|
Polishing (leather Processing)
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or by applying a chemical treatment, leaving a clean surface with a significant specular reflection (still limited by the index of refraction of the material according to the Fresnel equations). In some materials (such as metals, glasses, black or transparent stones), polishing is also able to reduce diffuse reflection to minimal values. When an unpolished surface is magnified thousands of times, it usually looks like a succession of mountains and valleys. By repeated abrasion, those "mountains" are worn down until they are flat or just small "hills." The process of polishing with abrasives starts with a coarse grain size and gradually proceeds to the finer ones to efficiently flatten the surface imperfections and to obtain optimal results. Mechanical properties The strength of polished products can be higher than their unpolished counterparts owing to the removal of stress concentrations presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. This behavior was first described by Hero of Alexandria ( AD c. 10–70). Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the optical and electronic response functions of the material to electromagnetic waves. Optical processes, which comprise reflection and refraction, are expressed by the difference of the refractive index on both sides of the boundary, whereas reflectance and absorption are the real and imaginary parts of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Polishing
French polishing is a wood finishing technique that results in a very high gloss surface, with a deep colour and chatoyancy. French polishing consists of applying many thin coats of shellac dissolved in denatured alcohol using a rubbing pad lubricated with one of a variety of oils. The rubbing pad is made of absorbent cotton or wool cloth wadding inside of a piece of fabric (usually soft cotton cloth) and is commonly referred to as a ''fad'', also called a rubber, tampon, or (Spanish for "rag doll"). ''French polish'' is a process, not a material. The main material is shellac, although there are several other shellac-based finishes, not all of which class as French polishing. The French Polish technique is an excellent method to accent exotic wood grain. The finish is softer than modern varnishes and lacquers, and is particularly sensitive to spills of water or alcohol, which may produce white cloudy marks, as does heat damage. On the other hand, French Polish is simpler to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry. Chemical processes by main basic material Certain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum, and fertilizer). However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of the chemical reactions. Cement (the paste within concrete) * Calcination – Limestone, which is largely composed of fossilized calcium carbonate (CaCO3), breaks down at high temperatures into useable calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (), which gets released as a by-product. This chemical reaction, call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grinding And Lapping
Grind is the cross-sectional shape of a blade. Grind, grinds, or grinding may also refer to: Grinding action * Grinding (abrasive cutting), a method of crafting * Grinding (dance), suggestive club dancing * Grinding (video gaming), repetitive and uninteresting gameplay * Bruxism, grinding of the teeth * Grind (sport), a sliding stance usually performed in extreme sports such as aggressive skating and boardsports; Grinds (skateboarding) * Grind (whaling), pilot whale hunting in the Faroe Islands * Grinds, private tutoring, in Ireland * Mill (grinding) * Grinding, the operation of the winches on a yacht; the work done by a grinder (sailing position) Geography * Grind, a village in Lăpugiu de Jos Commune, Hunedoara County, Romania * Grind (Unirea), a tributary of the Unirea in Cluj and Alba Counties, Romania Film and TV * ''Grind'' (2003 film), about amateur skaters * ''The Grind'' (1915 film), a silent movie * ''Grind'' (1997 film), starring Billy Crudup and Adrienne Shelly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decorative Arts
] The decorative arts are arts or crafts whose object is the design and manufacture of objects that are both beautiful and functional. It includes most of the arts making objects for the interiors of buildings, and interior design, but not usually architecture. Ceramic art, metalwork, furniture, jewellery, fashion, various forms of the textile arts and glassware are major groupings. Applied arts largely overlaps with decorative arts, and the modern making of applied art is usually called design. The decorative arts are often categorized in distinction to the " fine arts", namely painting, drawing, photography, and large-scale sculpture, which generally produce objects solely for their aesthetic quality and capacity to stimulate the intellect. Distinction from the fine arts The distinction between the decorative and fine arts essentially arose from the post-Renaissance art of the West, where the distinction is for the most part meaningful. This distinction is much less meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Polishing
Vapor polishing is a method of polishing plastics to reduce the surface roughness or improve clarity. Typically, a component is exposed to a chemical vapor causing the surface to flow thereby improving the surface finish. This method of polishing is frequently used to return clear materials to an optical quality finish after machining. Vapor polishing works well in the internal features of components. Feature size changes of the plastic component generally do not occur. Post stress relieving is usually required as vapor polishing sets up surface stresses that can cause crazing. Plastics that respond well to vapor polishing are polycarbonate, acrylic, polysulfone, PEI, and ABS. The technique is also being used to improve the surface of objects created with 3D printing 3D printing or additive manufacturing is the Manufacturing, construction of a three-dimensional object from a computer-aided design, CAD model or a digital 3D modeling, 3D model. It can be done in a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Polishing
Fire polishing, also known as flame polishing, is a method of polishing a material, usually glass or thermoplastics, by exposing it to a flame or heat. When the surface of the material briefly melts, surface tension smooths the surface. Operator skill is critical with this method. When done properly, flame plastic polishing produces the clearest finish, especially when polishing acrylic. This method is most applicable to flat external surfaces. Flame polishing is frequently used in acrylic plastic fabrication because of its high speed compared to abrasive methods. In this application, an oxyhydrogen torch is typically used, one reason being that the flame chemistry is unlikely to contaminate the plastic. Flame polishing is essential to creation of the glass pipettes used for the patch clamp technique of voltage clamping. Equipment Various machines and torches/gas burners are used in the flame polishing process. Depending on the heating requirements for an intended application, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabrication And Testing Of Optical Components
Optical manufacturing and testing spans an enormous range of manufacturing procedures and optical test configurations. The manufacture of a conventional spherical lens typically begins with the generation of the optic's rough shape by grinding a glass blank. This can be done, for example, with ring tools. Next, the lens surface is polished to its final form. Typically this is done by lapping—rotating and rubbing the rough lens surface against a tool with the desired surface shape, with a mixture of abrasives and fluid in between. Typically a carved pitch tool is used to polish the surface of a lens. The mixture of abrasive is called slurry and it is typically made from cerium or zirconium oxide in water with lubricants added to facilitate pitch tool movement without sticking to the lens. The particle size in the slurry is adjusted to get the desired shape and finish. During polishing, the lens may be tested to confirm that the desired shape is being produced, and to ensure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
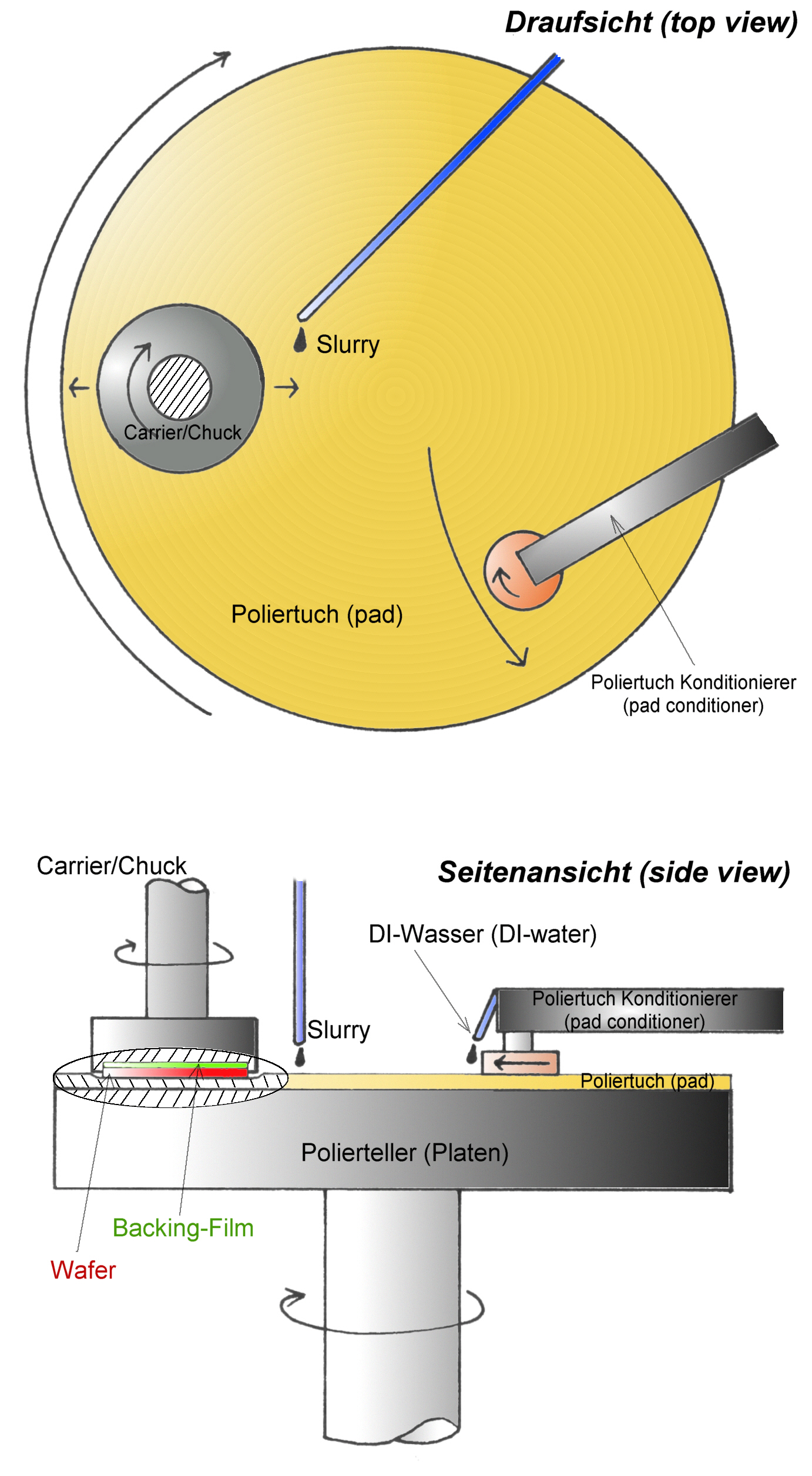
Chemical-mechanical Polishing
Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) or planarization is a process of smoothing surfaces with the combination of chemical and mechanical forces. It can be thought of as a hybrid of chemical etching and free abrasive polishing. Description The process uses an abrasive and corrosive chemical slurry (commonly a colloid) in conjunction with a polishing pad and retaining ring, typically of a greater diameter than the wafer. The pad and wafer are pressed together by a dynamic polishing head and held in place by a plastic retaining ring. The dynamic polishing head is rotated with different axes of rotation (i.e., not concentric). This removes material and tends to even out any irregular topography, making the wafer flat or planar. This may be necessary to set up the wafer for the formation of additional circuit elements. For example, CMP can bring the entire surface within the depth of field of a photolithography system, or selectively remove material based on its position. Typical depth-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Finishing
Wood finishing refers to the process of refining or protecting a wooden surface, especially in the production of furniture where typically it represents between 5 and 30% of manufacturing costs. Finishing is the final step of the manufacturing process that gives wood surfaces desirable characteristics, including enhanced appearance and increased resistance to moisture and other environmental agents. Finishing can also make wood easier to clean and keep it sanitized, sealing pores that can be breeding grounds for bacteria. Finishing can also influence other wood properties, for example tonal qualities of musical instruments and hardness of flooring. In addition, finishing provides a way of giving low-value woods the appearance of ones that are expensive and difficult to obtain. Planning the finish Finishing of wood requires careful planning to ensure that the finished piece looks attractive, performs well in service and meets safety and environmental requirements. Planning fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodablasting
Soda blasting is a mild form of abrasive blasting in which sodium bicarbonate particles are blasted against a surface using compressed air. It has a much milder abrasive effect than sandblasting. An early use was in the conservation-restoration of the Statue of Liberty in the 1980s. Soda blasting is a non-destructive method for many applications in cleaning, paint and varnish stripping, automotive restoration, industrial equipment maintenance, rust removal, graffiti removal, molecular steel passivation against rust, oil removal by saponification and translocation, masonry cleaning and restoration, soot remediation, boat hull cleaning and for food processing facilities and equipment and tooth cleaning at the dental laboratory. Applications Soda blasting can be used for cleaning timber, wood, oak beams, oak floors, doors, stairs & banisters, cars, boat hulls, masonry, and food processing equipment. Soda blasting can also be used to remove graffiti. and to clean structural steel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''λ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)
