|
Phylogenetic Invariants
Phylogenetic invariants are polynomial relationships between the frequencies of various site patterns in an idealized DNA multiple sequence alignment. They have received substantial study in the field of biomathematics, and they can be used to choose among phylogenetic tree topologies in an empirical setting. The primary advantage of phylogenetic invariants relative to other methods of phylogenetic estimation like maximum likelihood or Bayesian MCMC analyses is that invariants can yield information about the tree without requiring the estimation of branch lengths of model parameters. The idea of using phylogenetic invariants was introduced independently by James Cavender and Joseph Felsenstein and by James A. Lake in 1987. At this point the number of programs that allow empirical datasets to be analyzed using invariants is limited. However, phylogenetic invariants may provide solutions to other problems in phylogenetics and they represent an area of active research for that reason. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups of organisms. These relationships are determined by Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference methods that focus on observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, or morphology. The result of such an analysis is a phylogenetic tree—a diagram containing a hypothesis of relationships that reflects the evolutionary history of a group of organisms. The tips of a phylogenetic tree can be living taxa or fossils, and represent the "end" or the present time in an evolutionary lineage. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about the ancestral line, and doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi-squared Test
A chi-squared test (also chi-square or test) is a statistical hypothesis test used in the analysis of contingency tables In statistics, a contingency table (also known as a cross tabulation or crosstab) is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the (multivariate) frequency distribution of the variables. They are heavily used in survey research, business ... when the sample sizes are large. In simpler terms, this test is primarily used to examine whether two categorical variables (''two dimensions of the contingency table'') are independent in influencing the test statistic (''values within the table''). The test is Validity (statistics), valid when the test statistic is chi-squared distribution, chi-squared distributed under the null hypothesis, specifically Pearson's chi-squared test and variants thereof. Pearson's chi-squared test is used to determine whether there is a Statistical significance, statistically significant difference between the expected frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substitution Model
In biology, a substitution model, also called models of DNA sequence evolution, are Markov models that describe changes over evolutionary time. These models describe evolutionary changes in macromolecules (e.g., DNA sequences) represented as sequence of symbols (A, C, G, and T in the case of DNA). Substitution models are used to calculate the likelihood of phylogenetic trees using multiple sequence alignment data. Thus, substitution models are central to maximum likelihood estimation of phylogeny as well as Bayesian inference in phylogeny. Estimates of evolutionary distances (numbers of substitutions that have occurred since a pair of sequences diverged from a common ancestor) are typically calculated using substitution models (evolutionary distances are used input for distance methods such as neighbor joining). Substitution models are also central to phylogenetic invariants because they are necessary to predict site pattern frequencies given a tree topology. Substitution mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PAUP*
PAUP* (Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony *and other methods) is a computational phylogenetics program for inferring evolutionary trees (Phylogenetics, phylogenies), written by David L. Swofford. Originally, as the name implies, PAUP only implemented parsimony, but from version 4.0 (when the program became known as PAUP*) it also supports distance matrix and likelihood methods. Version 3.0 ran on Macintosh computers and supported a rich, user-friendly graphical interface. Together with the program MacClade, with which it shares the NEXUS data format, PAUP* was the phylogenetic software of choice for many phylogenetists. Version 4.0 added support for Windows (graphical shell and command line) and Unix (command line only) platforms. However, the graphical user interface for the Macintosh does not support versions of Mac OS X higher than 10.14 (although a GUI for later versions of Mac OS is planned). PAUP* is also available as a plugin for Geneious. PAUP*, which now sports th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ENCODE
The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) is a public research project which aims to identify functional elements in the human genome. ENCODE also supports further biomedical research by "generating community resources of genomics data, software, tools and methods for genomics data analysis, and products resulting from data analyses and interpretations." The current phase of ENCODE (2016-2019) is adding depth to its resources by growing the number of cell types, data types, assays and now includes support for examination of the mouse genome. History ENCODE was launched by the US National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) in September 2003. Intended as a follow-up to the Human Genome Project, the ENCODE project aims to identify all functional elements in the human genome. The project involves a worldwide consortium of research groups, and data generated from this project can be accessed through public databases. The initial release of ENCODE was in 2013 and since has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHYLIP
PHYLogeny Inference Package (PHYLIP) is a free computational phylogenetics package of programs for inferring evolutionary trees (Phylogenetics, phylogenies). It consists of 65 Porting, portable programs, i.e., the source code is written in the programming language C. As of version 3.696, it is licensed as open-source software; versions 3.695 and older were proprietary software freeware. Releases occur as source code, and as precompiled executables for many operating systems including Windows (95, 98, ME, NT, 2000, XP, Vista), Mac OS 8, Mac OS 9, OS X, Linux (Debian, Red Hat); and FreeBSD from FreeBSD.org. Full documentation is written for all the programs in the package and is included therein. The programs in the phylip package were written by Professor Joseph Felsenstein, of the Department of Genome Sciences and the Department of Biology, University of Washington, Seattle. Methods (implemented by each program) that are available in the package include parsimony, distance matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singular Value Decomposition
In linear algebra, the singular value decomposition (SVD) is a factorization of a real or complex matrix. It generalizes the eigendecomposition of a square normal matrix with an orthonormal eigenbasis to any \ m \times n\ matrix. It is related to the polar decomposition. Specifically, the singular value decomposition of an \ m \times n\ complex matrix is a factorization of the form \ \mathbf = \mathbf\ , where is an \ m \times m\ complex unitary matrix, \ \mathbf\ is an \ m \times n\ rectangular diagonal matrix with non-negative real numbers on the diagonal, is an n \times n complex unitary matrix, and \ \mathbf\ is the conjugate transpose of . Such decomposition always exists for any complex matrix. If is real, then and can be guaranteed to be real orthogonal matrices; in such contexts, the SVD is often denoted \ \mathbf^\mathsf\ . The diagonal entries \ \sigma_i = \Sigma_\ of \ \mathbf\ are uniquely determined by and are known as the singular values ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Hillis
David Mark Hillis (born December 21, 1958 in Copenhagen, Denmark) is an American evolutionary biologist, and the Alfred W. Roark Centennial Professor of Biology at the University of Texas at Austin. He is best known for his studies of molecular evolution, phylogeny, and vertebrate systematics. He created the popular Hillis Plot depiction of the evolutionary tree of life. Early life David Hillis was born in Copenhagen, Denmark in 1958, the son of William Hillis, an epidemiologist, and Aryge Briggs Hillis, a biostatistician. Hillis lived his early years in Denmark, Belgian Congo, India, and the United States, where he developed his interests in biology and biodiversity. He has two sons, Erec and Jonathan. His younger son, Jonathan Hillis, served in 2011 as the National Chief of the Order of the Arrow, the Honor Society of the Boy Scouts of America. His brother is computer scientist W. Daniel Hillis, and his sister is Argye E. Hillis, a professor of neurology at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbor Joining
In bioinformatics, neighbor joining is a bottom-up (agglomerative) clustering method for the creation of phylogenetic trees, created by Naruya Saitou and Masatoshi Nei in 1987. Usually based on DNA or protein sequence data, the algorithm requires knowledge of the distance between each pair of taxa (e.g., species or sequences) to create the phylogenetic tree. The algorithm Neighbor joining takes a distance matrix, which specifies the distance between each pair of taxa, as input. The algorithm starts with a completely unresolved tree, whose topology corresponds to that of a star network, and iterates over the following steps, until the tree is completely resolved, and all branch lengths are known: # Based on the current distance matrix, calculate a matrix Q (defined below). # Find the pair of distinct taxa i and j (i.e. with i \neq j) for which Q(i,j) is smallest. Make a new node that joins the taxa i and j, and connect the new node to the central node. For example, in part (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or other physical processes are possible. This relates to the philosophical concept to the extent that people may be considered to have as much freedom as they are physically able to exercise. Applications Statistics In statistics, degrees of freedom refers to the number of variables in a statistic calculation that can vary. It can be calculated by subtracting the number of estimated parameters from the total number of values in the sample. For example, a sample variance calculation based on n samples will have n-1 degrees of freedom, because sample variance is calculated using the sample mean as an estimate of the actual mean. Mathematics In mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newick Format
In mathematics, Newick tree format (or Newick notation or New Hampshire tree format) is a way of representing graph-theoretical trees with edge lengths using parentheses and commas. It was adopted by James Archie, William H. E. Day, Joseph Felsenstein, Wayne Maddison, Christopher Meacham, F. James Rohlf, and David Swofford, at two meetings in 1986, the second of which was at Newick's restaurant in Dover, New Hampshire, US. The adopted format is a generalization of the format developed by Meacham in 1984 for the first tree-drawing programs in Felsenstein's PHYLIP package. Examples The following tree: could be represented in Newick format in several ways ((,)); ''no nodes are named'' (A,B,(C,D)); ''leaf nodes are named'' (A,B,(C,D)E)F; ''all nodes are named'' (:0.1,:0.2,(:0.3,:0.4):0.5); ''all but root node have a distance to parent'' (:0.1,:0.2,(:0.3,:0.4):0.5):0.0; ''all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
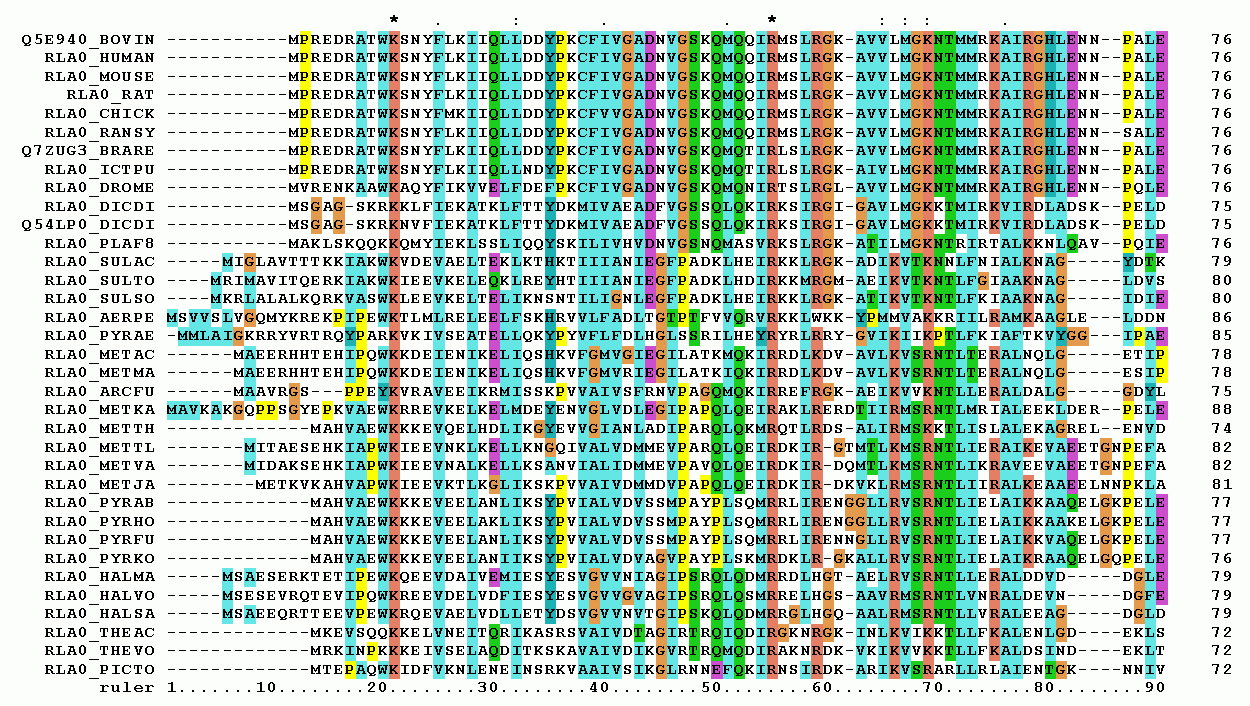
Multiple Sequence Alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutionary relationship by which they share a linkage and are descended from a common ancestor. From the resulting MSA, sequence homology can be inferred and phylogenetic analysis can be conducted to assess the sequences' shared evolutionary origins. Visual depictions of the alignment as in the image at right illustrate mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes) that appear as differing characters in a single alignment column, and insertion or deletion mutations (indels or gaps) that appear as hyphens in one or more of the sequences in the alignment. Multiple sequence alignment is often used to assess sequence conservation of protein domains, tertiary and secondary structures, and even individual amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |