|
Pinacoderm
The pinacoderm is the outermost layer of body cells (pinacocytes) of organisms of the phylum Porifera (sponges), equivalent to the epidermis in other animals. Structure The pinacoderm is composed of pinacocytes, flattened epithelial cells that can expand or contract to slightly alter the size and shape of the sponge. It also contains porocytes, oval-shaped cells extending from the pinacoderm to the choanoderm (the body layer containing choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a t ...). References Sponge anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacocytes
The pinacoderm is the outermost layer of body cells (pinacocytes) of organisms of the phylum Porifera (sponges), equivalent to the epidermis in other animals. Structure The pinacoderm is composed of pinacocytes, flattened epithelial cells that can expand or contract to slightly alter the size and shape of the sponge. It also contains porocytes, oval-shaped cells extending from the pinacoderm to the choanoderm (the body layer containing choanocytes Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a t ...). References Sponge anatomy {{animal-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porifera
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porocytes
Porocytes are tubular cells which make up the pores of a sponge known as ostia. Description Covering the sponge is a layer of cells known as the pinacoderm, which is composed of pinacocytes. In a sponge, pinacocytes are a thin, elastic layer which keeps water out. Between the pinacocytes, there are the porocytes that allow water into the sponge. Myocytes are small muscular cells that open and close the porocytes. They also form a circular ring around the osculum and help in closing and opening of it. Once through the pores, water travels down canals. The opening to a porocyte is a pore known as an ostium. In sponges, like Scypha, there are some cells that have an intracellular pore. These cells are known as porocytes. They are present in the Leucosolenia (an asconoid sponge) in the body wall through which water enters the body or they are present in Scypha ''Sycon'' is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Sycettidae. These sponges are small, growing up to 7.5&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choanoderm
The choanoderm is a type of cell layer composed of flagellated collar cells, or choanocytes, found in sponges. The sponge body is mostly a connective tissue; the mesohyl, over which are applied epithelioid monolayers of cells, the outer pinacoderm and the inner choanoderm. Importance Most aspects of sponge biology, including feeding, reproduction, and gas exchange, depend on a low pressure flow of water generated by the flagella of the choanoderm. Three grades of organization, asconoid, syconoid, and leuconoid, reflect the degree of elaboration of the choanoderm layer and mesohyl. In the asconoid plan the interior water space, or atrium Atrium may refer to: Anatomy * Atrium (heart), an anatomical structure of the heart * Atrium, the genital structure next to the genital aperture in the reproductive system of gastropods * Atrium of the ventricular system of the brain * Pulmona ..., is large and unpartitioned. In the syconoid plan the periphery of the atrium is divided int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis (skin)
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacocyte
Pinacocytes are flat cells found on the outside of the sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge. Pinacocytes are not specific to the sponge however. It was discovered that pinacocytes do not have as many sponge specific genes. These genes suggest that pinacocytes had evolved before the metazoan time period, which is, before porifera had evolved. Function Pinacocytes are part of the epithelium in sponges. They play a role in movement (contracting and stretching), cell adhesion, signaling, phagocytosis, and polarity. Pinacocytes are filled with mesohyl which is a gel like substance that helps maintain the shape and structure of the sponge. Types Basipinacocytes These are the cells in contact with the sponge's substrate (the surface to which it is attached). Exopinacocytes These are found on the exterior of the sponge. Exopinococytes produce spicules which is a needle like process that serves as structure for the organism. Endopinacocytes These line the sponge's inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
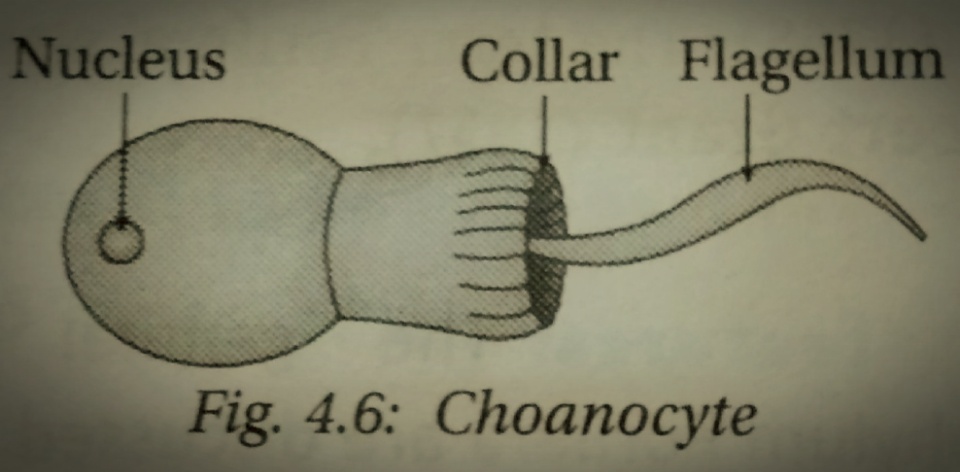
Choanocytes
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane. They make up the choanoderm, a type of cell layer found in sponges. The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans). The flagellae beat regularly, creating a water flow across the microvilli which can then filter nutrients from the water taken from the collar of the sponge. Food particles are then phagocytosed by the cell. Anderson, D. (2001) ''Invertebrate Zoology'' Oxford University Press Location Choanocytes are found dotting the surface of the spongocoel in asconoid sponges and the radial canals in syconoid sponges, but they comprise entirely the chambers in leuconoid sponges. Function By cooperatively moving their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |