|
Phycomycosis
Phycomycosis is an uncommon condition of the gastrointestinal tract and skin most commonly found in dogs and horses. The condition is caused by a variety of molds and fungi, and individual forms include pythiosis, zygomycosis, and lagenidiosis. Pythiosis is the most common type and is caused by ''Pythium'', a type of water mould. Zygomycosis can also be caused by two types of zygomycetes, ''Entomophthorales'' (such as '' Basidiobolus'' and ''Conidiobolus'') and ''Mucorales'' (such as ''Mucor'', ''Mortierella'', ''Absidia'', ''Rhizopus'', ''Rhizomucor'', and ''Saksenaea''). The latter type of zygomycosis is also referred to as mucormycosis. Lagenidiosis is caused by a ''Lagenidium'' species, which like ''Pythium'' is a water mould. Since both pythiosis and lagenidiosis are caused by organisms from the class Oomycetes, they are sometimes collectively referred to as oomycosis. Pythiosis Pythiosis is caused by ''Pythium insidiosum'' and occurs most commonly in dogs and horses, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
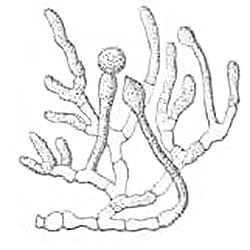
Basidiobolus
''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is a filamentous fungus with worldwide distribution. The fungus was first isolated by Eidam in 1886. It can saprophytically live in the intestines of mainly cold-blooded vertebrates and on decaying fruits and soil. The fungus prefers glucose as a carbon source and grows rapidly at room temperature. ''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is also known as a cause of subcutaneous zygomycosis, usually causing granulomatous infections on a host's limbs. Infections are generally geographically limited to tropical and subtropical regions such as East and West Africa. Subcutaneous zygomycosis caused by ''B. ranarum'' is a rare disease and predominantly affects children and males. Common subcutaneous zygomycosis shows characteristic features and is relatively easy to be diagnosed; while, certain rare cases might show non-specific clinical features that might pose a difficulty on its identification. Although disease caused by this fungus is known to resolve spontaneously on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
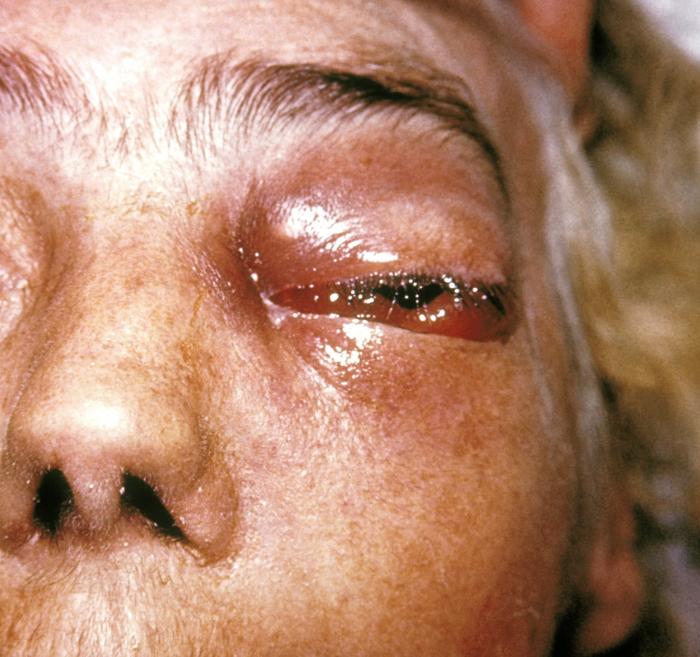
Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the infection occurs. It most commonly infects the nose, sinuses, eye, and brain resulting in a runny nose, one-sided facial swelling and pain, headache, fever, blurred vision, bulging or displacement of the eye (proptosis), and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs, stomach and intestines, and skin. It is spread by spores of molds of the order Mucorales, most often through inhalation, contaminated food, or contamination of open wounds. These fungi are common in soils, decomposing organic matter (such as rotting fruit and vegetables), and animal manure, but usually do not affect people. It is not transmitted between people. Risk factors include diabetes with persistently high blood sugar levels or diabetic ketoacido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absidia
