|
Photoacoustic Imaging
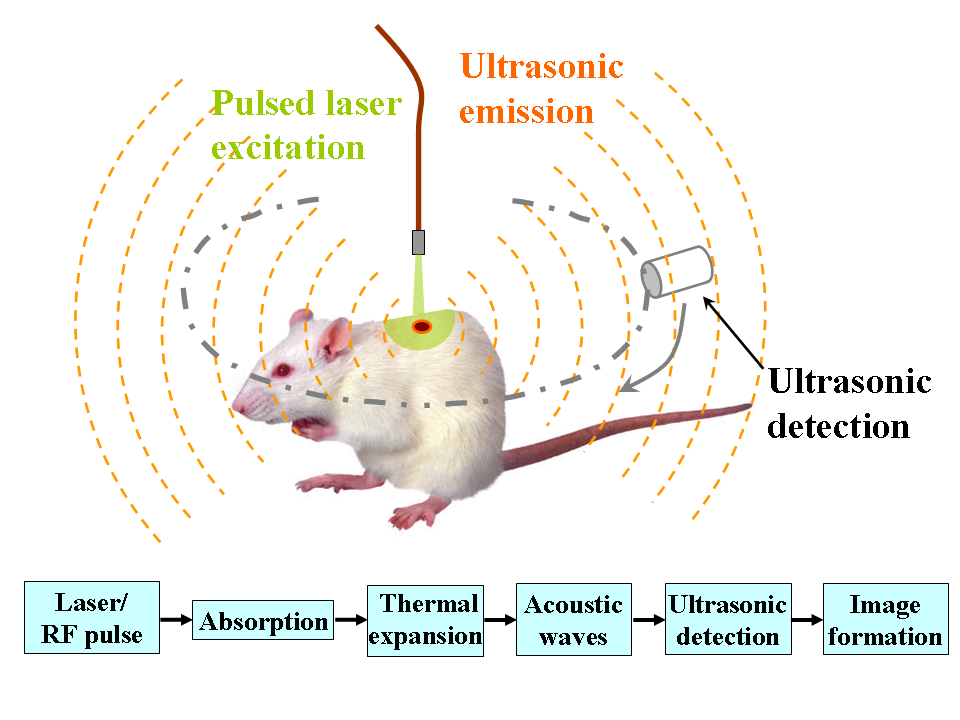
Photoacoustic imaging or optoacoustic imaging is a biomedical imaging modality based on the photoacoustic effect. Non-ionizing laser pulses are delivered into biological tissues and part of the energy will be absorbed and converted into heat, leading to transient thermoelastic expansion and thus wideband (i.e. MHz) ultrasonic emission. The generated ultrasonic waves are detected by ultrasonic transducers and then analyzed to produce images. It is known that optical absorption is closely associated with physiological properties, such as hemoglobin concentration and oxygen saturation. As a result, the magnitude of the ultrasonic emission (i.e. photoacoustic signal), which is proportional to the local energy deposition, reveals physiologically specific optical absorption contrast. 2D or 3D images of the targeted areas can then be formed. Biomedical imaging The optical absorption in biological tissues can be due to endogenous molecules such as hemoglobin or melanin, or exogenousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoacoustic Effect
The photoacoustic effect or optoacoustic effect is the formation of sound waves following light absorption in a material sample. In order to obtain this effect the light intensity must vary, either periodically (''modulated light'') or as a single flash (''pulsed light'').Rosencwaig, A. (1980''Photoacoustics and photoacoustic spectroscopy'' Chemical Analysis: a Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry and Its Applications, Vol. 57. New York:John Wiley & Sons, . The photoacoustic effect is quantified by measuring the formed sound (pressure changes) with appropriate detectors, such as microphones or piezoelectric sensors. The time variation of the electric output (current or voltage) from these detectors is the photoacoustic signal. These measurements are useful to determine certain properties of the studied sample. For example, in photoacoustic spectroscopy, the photoacoustic signal is used to obtain the actual absorption of light in either opaque or transparent objects. It is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Laser Acoustic Microscopy
Scan may refer to: Acronyms * Schedules for Clinical Assessment in Neuropsychiatry (SCAN), a psychiatric diagnostic tool developed by WHO * Shared Check Authorization Network (SCAN), a database of bad check writers and collection agency for bad checks * Space Communications and Navigation Program (SCaN) * Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (journal) * Scientific content analysis (SCAN), also known as statement analysis Businesses * Scan Furniture, Washington, D.C., US chain * SCAN Health Plan, not-for-profit health care company based in Long Beach, California * Scan AB or Scan Foods UK Ltd, the Swedish and UK subsidiaries of the Finnish HKScan Oyj * Seattle Community Access Network, Seattle, Washington, US TV channel * Scan (company), a software company based in Provo, Utah, US Electronics or computer related * 3D scanning * Counter-scanning, in physical micro and nanotopography measuring instruments like scanning probe microscope * Elevator algorithm (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoacoustic Microscopy
Photoacoustic microscopy is an imaging method based on the photoacoustic effect and is a subset of photoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustic microscopy takes advantage of the local temperature rise that occurs as a result of light absorption in tissue. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser beam, tissues undergo thermoelastic expansion, resulting in the release of a wide-band acoustic wave that can be detected using a high-frequency ultrasound transducer. Since ultrasonic scattering in tissue is weaker than optical scattering, photoacoustic microscopy is capable of achieving high-resolution images at greater depths than conventional microscopy methods. Furthermore, photoacoustic microscopy is especially useful in the field of biomedical imaging due to its scalability. By adjusting the optical and acoustic foci, lateral resolution may be optimized for the desired imaging depth. Photoacoustic signal The goal of photoacoustic microscopy is to find the local pressure rise p_0, which can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multispectral Optoacoustic Tomography
Multi-spectral optoacoustic tomography (MSOT), also known as functional photoacoustic tomography (fPAT), is an imaging technology that generates high-resolution optical images in scattering media, including biological tissues. MSOT illuminates tissue with light of transient energy, typically light pulses lasting 1-100 nanoseconds. The tissue absorbs the light pulses, and as a result undergoes thermo-elastic expansion, a phenomenon known as the optoacoustic or photoacoustic effect. This expansion gives rise to ultrasound waves (photoechoes) that are detected and formed into an image. Image formation can be done by means of hardware (e.g. acoustic focusing or optical focusing) or computed tomography (mathematical image formation). Unlike other types of optoacoustic imaging, MSOT involves illuminating the sample with multiple wavelengths, allowing it to detect ultrasound waves emitted by different photoabsorbing molecules in the tissue, whether endogenous (oxygenated and deoxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Learning In Photoacoustic Imaging
Deep learning in photoacoustic imaging combines the hybrid imaging modality of photoacoustic imaging (PA) with the rapidly evolving field of deep learning. Photoacoustic imaging is based on the photoacoustic effect, in which optical absorption causes a rise in temperature, which causes a subsequent rise in pressure via thermo-elastic expansion. This pressure rise propagates through the tissue and is sensed via ultrasonic transducers. Due to the proportionality between the optical absorption, the rise in temperature, and the rise in pressure, the ultrasound pressure wave signal can be used to quantify the original optical energy deposition within the tissue. Photoacoustic imaging has applications of deep learning in both Photoacoustic imaging#Photoacoustic microscopy, photoacoustic computed tomography (PACT) and photoacoustic microscopy (PAM). PACT utilizes wide-field optical excitation and an array of unfocused ultrasound transducers. Similar to CT scan, other computed tomography m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canvas
Canvas is an extremely durable plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, shelters, as a support for oil painting and for other items for which sturdiness is required, as well as in such fashion objects as handbags, electronic device cases, and shoes. It is popularly used by artists as a painting surface, typically stretched across a wooden frame. Modern canvas is usually made of cotton or linen, or sometimes polyvinyl chloride (PVC), although historically it was made from hemp. It differs from other heavy cotton fabrics, such as denim, in being plain weave rather than twill weave. Canvas comes in two basic types: plain and duck. The threads in duck canvas are more tightly woven. The term ''duck'' comes from the Dutch word for cloth, ''doek''. In the United States, canvas is classified in two ways: by weight (ounces per square yard) and by a graded number system. The numbers run in reverse of the weight so a number 10 canvas is lighter than number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Painting
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments with a medium of drying oil as the binder. It has been the most common technique for artistic painting on wood panel or canvas for several centuries, spreading from Europe to the rest of the world. The advantages of oil for painting images include "greater flexibility, richer and denser colour, the use of layers, and a wider range from light to dark". But the process is slower, especially when one layer of paint needs to be allowed to dry before another is applied. The oldest known oil paintings were created by Buddhist artists in Afghanistan and date back to the 7th century AD. The technique of binding pigments in oil was later brought to Europe in the 15th century, about 900 years later. The adoption of oil paint by Europeans began with Early Netherlandish painting in Northern Europe, and by the height of the Renaissance, oil painting techniques had almost completely replaced the use of tempera paints in the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and airbrushes, can be used. In art, the term ''painting ''describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate multiple other materials, including sand, clay, paper, plaster, gold leaf, and even whole objects. Painting is an important form in the visual arts, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture (as in gestural painting), narration (as in narrative art), and abstraction (as in abstract art). Paintings can be naturalistic and representational (as in still life and landscape painting), photographic, abstract, nar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Of Art
A work of art, artwork, art piece, piece of art or art object is an artistic creation of aesthetic value. Except for "work of art", which may be used of any work regarded as art in its widest sense, including works from literature and music, these terms apply principally to tangible, physical forms of visual art: *An example of fine art, such as a painting or sculpture. *Objects in the decorative arts or applied arts that have been designed for aesthetic appeal, as well as any functional purpose, such as a piece of jewellery, many ceramics and much folk art. *An object created for principally or entirely functional, religious or other non-aesthetic reasons which has come to be appreciated as art (often later, or by cultural outsiders). *A non-ephemeral photograph or film. *A work of installation art or conceptual art. Used more broadly, the term is less commonly applied to: *A fine work of architecture or landscape design *A production of live performance, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color that is seen by our eyes is the one not absorbed by the reflecting object within a certain wavelength spectrum of visible light. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two separate molecular orbitals falls within the range of the visible spectrum. Visible light that hits the chromophore can thus be absorbed by exciting an electron from its ground state into an excited state. In biological molecules that serve to capture or detect light energy, the chromophore is the moiety that causes a conformational change in the molecule when hit by light. Conjugated pi-bond system chromophores Just like how two adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule will form a pi-bond, three or more adjacent p-orbitals in a molecule can form a conjugated pi-system. In a conjugated pi-system, electrons are able to capture certain photons as the electrons resonate along a certain distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Pressure
Sound pressure or acoustic pressure is the local pressure deviation from the ambient (average or equilibrium) atmospheric pressure, caused by a sound wave. In air, sound pressure can be measured using a microphone, and in water with a hydrophone. The SI unit of sound pressure is the pascal (Pa). Mathematical definition A sound wave in a transmission medium causes a deviation (sound pressure, a ''dynamic'' pressure) in the local ambient pressure, a ''static'' pressure. Sound pressure, denoted ''p'', is defined by p_\text = p_\text + p, where * ''p''total is the total pressure, * ''p''stat is the static pressure. Sound measurements Sound intensity In a sound wave, the complementary variable to sound pressure is the particle velocity. Together, they determine the sound intensity of the wave. ''Sound intensity'', denoted I and measured in W· m−2 in SI units, is defined by \mathbf I = p \mathbf v, where * ''p'' is the sound pressure, * v is the particle velocity. Acoustic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoacoustic Microscopy
Photoacoustic microscopy is an imaging method based on the photoacoustic effect and is a subset of photoacoustic tomography. Photoacoustic microscopy takes advantage of the local temperature rise that occurs as a result of light absorption in tissue. Using a nanosecond pulsed laser beam, tissues undergo thermoelastic expansion, resulting in the release of a wide-band acoustic wave that can be detected using a high-frequency ultrasound transducer. Since ultrasonic scattering in tissue is weaker than optical scattering, photoacoustic microscopy is capable of achieving high-resolution images at greater depths than conventional microscopy methods. Furthermore, photoacoustic microscopy is especially useful in the field of biomedical imaging due to its scalability. By adjusting the optical and acoustic foci, lateral resolution may be optimized for the desired imaging depth. Photoacoustic signal The goal of photoacoustic microscopy is to find the local pressure rise p_0, which can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpeg/1200px-Fall_Leaves_(199582361).jpeg)
