|
Predicate Completion
Predicate or predication may refer to: * Predicate (grammar), in linguistics * Predication (philosophy) * several closely related uses in mathematics and formal logic: ** Predicate (mathematical logic) ** Propositional function ** Finitary relation, or n-ary predicate ** Boolean-valued function ** Syntactic predicate, in formal grammars and parsers ** Functional predicate * Predication (computer architecture) *in United States law, the basis or foundation of something ** Predicate crime **Predicate rules, in the U.S. Title 21 CFR Part 11 * Predicate, a term used in some European context for either nobles' honorifics or for nobiliary particle A nobiliary particle is used in a surname or family name in many Western cultures to signal the nobility of a family. The particle used varies depending on the country, language and period of time. In some languages, it is the same as a regular p ...s See also * Predicate logic {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
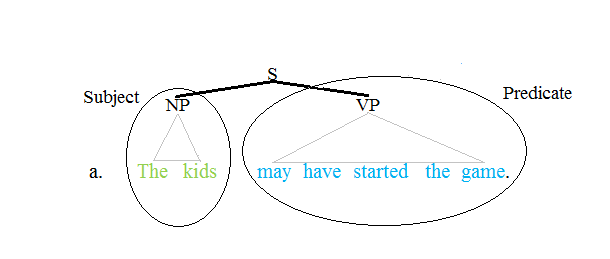
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predication (philosophy)
Predication in philosophy refers to an act of judgement where one term is subsumed under another. A comprehensive conceptualization describes it as the understanding of the relation expressed by a predicative structure primordially (i.e. both originally and primarily) through the opposition between particular and general or the one and the many. Predication is also associated or used interchangeably with the concept of ''attribution'' where both terms pertain to the way judgment and ideas acquire a new property in the second operation of the mind (or the mental operation of judging). Background Predication emerged when ancient philosophers began exploring reality and the two entities that divide it: properties and the things that bear them. These thinkers investigated what the division between thing and property amounted to. It was argued that the relationship resembled the logical analysis of a sentence wherein the division of subject and predicate arises spontaneously. It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (mathematical Logic)
In logic, a predicate is a symbol which represents a property or a relation. For instance, in the first order formula P(a), the symbol P is a predicate which applies to the individual constant a. Similarly, in the formula R(a,b), R is a predicate which applies to the individual constants a and b. In the semantics of logic, predicates are interpreted as relations. For instance, in a standard semantics for first-order logic, the formula R(a,b) would be true on an interpretation if the entities denoted by a and b stand in the relation denoted by R. Since predicates are non-logical symbols, they can denote different relations depending on the interpretation used to interpret them. While first-order logic only includes predicates which apply to individual constants, other logics may allow predicates which apply to other predicates. Predicates in different systems * In propositional logic, atomic formulas are sometimes regarded as zero-place predicates In a sense, these are null ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propositional Function
In propositional calculus, a propositional function or a predicate is a sentence expressed in a way that would assume the value of true or false, except that within the sentence there is a variable (''x'') that is not defined or specified (thus being a free variable), which leaves the statement undetermined. The sentence may contain several such variables (e.g. ''n'' variables, in which case the function takes ''n'' arguments). Overview As a mathematical function, ''A''(''x'') or ''A''(''x'', ''x'', ..., ''x''), the propositional function is abstracted from predicates or propositional forms. As an example, consider the predicate scheme, "x is hot". The substitution of any entity for ''x'' will produce a specific proposition that can be described as either true or false, even though "''x'' is hot" on its own has no value as either a true or false statement. However, when a value is assigned to ''x'' , such as lava, the function then has the value ''true''; while one assigns to '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finitary Relation
In mathematics, a finitary relation over sets is a subset of the Cartesian product ; that is, it is a set of ''n''-tuples consisting of elements ''x''''i'' in ''X''''i''. Typically, the relation describes a possible connection between the elements of an ''n''-tuple. For example, the relation "''x'' is divisible by ''y'' and ''z''" consists of the set of 3-tuples such that when substituted to ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'', respectively, make the sentence true. The non-negative integer ''n'' giving the number of "places" in the relation is called the ''arity'', ''adicity'' or ''degree'' of the relation. A relation with ''n'' "places" is variously called an ''n''-ary relation, an ''n''-adic relation or a relation of degree ''n''. Relations with a finite number of places are called ''finitary relations'' (or simply ''relations'' if the context is clear). It is also possible to generalize the concept to ''infinitary relations'' with infinite sequences. An ''n''-ary relation over sets is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean-valued Function
A Boolean-valued function (sometimes called a Predicate (logic), predicate or a proposition) is a function (mathematics), function of the type f : X → B, where X is an arbitrary Set (mathematics), set and where B is a Boolean domain, i.e. a generic two-element set, (for example B = ), whose elements are interpreted as logical values, for example, 0 = false (logic), false and 1 = truth value, true, i.e., a single bit of information. In the formal sciences, mathematics, mathematical logic, statistics, and their applied disciplines, a Boolean-valued function may also be referred to as a characteristic function, indicator function, predicate, or proposition. In all of these uses, it is understood that the various terms refer to a mathematical object and not the corresponding semiotic sign or syntactic expression. In semantics, formal semantic theories of truth, a truth predicate is a predicate on the Sentence (mathematical logic), sentences of a formal language, interpreted for logi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Predicate
A syntactic predicate specifies the syntactic validity of applying a production in a formal grammar and is analogous to a semantic predicate that specifies the semantic validity of applying a production. It is a simple and effective means of dramatically improving the recognition strength of an LL parser by providing arbitrary lookahead. In their original implementation, syntactic predicates had the form “( α )?” and could only appear on the left edge of a production. The required syntactic condition α could be any valid context-free grammar fragment. More formally, a syntactic predicate is a form of production intersection, used in parser specifications or in formal grammars. In this sense, the term ''predicate'' has the meaning of a mathematical indicator function. If ''p1'' and ''p2,'' are production rules, the language generated by ''both'' ''p1'' ''and'' ''p2'' is their set intersection. As typically defined or implemented, syntactic predicates implicitly order the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Predicate
In formal logic and related branches of mathematics, a functional predicate, or function symbol, is a logical symbol that may be applied to an object term to produce another object term. Functional predicates are also sometimes called mappings, but that term has additional meanings in mathematics. In a model, a function symbol will be modelled by a function. Specifically, the symbol ''F'' in a formal language is a functional symbol if, given any symbol ''X'' representing an object in the language, ''F''(''X'') is again a symbol representing an object in that language. In typed logic, ''F'' is a functional symbol with ''domain'' type T and ''codomain'' type U if, given any symbol ''X'' representing an object of type T, ''F''(''X'') is a symbol representing an object of type U. One can similarly define function symbols of more than one variable, analogous to functions of more than one variable; a function symbol in zero variables is simply a constant symbol. Now consider a mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predication (computer Architecture)
In computer science, predication is an computer architecture, architectural feature that provides an alternative to conditional transfer of control flow, control, as implemented by conditional branch (computer science), branch instruction (computer science), machine instructions. Predication works by having conditional (''predicated'') non-branch instructions associated with a ''predicate'', a Boolean data type, Boolean value used by the instruction to control whether the instruction is allowed to modify the architectural state or not. If the predicate specified in the instruction is true, the instruction modifies the architectural state; otherwise, the architectural state is unchanged. For example, a predicated move instruction (a conditional move) will only modify the destination if the predicate is true. Thus, instead of using a conditional branch to select an instruction or a sequence of instructions to execute based on the predicate that controls whether the branch occurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate Crime
In the criminal law of the United States, a predicate crime or offense is a crime which is a component of a larger crime. The larger crime may be racketeering, money laundering, financing of terrorism, etc. For example, to violate the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organization Act (RICO), a person must "engage in a pattern of racketeering activity", and in particular, must have committed at least two predicate crimes within 10 years. These include bribery, blackmail, extortion, fraud, theft, money laundering, counterfeiting, and illegal gambling. Crimes are predicate to a larger crime if they have a similar purpose to the larger crime. For example, using false identification is itself a crime; it may be a predicate offense to larceny or fraud if it is used to withdraw money from a bank account. Predicate crimes can be charged separately or together with the larger crime. Money Laundering Crimes that are specific to anti-money laundering (AML) programs have been referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title 21 CFR Part 11
Title 21 CFR Part 11 is the part of Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations that establishes the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations on electronic records and electronic signatures (ERES). Part 11, as it is commonly called, defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records (Title 21 CFR Part 11 Section 11.1 (a)). Coverage Practically speaking, Part 11 applies to drug makers, medical device manufacturers, biotech companies, biologics developers, CROs, and other FDA-regulated industries, with some specific exceptions. It requires that they implement controls, including audits, system validations, audit trails, electronic signatures, and documentation for software and systems involved in processing the electronic data that FDA predicate rules require them to maintain. A predicate rule is any requirement set forth in the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorifics
An honorific is a title that conveys esteem, courtesy, or respect for position or rank when used in addressing or referring to a person. Sometimes, the term "honorific" is used in a more specific sense to refer to an honorary academic title. It is also often conflated with systems of honorific speech in linguistics, which are grammatical or morphological ways of encoding the relative social status of speakers. Honorifics can be used as prefixes or suffixes depending on the appropriate occasion and presentation in accordance with style and customs. Typically, honorifics are used as a style in the grammatical third person, and as a form of address in the second person. Use in the first person, by the honored dignitary, is uncommon or considered very rude and egotistical. Some languages have anti-honorific (''despective'' or ''humilific'') first person forms (expressions such as "your most humble servant" or "this unworthy person") whose effect is to enhance the relative honor acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |