choanocytes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are 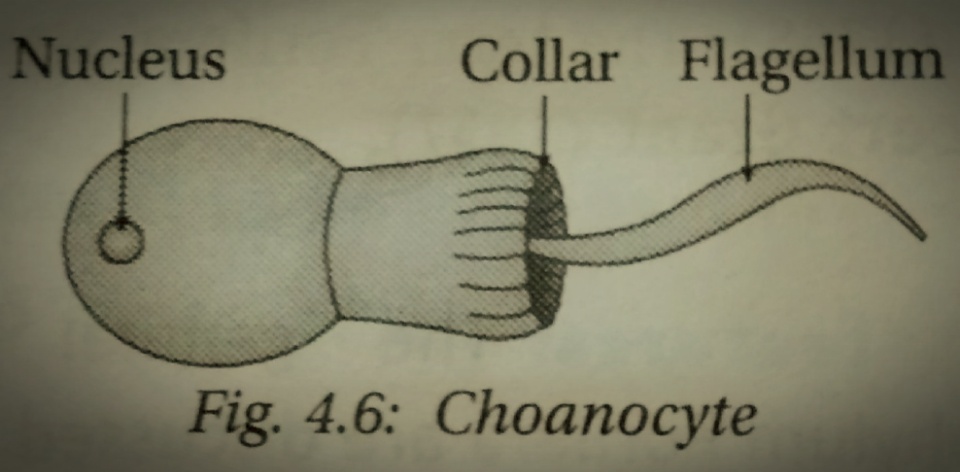 They make up the
They make up the
cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
s that line the interior of asconoid
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through th ...
, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through ...
that contain a central flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane.
 They make up the
They make up the choanoderm
The choanoderm is a type of cell layer composed of flagellated collar cells, or choanocytes, found in sponges. The sponge body is mostly a connective tissue; the mesohyl, over which are applied epithelioid monolayers of cells, the outer pinacoder ...
, a type of cell layer found in sponges
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through ...
. The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconn ...
which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans). The flagellae beat regularly, creating a water flow across the microvilli which can then filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
nutrients from the water taken from the collar of the sponge. Food particles are then phagocytosed
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is c ...
by the cell. Anderson, D. (2001) ''Invertebrate Zoology'' Oxford University Press
Location
Choanocytes are found dotting the surface of the spongocoel inasconoid
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through th ...
sponges and the radial canals in syconoid sponges, but they comprise entirely the chambers in leuconoid sponges.
Function
By cooperatively moving their flagella, choanocytes filter particles out of the water and into thespongocoel
A spongocoel (), also called paragaster (or paragastric cavity), is the large, central cavity of sponges. Water enters the spongocoel through hundreds of tiny pores ( ostia) and exits through the larger opening (osculum). Depending on the body pla ...
, and out through the osculum
The osculum (plural "oscula") is an excretory structure in the living sponge, a large opening to the outside through which the current of water exits after passing through the spongocoel. Wastes diffuse into the water and the water is pumped th ...
. This improves both respiratory and digestive functions for the sponge, pulling in oxygen and nutrients and allowing a rapid expulsion of carbon dioxide and other waste products. Although all cells in a sponge are capable of living on their own, choanocytes carry out most of the sponge's ingestion, passing digested materials to the amoebocytes An amebocyte or amoebocyte () is a mobile cell (moving like an amoeba) in the body of invertebrates including cnidaria, echinoderms, molluscs, tunicates, sponges and some chelicerates. They move by pseudopodia. Similarly to some of the white bloo ...
for delivery to other cells.
Choanocytes can also turn into spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and ...
s when needed for sexual reproduction, due to the lack of reproductive organs in sponges (amoebocytes become the oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ...
s).
Evolutionary Significance
Choanocytes bear a superficial resemblance toChoanoflagellates
The choanoflagellates are a group of free-living unicellular and colonial flagellate eukaryotes considered to be the closest living relatives of the animals. Choanoflagellates are collared flagellates, having a funnel shaped collar of interconn ...
. Molecular phylogenies indicate that choanoflagellates and metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
are sister groups. One can see some modern choanoflagellates living in small colonies. The evolutionary relationship between the two cell types is debated. Jasmine L. Mah, Karen K. Christensen‐Dalsgaard, Sally P. Leys "Choanoflagellate and choanocyte collar‐flagellar systems and the assumption of homology", 2014, https://doi.org/10.1111/ede.12060
See also
*Choanoderm
The choanoderm is a type of cell layer composed of flagellated collar cells, or choanocytes, found in sponges. The sponge body is mostly a connective tissue; the mesohyl, over which are applied epithelioid monolayers of cells, the outer pinacoder ...
References
{{reflist Histology Animal cells Sponge anatomy