|
Poikilocytosis
Poikilocytosis is variation in the shapes of red blood cells. Poikilocytes may be oval, teardrop-shaped, sickle-shaped or irregularly contracted. Normal red blood cells are round, flattened disks that are thinner in the middle than at the edges. A ''poikilocyte'' is an abnormally-shaped red blood cell. Generally, poikilocytosis can refer to an increase in abnormal red blood cells of any shape, where they make up 10% or more of the total population of red blood cells. Types Membrane abnormalities # Acanthocytes or Spur/Spike cells # Codocytes or Target cells # Echinocytes and Burr cells # Elliptocytes and Ovalocytes # Spherocytes # Stomatocytes or Mouth cells # Drepanocytes or Sickle Cells # Degmacytes or "bite cells" Trauma # Dacrocytes or Teardrop Cells # Keratocytes # Microspherocytes and Pyropoikilocytes # Schistocytes # Semilunar bodies Diagnosis Poikilocytosis may be diagnosed with a test called a blood smear. During a blood smear, a medical technologist spre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisocytosis
Anisocytosis is a medical term meaning that a patient's red blood cells are of unequal size. This is commonly found in anemia and other blood conditions. False diagnostic flagging may be triggered on a complete blood count by an elevated WBC count, agglutinated RBCs, RBC fragments, giant platelets or platelet clumps. In addition, it is a characteristic feature of bovine blood. The red cell distribution width (RDW) is a measurement of anisocytosis and is calculated as a coefficient of variation of the distribution of RBC volumes divided by the mean corpuscular volume ( MCV). Types Anisocytosis is identified by RDW and is classified according to the size of RBC measured by MCV. According to this, it can be divided into *Anisocytosis with microcytosis – Iron deficiency, sickle cell anemia *Anisocytosis with macrocytosis – Folate or vitamin B12 deficiency, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, cytotoxic chemotherapy, chronic liver disease, myelodysplastic syndrome Increased RDW is seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
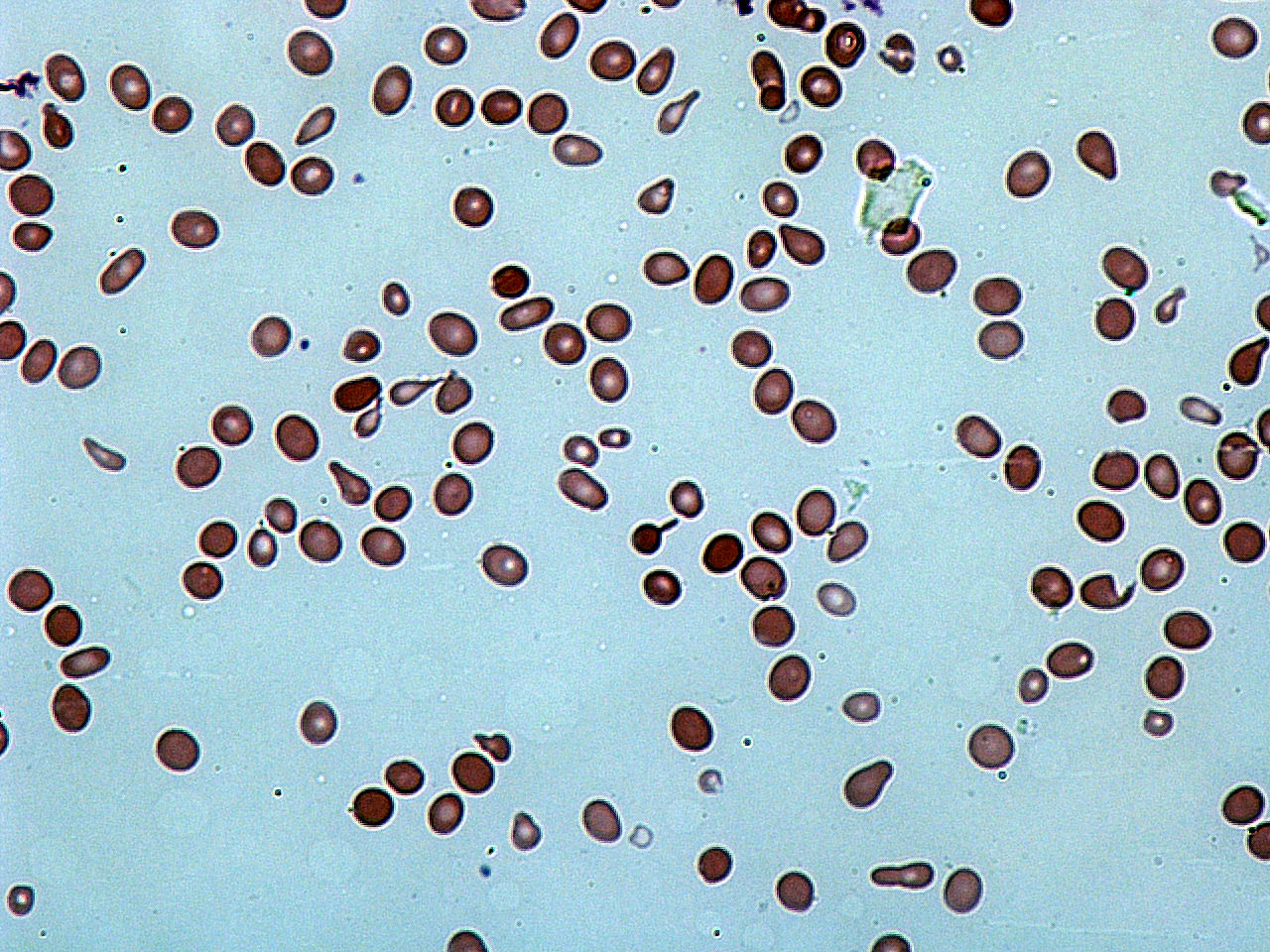
Echinocytes
Echinocyte (from the Greek word ''echinos'', meaning 'hedgehog' or 'sea urchin'), in human biology and medicine, refers to a form of red blood cell that has an abnormal cell membrane characterized by many small, evenly spaced thorny projections.Mentzer WC. Spiculated cells (echinocytes and acanthocytes) and target cells. UpToDate (release: 20.12- C21.4/ref> A more common term for these cells is burr cells. Physiology Echinocytes are frequently confused with acanthocytes, but the mechanism of cell membrane alteration is different. Echinocytosis is a reversible condition of red blood cells that is often merely an artifact produced by EDTA, which is used as an anticoagulant in sampled blood. Echinocytes can be distinguished from acanthocytes by the shape of the projections, which are smaller and more numerous than in acanthocytes and are evenly spaced. Echinocytes also exhibit central pallor, or lightening of color in the center of the cell under Wright staining. Causes In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degmacyte
A degmacyte or bite cell is an abnormally shaped mature red blood cell with one or more semicircular portions removed from the cell margin, known as "bites". These "bites" result from the mechanical removal of denatured hemoglobin during splenic filtration as red cells attempt to migrate through endothelial slits from splenic cords into the splenic sinuses. Bite cells are known to be a result from processes of oxidative hemolysis, such as Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, in which uncontrolled oxidative stress causes hemoglobin to denature and form Heinz bodies. Bite cells can contain more than one "bite." The "bites" in degmacytes are smaller than the missing red blood cell fragments seen in schistocytes. Degmacytes usually appear smaller, denser, and more contracted than a normal red blood cell due to the bites. The appearance of the "bites" in red blood cells may vary in number, smoothness, and size. These cells can also exhibit other peripheral effects. Bli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celiac Disease
Coeliac disease ( British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others. Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a group of various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folic Acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division. As humans cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements. Folate in the form of folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby. Low levels in early pregnancy are believed to be the cause of more than half of babies born with NTDs. More than 80 countries use either mandatory or voluntary fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and for humans, the only vitamin that must be sourced from animal-derived foods or from supplements. Only some archaea and bacteria can synthesize vitamin B12. Most people in developed countries get enough B12 from the consumption of meat or foods with animal sources. Foods containing vitamin B12 include meat, clams, liver, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Many breakfast cereals ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Film
A blood smear, peripheral blood smear or blood film is a thin layer of blood smeared on a glass microscope slide and then stained in such a way as to allow the various blood cells to be examined microscopically. Blood smears are examined in the investigation of hematological (blood) disorders and are routinely employed to look for blood parasites, such as those of malaria and filariasis. Preparation A blood smear is made by placing a drop of blood on one end of a slide, and using a ''spreader slide'' to disperse the blood over the slide's length. The aim is to get a region, called a monolayer, where the cells are spaced far enough apart to be counted and differentiated. The monolayer is found in the "feathered edge" created by the spreader slide as it draws the blood forward. The slide is left to air dry, after which the blood is fixed to the slide by immersing it briefly in methanol. The fixative is essential for good staining and presentation of cellular detail. After f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semilunar Body
Semilunar can refer to: * Semilunar valves * Semilunar ganglion, or the trigeminal ganglion * An older name for the Lunate bone * In neurology, the semilunar fasciculus Semilunar can refer to: * Semilunar valves * Semilunar ganglion A trigeminal ganglion (or Gasserian ganglion, or semilunar ganglion, or Gasser's ganglion) is the sensory ganglion at the base of each of the two trigeminal nerves (CN V), occupy .... {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schistocyte
A schistocyte or schizocyte (from Greek for "divided" and for "hollow" or "cell") is a fragmented part of a red blood cell. Schistocytes are typically irregularly shaped, jagged, and have two pointed ends. Several microangiopathic diseases, including disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombotic microangiopathies, generate fibrin strands that sever red blood cells as they try to move past a thrombus, creating schistocytes. Schistocytes are often seen in patients with hemolytic anemia. They are frequently a consequence of mechanical artificial heart valves, hemolytic uremic syndrome, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, among other causes. Excessive schistocytes present in blood can be a sign of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA). Appearance Schistocytes are fragmented red blood cells that can take on different shapes. They can be found as triangular, helmet shaped, or comma shaped with pointed edges. Schistocytes are most often found to be microcytic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_of_echinocytes.png)



