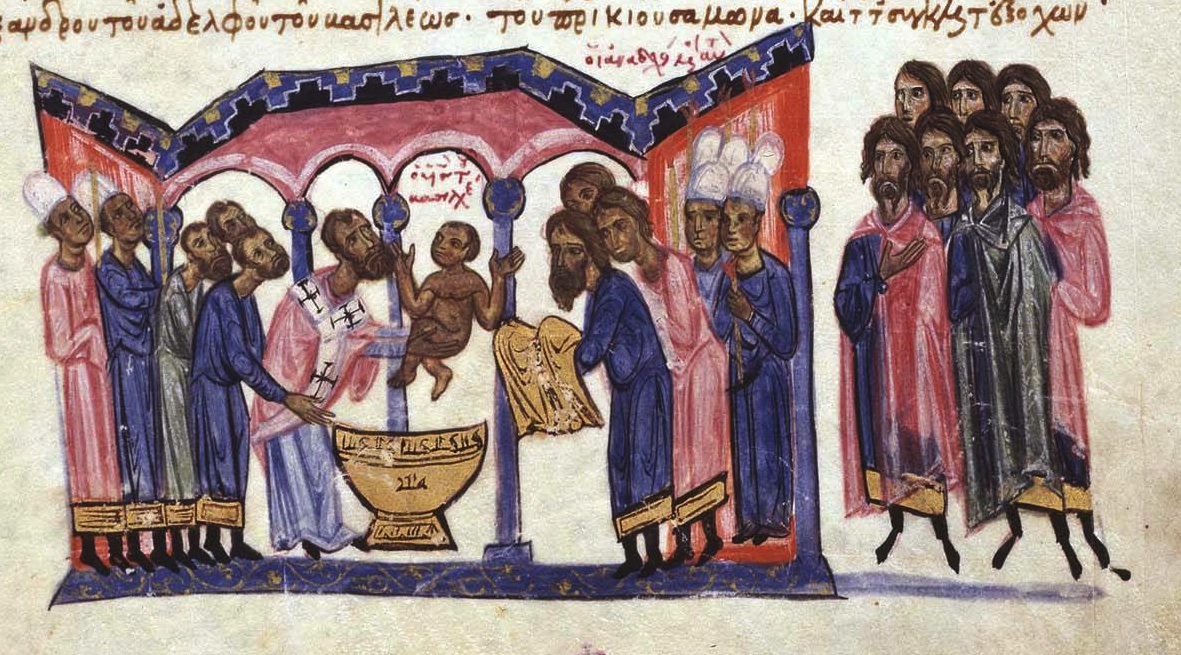
Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, and the nephew of his predecessor Alexander. Most of his reign was dominated by co-regents: from 913 until 919 he was under the regency of his mother, while from 920 until 945 he shared the throne with Romanos Lekapenos, whose daughter Helena he married, and his sons. Constantine VII is best known for the ''Geoponika'' (τά γεοπονικά), an important agronomic treatise compiled during his reign, and three, perhaps four, books; '' De Administrando Imperio'' (bearing in Greek the heading Πρὸς τὸν ἴδιον υἱὸν Ῥωμανόν), '' De Ceremoniis'' (Περὶ τῆς Βασιλείου Τάξεως), '' De Thematibus'' (Περὶ θεμάτων Άνατολῆς καὶ Δύσεως), and ''Vita Basilii'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primicerius
The Latin term ''primicerius'', hellenized as ''primikērios'' ( el, πριμικήριος), was a title applied in the later Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire to the heads of administrative departments, and also used by the Church to denote the heads of various colleges. Etymologically the term derives from ''primus in cera'', which is to say ''in tabula cerata'', the first name in a list of a class of officials, which was usually inscribed on a waxed tablet. Civil and military From their origin in the court of the Dominate, there were several ''primicerii'' (''primikērioi'' in Greek, from the 12th century usually spelled ''primmikērioi''). In the court, there was the ''primicerius sacri cubiculi'' (in Byzantine times the ''primikērios'' of the ''kouboukleion''), in charge of the emperor's bedchamber, almost always a eunuch. The title was also given to court officials in combination with other offices connected to the imperial person, such as the special treasury (''eidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praeses
''Praeses'' (Latin ''praesides'') is a Latin word meaning "placed before" or "at the head". In antiquity, notably under the Roman Dominate, it was used to refer to Roman governors; it continues to see some use for various modern positions. Roman governors ''Praeses'' began to be used as a generic description for provincial governors—often through paraphrases, such as ''qui praeest'' ("he who presides")—already since the early Principate, but came in general use under the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. The jurist Aemilius Macer, who wrote at the time of Caracalla (reigned 198–217), insists that the term was applied only to the governors who were also senators—thereby excluding the equestrian '' procuratores''—but, while this may reflect earlier usage, it was certainly no longer the case by the time he wrote. In the usage of the 2nd and 3rd centuries, the term appears originally to have been used as an honorific, affixed to the formal gubernatorial titles (''legatus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokathemenos
( gr, προκαθήμενος, , the presiding one) is a Greek term for a president or chairman. In the Byzantine Empire, the term appeared in a technical use during the 12th century. In the central administration, the of the (state courts) is attested since 1166. This was one of the four highest tribunals of the Komnenian period, along with those headed by the , the , and the . In 1186, a of the (the financial bureaux) is recorded as being charged by Emperor Isaac II Angelos with collecting fines from those who disobeyed one of his chrysobulls. The modern historian Ernst Stein proposed to identify this office with the of the , but this is conjectural. In addition, from the 12th century on, and particularly during the 13th and 14th centuries, the term was used for the governors of individual towns. Stein again suggested that these were civilian governors, while the garrison was commanded by a . In the ''Book of Offices'' of pseudo-Kodinos, written shortly after the mid-14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis. Originally, the term referred to the bishop of the chief city of a historical Roman province, whose authority in relation to the other bishops of the province was recognized by the First Council of Nicaea (AD 325). The bishop of the provincial capital, the metropolitan, enjoyed certain rights over other bishops in the province, later called " suffragan bishops". The term ''metropolitan'' may refer in a similar sense to the bishop of the chief episcopal see (the "metropolitan see") of an ecclesiastical province. The head of such a metropolitan see has the rank of archbishop and is therefore called the metropolitan archbishop of the ecclesiastical province. Metropolitan (arch)bishops preside over synods of the bishops of their ecclesiastical province, and canon law and traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is called episcopacy. Organizationally, several Christian denominations utilize ecclesiastical structures that call for the position of bishops, while other denominations have dispensed with this office, seeing it as a symbol of power. Bishops have also exercised political authority. Traditionally, bishops claim apostolic succession, a direct historical lineage dating back to the original Twelve Apostles or Saint Paul. The bishops are by doctrine understood as those who possess the full priesthood given by Jesus Christ, and therefore may ordain other clergy, including other bishops. A person ordained as a deacon, priest (i.e. presbyter), and then bishop is understood to hold the fullness of the ministerial priesthood, given responsibility b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamys
The chlamys (Ancient Greek: χλαμύς : chlamýs, genitive: χλαμύδος : chlamydos) was a type of an ancient Greek cloak.Ancient Greek Dress ''Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History'', , 2000–2013. Retrieved 7 October 2013. By the time of the it was, although in a much larger form, part of the state costume of the emperor and high officials. It survived as such until at least the 12th century AD. The ephaptis (Ancient Greek: ἐφαπτίς) was a similar garment, typically worn by infantrymen. ...
|
Tunic
A tunic is a garment for the body, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the knees. The name derives from the Latin ''tunica'', the basic garment worn by both men and women in Ancient Rome, which in turn was based on earlier Greek garments that covered wearers' waists. Ancient era Indian tunic Indus valley civilization figurines depict both women and men wearing a tunic-like garment. A terracotta model called Lady of the spiked throne depicts two standing turban-wearing men wearing what appears to be a conical gown marked by a dense series of thin vertical incisions that might suggest stiffened cloth. A similar gold disc in the al-Sabah Collection from the Kuwait National Museum appears to be from the Indus Valley civilization depicts similar conical tunic-wearing men holding two bulls by their tails under a pipal tree shown in an Indus-like mirror symmetry. A mother goddess figurine from the National Museum new Delhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komnenian Period
The Byzantine Empire was ruled by emperors of the Komnenos dynasty for a period of 104 years, from 1081 to about 1185. The ''Komnenian'' (also spelled ''Comnenian'') period comprises the reigns of five emperors, Alexios I Komnenos, Alexios I, John II Komnenos, John II, Manuel I Komnenos, Manuel I, Alexios II Komnenos, Alexios II and Andronikos I Komnenos, Andronikos I. It was a period of sustained, though ultimately incomplete, restoration of the military, territorial, economic and political position of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantium under the Komnenoi played a key role in the history of the Crusades in the Holy Land, while also exerting enormous cultural and political influence in Europe, the Near East, and the lands around the Mediterranean Sea. The Komnenian emperors, particularly John and Manuel, exerted great influence over the Crusader states of Outremer, whilst Alexios I played a key role in the course of the First Crusade, which he helped bring about. Moreover, it was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Ceremoniis
The ''De Ceremoniis'' (fully ''De cerimoniis aulae Byzantinae'') is the conventional Latin name for a Greek book of ceremonial protocol at the court of the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople. Its Greek title is often cited as ("Explanation of the Order of the Palace"), taken from the work's preface, or ("On the Order of the Palace"). In non-specialist English sources, it tends to be called the ''Book of Ceremonies of Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos'' (variably spelt), a formula used by writers including David Talbot Rice and the modern English translation. History and Sources It was written or at least commissioned by Emperor Constantine VII (reigned 913-959), probably around 956-959. The compilation of Rep. I 17 (Leipzig, Universitätsbibliothek) was partially revised later under Nikephoros II (963-969), perhaps under the supervision of Basil Lekapenos, the imperial ''parakoimomenos'', and it also contains earlier descriptions of the 6th century."De Ceremoniis" in ''The Ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |