|
Promptuary
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuary Diagram 2
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
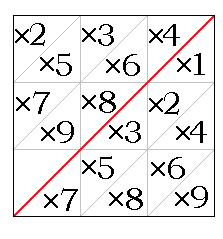
Promptuary Diagram 1
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuary Diagram 3
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuary Diagram 4
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuary Diagram 5
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promptuary Diagram 6
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Napier
John Napier of Merchiston (; 1 February 1550 – 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8th Laird of Merchiston. His Latinized name was Ioannes Neper. John Napier is best known as the discoverer of logarithms. He also invented the so-called " Napier's bones" and made common the use of the decimal point in arithmetic and mathematics. Napier's birthplace, Merchiston Tower in Edinburgh, is now part of the facilities of Edinburgh Napier University. There is a memorial to him at St Cuthbert's at the west side of Edinburgh. Life Napier's father was Sir Archibald Napier of Merchiston Castle, and his mother was Janet Bothwell, daughter of the politician and judge Francis Bothwell, and a sister of Adam Bothwell who became the Bishop of Orkney. Archibald Napier was 16 years old when John Napier was born. There are no records of Napier's early education, but many believe that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
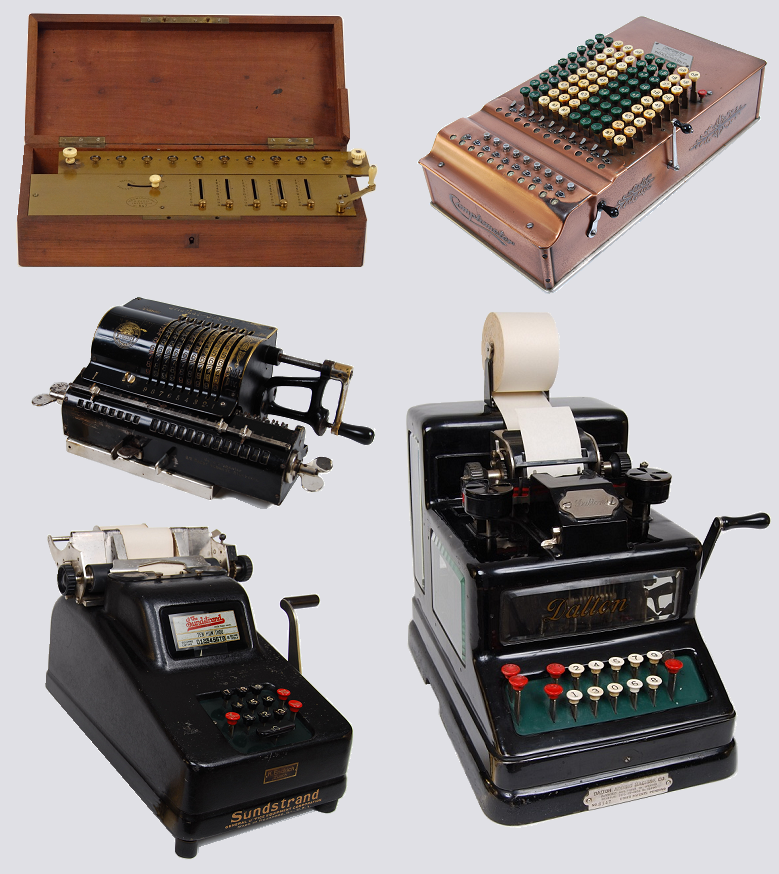
Calculating Machine
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or (historically) a simulation such as an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators were comparable in size to small desktop computers and have been rendered obsolete by the advent of the electronic calculator and the digital computer. Surviving notes from Wilhelm Schickard in 1623 reveal that he designed and had built the earliest of the modern attempts at mechanizing calculation. His machine was composed of two sets of technologies: first an abacus made of Napier's bones, to simplify multiplications and divisions first described six years earlier in 1617, and for the mechanical part, it had a dialed pedometer to perform additions and subtractions. A study of the surviving notes shows a machine that would have jammed after a few entries on the same dial, and that it could be damaged if a carry had to be propagated over a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diccionario Enciclopédico Hispano-americano De Literatura, Ciencias Y Artes
The ''Diccionario enciclopédico hispano-americano de literatura, ciencias y artes'' (1887–99) was a Spanish language general encyclopedia produced by Montaner y Simón in Barcelona, Spain , image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , i .... References Further reading * External links * (fulltext) Spanish encyclopedias 1887 non-fiction books Spanish online encyclopedias Reference works in the public domain 19th-century encyclopedias {{encyclopedia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Calculators
Mechanical may refer to: Machine * Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement * Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic * Mechanical energy, the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy * Mechanical system, a system that manages the power of forces and movements to accomplish a task * Mechanism (engineering), a portion of a mechanical device Other * Mechanical (character), one of several characters in Shakespeare's ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' * A kind of typeface in the VOX-ATypI classification See also * Machine, especially in opposition to an electronic item * ''Mechanical Animals'', the third full-length studio release by Marilyn Manson * Manufactured or artificial, especially in opposition to a biological or natural component * Automation, using machine decisions and processing instead of human * Mechanization, using machine labor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kensington
Kensington is a district in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in the West of Central London. The district's commercial heart is Kensington High Street, running on an east–west axis. The north-east is taken up by Kensington Gardens, containing the Albert Memorial, the Serpentine Gallery and Speke's monument. South Kensington and Gloucester Road are home to Imperial College London, the Royal College of Music, the Royal Albert Hall, Natural History Museum, Victoria and Albert Museum, and Science Museum. The area is also home to many embassies and consulates. Name The manor of ''Chenesitone'' is listed in the Domesday Book of 1086, which in the Anglo-Saxon language means "Chenesi's ton" (homestead/settlement). One early spelling is ''Kesyngton'', as written in 1396. History The manor of Kensington, in the county of Middlesex, was one of several hundred granted by King William the Conqueror (1066-1089) to Geoffrey de Montbray (or Mowbray), Bishop of Coutances in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblioteca Nacional De España
The Biblioteca Nacional de España (''National Library of Spain'') is a major public library, the largest in Spain, and one of the largest in the world. It is located in Madrid, on the Paseo de Recoletos. History The library was founded by King Philip V in 1711 as the Palace Public Library (Biblioteca Pública de Palacio). The Royal Letters Patent that he granted, the predecessor of the current legal deposit requirement, made it mandatory for printers to submit a copy of every book printed in Spain to the library. In 1836, the library's status as Crown property was revoked and ownership was transferred to the Ministry of Governance (Ministerio de la Gobernación). At the same time, it was renamed the Biblioteca Nacional. During the 19th century, confiscations, purchases and donations enabled the Biblioteca Nacional to acquire the majority of the antique and valuable books that it currently holds. In 1892 the building was used to host the Historical American Exposition. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_01.jpg)