''Absidia'' is a genus of zygote fungi in the family Cunninghamellaceae. ''Absidia'' species are ubiquitous in most environments where they are often associated with warm decaying plant matter, such as compost heaps. Some species in the genus can cause phycomycosis. Taxonomy The genus was first described in 1878 by Philippe Édouard Léon Van Tieghem. Species The genus includes the following species: * ''Absidia aegyptiaca'' * '' Absidia anomala'' * ''Absidia atrospora'' * ''Absidia caerulea'' * ''Absidia californica'' * ''Absidia clavata'' * ''Absidia cuneospora'' * ''Absidia cylindrospora'' * ''Absidia dubia'' * ''Absidia fassatiae'' * ''Absidia glauca'' * ''Absidia griseola'' * ''Absidia heterospora'' * ''Absidia idahoensis'' * ''Absidia inflata'' * ''Absidia macrospora'' * ''Absidia narayanai'' * ''Absidia pseudocylindrospora'' * ''Absidia psychrophilia'' * ''Absidia reflexa'' * ''Absidia repens'' * ''Absidia spinosa'' * ''Absidia tuneta'' * ''Absidia ushtrina'' Synonyms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythium Insidiosum
''Pythium insidiosum'' is a species of ''Pythium'' and a member of the class oomycota. ''Pythium insidiosum'' is mainly found in standing water and occasionally soil. Unlike most ''Pythium'' species, which are generally pathogens of terrestrial plants, ''Pythium insidiosum'' is a pathogen of mammals. It causes pythiosis, mainly in horses, dogs, and humans. It can also cause disease in cats. It is a non-transmissible disease and occurs mainly in tropical climate, endemic to Thailand, affecting mainly humans and horses and in Brazil, affecting mainly horses. Infection can occur in healthy mammals. The pathogen is well-adapted to mammalian body temperature, with an optimum temperature for growth of . The cell walls of ''Pythium insidiosum'' are composed of β-glucans and cellulose (compared to the chitin walls of fungi), and their cytoplasmic membranes lack sterol Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydroge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saksenaea
''Saksenaea'' is a genus of fungi in the Saksenaeaceae family. First described in 1953, the genus contains two pathogen In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...ic species capable of causing severe human infections. References Zygomycota genera {{Zygomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
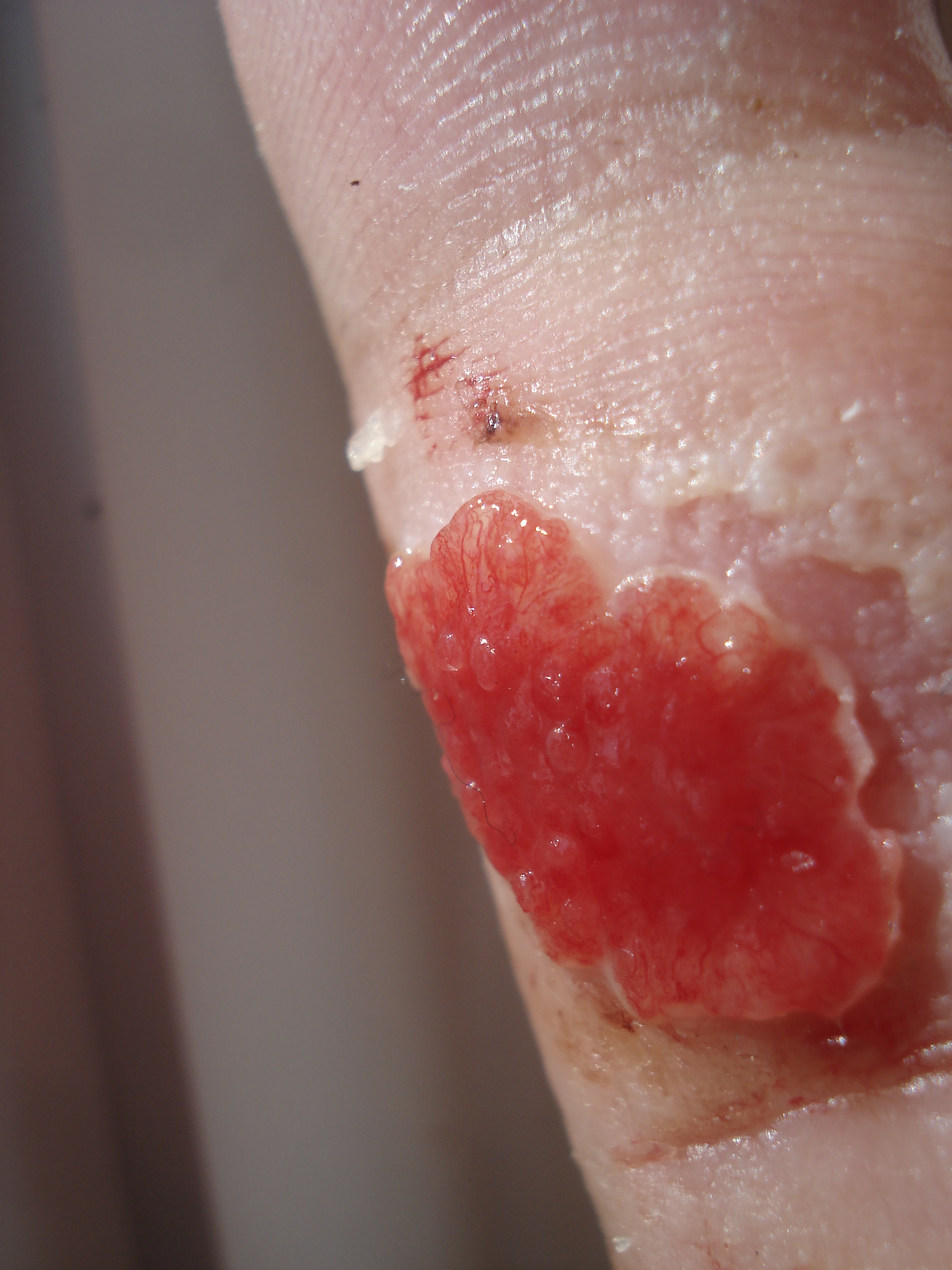
Granulation Tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size. Examples of granulation tissue can be seen in pyogenic granulomas and pulp polyps. Its histological appearance is characterized by proliferation of fibroblasts and new thin-walled, delicate capillaries (angiogenesis), infiltrated inflammatory cells in a loose extracellular matrix. Appearance During the migratory phase of wound healing, granulation tissue is: * light red or dark pink, being perfused with new capillary loops or "buds"; * soft to the touch; * moist; * bumpy (granular) in appearance, due to punctate hemorrhages; * pulsatile on palpation; * painless when healthy; Structure Granulation tissue is composed of tissue matrix supporting a variety of cell types, most of which can be associated with one of the following functions: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food ( chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and north-west of mainland Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia (continent), Australia and the Indian Ocean. Apart from the British Indian Ocean Territory and two out of atolls of Maldives, 26 atolls of Maldives in South Asia, Maritime Southeast Asia is the only other subregion of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere. Mainland Southeast Asia is completely in the Northern Hemisphere. East Timor and the southern portion of Indonesia are the only parts that are south of the Equator. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |