|
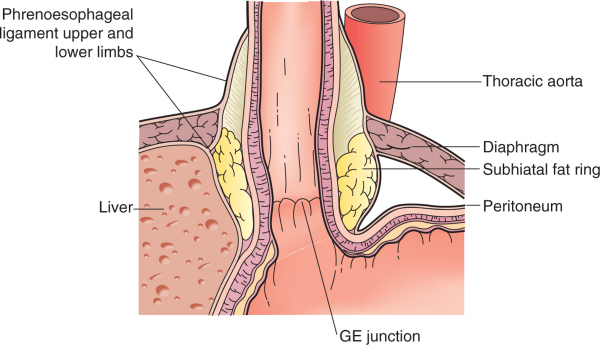
Phrenoesophageal Ligament
The phrenoesophageal ligament (phrenicoesophageal ligament, or phrenoesophageal membrane) is the ligament by which the esophagus is attached to the diaphragm. It is an extension of the inferior diaphragmatic fascia and is divided into an upper and lower limb which attach to the superior and inferior surfaces of the diaphragm respectively at the esophageal hiatus In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass. Structure It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine .... The upper limb attaches the esophagus to the superior surface of the diaphragm and the lower limb attaches the cardia region of the stomach to the inferior surface of the diaphragm at the cardiac notch of stomach. The ligament allows independent movement of the diaphragm and esophagus during respiration and swallowing. References * Full text' * * Ligaments {{l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophageal Hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass. Structure It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine. Fibers of the right crus cross one another below the hiatus. It is located approximately at level of the tenth thoracic vertebra ( T10) and the 8th or 9th intercostal spaces. The esophageal hiatus is situated in the muscular part of the diaphragm at the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra, and is elliptical in shape. It is placed superior, anterior, and slightly left of the aortic hiatus, and transmits the esophagus, the vagus nerve, the left inferior phrenic vessels, and some small esophageal arteries from left gastric vessels. The right crus of the diaphragm loops around forming a sling around the esophagus. Upon inspiration, this sling would constrict the esophagus, forming a functional (not anatomical) sphincter that prevents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardia
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Notch Of Stomach
The right margin of the oesophagus is continuous with the lesser curvature of the stomach, while the left margin joins the greater curvature The curvatures of the stomach refer to the greater and lesser curvatures. The greater curvature of the stomach is four or five times as long as the lesser curvature. Greater curvature The greater curvature of the stomach forms the lower lef ... at an acute angle, termed the cardiac notch (or cardial notch). See also * Cardiac notch of left lung References External links * () Digestive system Stomach {{digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |