|
Plankton Net
A plankton net is equipment used for collecting samples of plankton in standing bodies of water. It consists of a towing line and bridles, nylon mesh net, and a cod end. Plankton nets are considered one of the oldest, simplest and least expensive methods of sampling plankton. The plankton net can be used for both vertical and horizontal sampling. It allows researchers to analyse plankton both quantitatively (cell density, cell colony or biomass) and qualitatively (e.g. Chlorophyll-a as a primary production of phytoplankton) in water samples from the environment. Components ; Towing line and bridle : The towing line and bridle is the upper part of a plankton net and used to hold it. The towing lines connected to the triangle bridles are made of nylon rope and can be adjust to a level suitable for the user. ; Nylon mesh net : The nylon mesh net is the middle part of the plankton net and is used to filter the plankton in the water sample in accordance with the siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Upper Part Of Plankton Net
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid for the diameter of a sphere. In more modern usage, the length d of a diameter is also called the diameter. In this sense one speaks of diameter rather than diameter (which refers to the line segment itself), because all diameters of a circle or sphere have the same length, this being twice the radius r. :d = 2r \qquad\text\qquad r = \frac. For a convex shape in the plane, the diameter is defined to be the largest distance that can be formed between two opposite parallel lines tangent to its boundary, and the is often defined to be the smallest such distance. Both quantities can be calculated efficiently using rotating calipers. For a curve of constant width such as the Reuleaux triangle, the width and diameter are the same beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Voyage Of HMS Beagle
The second voyage of HMS ''Beagle'', from 27 December 1831 to 2 October 1836, was the second survey expedition of HMS ''Beagle'', under captain Robert FitzRoy who had taken over command of the ship on its first voyage after the previous captain, Pringle Stokes, committed suicide. FitzRoy had thought of the advantages of having someone onboard who could investigate geology, and sought a naturalist to accompany them as a supernumerary. At the age of 22, the graduate Charles Darwin hoped to see the tropics before becoming a parson and accepted the opportunity. He was greatly influenced by reading Charles Lyell's ''Principles of Geology'' during the voyage. By the end of the expedition, Darwin had made his name as a geologist and fossil collector and the publication of his journal (later known as ''The Voyage of the Beagle'') gave him wide renown as a writer. ''Beagle'' sailed across the Atlantic Ocean, and then carried out detailed hydrographic surveys around the coasts of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a Common descent, common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this Phylogenetics, branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by Burials and memorials in Westminster Abbey, burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh Medical School, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphirina
''Sapphirina'', whose members are commonly known as sea sapphires, is a genus of parasitic copepods in the family Sapphirinidae. Description Various species of male ''Sapphirina'' shine in different hues, from bright gold to deep blue. This is partially due to structural coloration in which microscopic layers of crystal plates inside their cells which are separated by minute distances, and these distances equal the same wavelength of the corresponding color of their "shine". The females are translucent, as are the males when they are not shining. Species The genus ''Sapphirina'' consists of the following species: * ''Sapphirina angusta'' Dana, 1849 * ''Sapphirina aureofurca'' Giesbrecht, 1891 * ''Sapphirina auronitens'' Claus, 1863 * '' Sapphirina bella'' Dana, 1849 * '' Sapphirina bicuspidata'' Giesbrecht, 1891 * '' Sapphirina clausii'' (Haeckel, 1864) * '' Sapphirina coruscans'' Dana, 1849 * '' Sapphirina cylindrica'' Lubbock, 1860 * '' Sapphirina danae'' Lubbock, 1856 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus '' Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
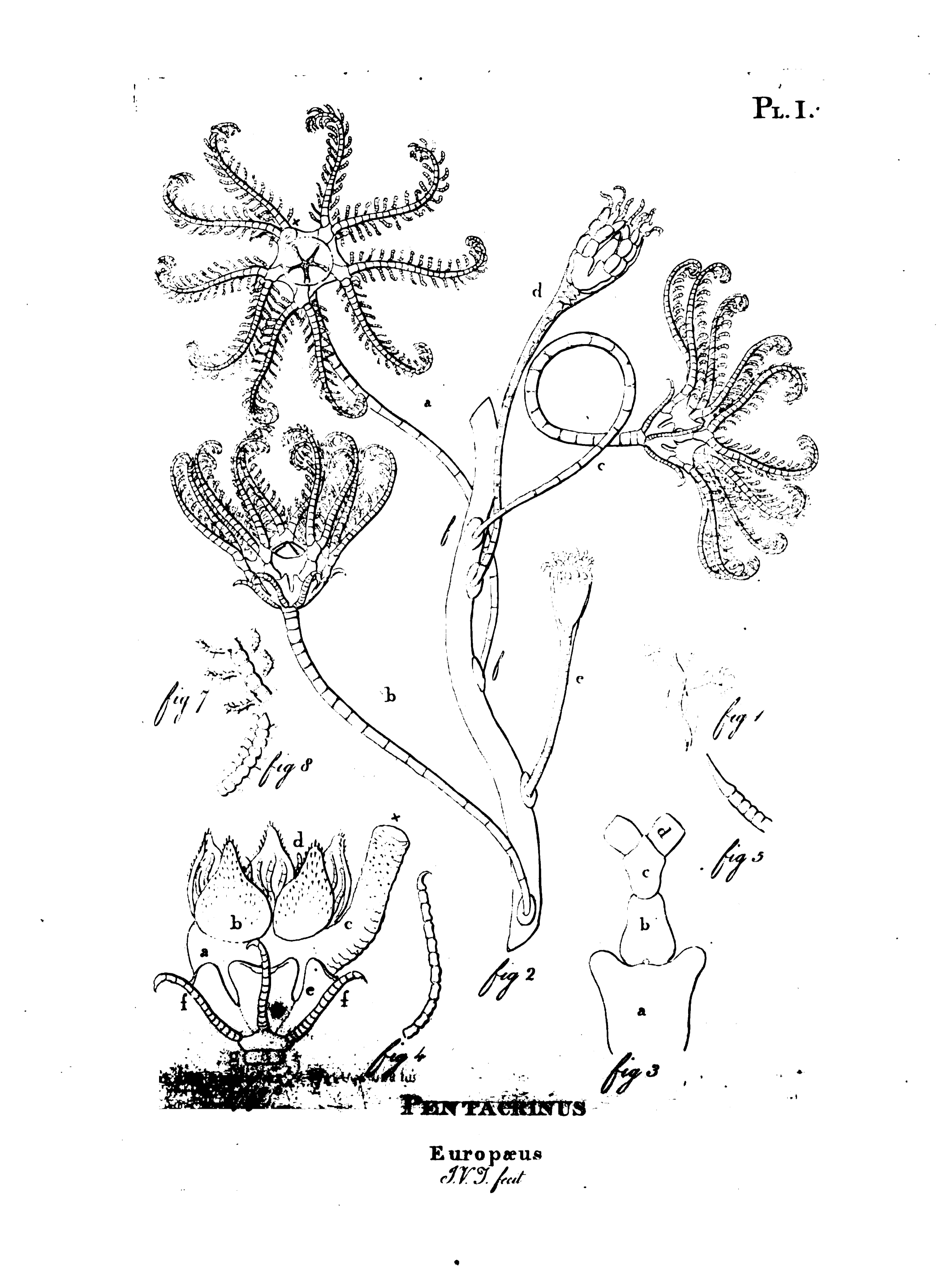
John Vaughan Thompson
John Vaughan Thompson FLS (19 November 1779 – 21 January 1847) was a British military surgeon, marine biologist, zoologist, botanist, and published naturalist. Early years John Vaughan Thompson was born in British controlled Brooklyn on Long-Island in the Province of New York, North America on the 19th November 1779. The family returned to England some time after the American victory in the American War of Independence. He studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh (1797–1798), reading anatomy, surgery, midwifery, and botany, before joining the Army in 1799. Work He grew up around Berwick-upon-Tweed where he wrote his first book ''A Catalogue of Plants Growing in the Vicinity of Berwick Upon Tweed'' which was published in 1807. In each of his military postings such as the ''West Indies and Guiana (1800–1809)'', ''Mauritius and Madagascar (1812–1816)'', he continued his natural history studies with two of his papers being read before the Linnean Society on Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Count
Cell counting is any of various methods for the counting or similar quantification of cells in the life sciences, including medical diagnosis and treatment. It is an important subset of cytometry, with applications in research and clinical practice. For example, the complete blood count can help a physician to determine why a patient feels unwell and what to do to help. Cell counts within liquid media (such as blood, plasma, lymph, or laboratory rinsate) are usually expressed as a number of cells per unit of volume, thus expressing a concentration (for example, 5,000 cells per milliliter). Uses Numerous procedures in biology and medicine require the counting of cells. By the counting of cells in a known small volume, the concentration can be mediated. Examples of the need for cell counting include: * In medicine, the concentration of various blood cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, can give crucial information regarding the health situation of a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
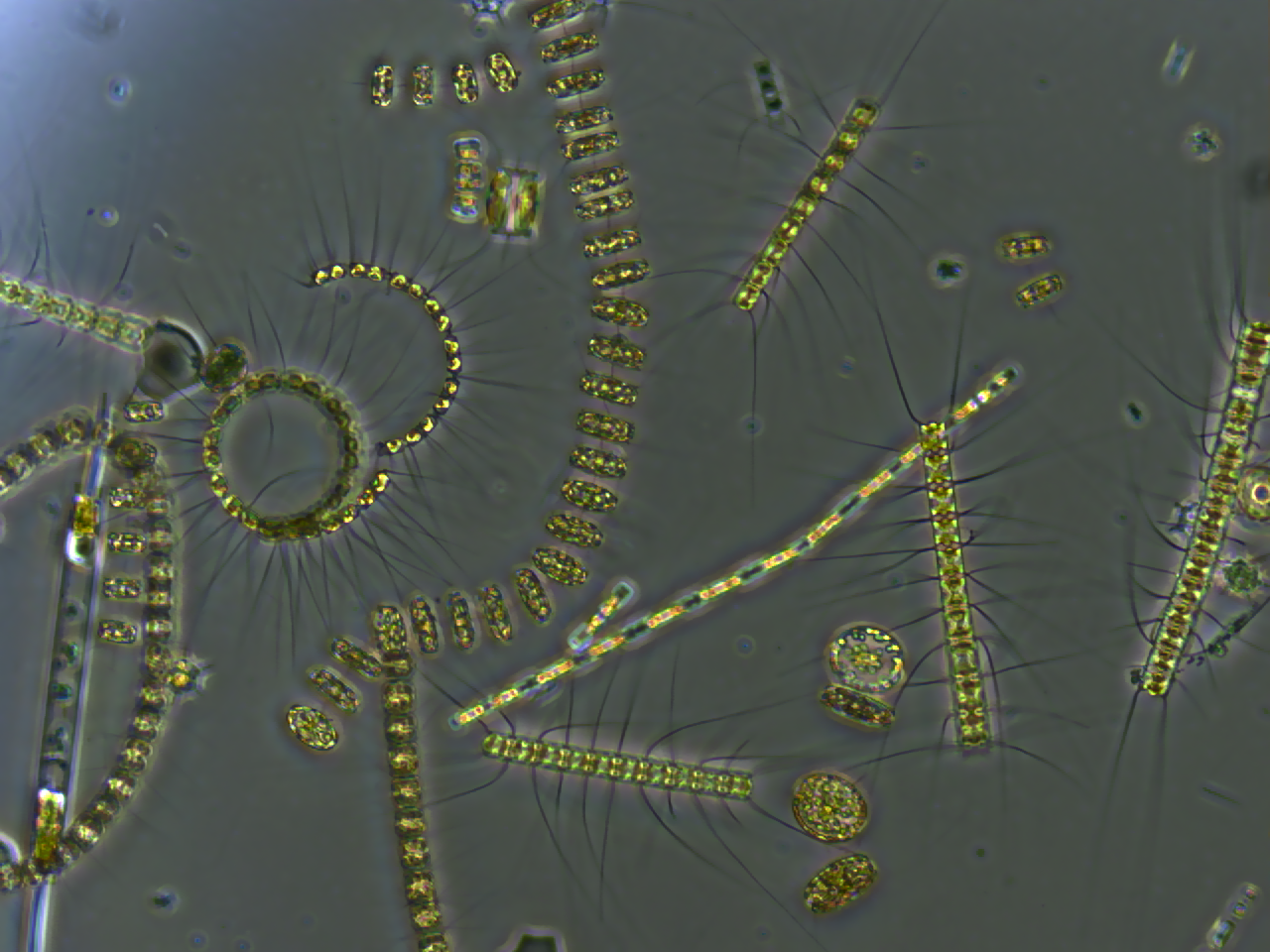
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size, shape, cargo or passenger capacity, or its ability to carry boats. Small boats are typically found on inland waterways such as rivers and lakes, or in protected coastal areas. However, some boats, such as the whaleboat, were intended for use in an offshore environment. In modern naval terms, a boat is a vessel small enough to be carried aboard a ship. Boats vary in proportion and construction methods with their intended purpose, available materials, or local traditions. Canoes have been used since prehistoric times and remain in use throughout the world for transportation, fishing, and sport. Fishing boats vary widely in style partly to match local conditions. Pleasure craft used in recreational boating include ski boats, pontoon boats, and sailboats. House boats may be used for vacationing or long-term residence. Lighters are use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)