|
Philosophy Of Color
The philosophy of color is a subset of the philosophy of perception that is concerned with the nature of the perceptual experience of color. Any explicit account of color perception requires a commitment to one of a variety of ontological In metaphysics, ontology is the philosophical study of being, as well as related concepts such as existence, becoming, and reality. Ontology addresses questions like how entities are grouped into categories and which of these entities exis ... or Metaphysics, metaphysical views, distinguishing namely between externalism/internalism, which relate respectively to color realism, the view that colors are physical properties that objects possess, and color fictionalism, the view that colors possess no such physical properties. History Philosophical concerns about the nature of color can be traced back at least as far as Anaxagoras (5th century BCE), who favoured color realism in his sophism: "Snow is frozen water. But water is dark in col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RBG Color Wheel
Joan Ruth Bader Ginsburg ( ; ; March 15, 1933September 18, 2020) was an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1993 until her death in 2020. She was nominated by President Bill Clinton to replace retiring justice Byron White, and at the time was generally viewed as a moderate consensus-builder. She eventually became part of the Ideological leanings of United States Supreme Court justices, liberal wing of the Court as the Court shifted to the right over time. Ginsburg was the first Jewish woman and the second woman to serve on the Court, after Sandra Day O'Connor. During her tenure, Ginsburg wrote notable majority opinions, including ''United States v. Virginia''(1996), ''Olmstead v. L.C.''(1999), ''Friends of the Earth, Inc. v. Laidlaw Environmental Services, Inc.''(2000), and ''City of Sherrill v. Oneida Indian Nation of New York''(2005). Ginsburg was born and grew up in Brooklyn, New York. Her older siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Churchland
Paul Montgomery Churchland (born October 21, 1942) is a Canadian philosopher known for his studies in neurophilosophy and the philosophy of mind. After earning a Ph.D. from the University of Pittsburgh under Wilfrid Sellars (1969), Churchland rose to the rank of full professor at the University of Manitoba before accepting the Valtz Family Endowed Chair in Philosophy at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) and a joint appointments in that institution's Institute for Neural Computation and on its Cognitive Science Faculty. As of February 2017, Churchland is recognised as Professor Emeritus at the UCSD, and is a member of the Board of Trustees of the Moscow Center for Consciousness Studies of Moscow State University. Churchland is the husband of philosopher Patricia Churchland, with whom he collaborates, and ''The New Yorker'' has reported the similarity of their views, e.g., on the mind-body problem, are such that the two are often discussed as if they are one person. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates. Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance. Color science includes the perception of color by the eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realism (visual Arts)
Realism in the arts is generally the attempt to represent subject matter truthfully, without artificiality and avoiding speculative and supernatural elements. The term is often used interchangeably with naturalism, although these terms are not synonymous. Naturalism, as an idea relating to visual representation in Western art, seeks to depict objects with the least possible amount of distortion and is tied to the development of linear perspective and illusionism in Renaissance Europe. Realism, while predicated upon naturalistic representation and a departure from the idealization of earlier academic art, often refers to a specific art historical movement that originated in France in the aftermath of the French Revolution of 1848. With artists like Gustave Courbet capitalizing on the mundane, ugly or sordid, realism was motivated by the renewed interest in the common man and the rise of leftist politics. The Realist painters rejected Romanticism, which had come to dominate Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualia
In philosophy of mind, qualia ( or ; singular form: quale) are defined as individual instances of subjective, conscious experience. The term ''qualia'' derives from the Latin neuter plural form (''qualia'') of the Latin adjective '' quālis'' () meaning "of what sort" or "of what kind" in a specific instance, such as "what it is like to taste a specific this particular apple now". Examples of qualia include the perceived sensation of ''pain'' of a headache, the ''taste'' of wine, as well as the ''redness'' of an evening sky. As qualitative characters of sensation, qualia stand in contrast to propositional attitudes, where the focus is on beliefs about experience rather than what it is directly like to be experiencing. Philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel Dennett once suggested that ''qualia'' was "an unfamiliar term for something that could not be more familiar to each of us: the ways things seem to us". Much of the debate over their importance hinges on the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictionalism
Fictionalism is the view in philosophy according to which statements that appear to be descriptions of the world should not be construed as such, but should instead be understood as cases of "make believe", of pretending to treat something as literally true (a "useful fiction"). Concept Fictionalism consists in at least the following three theses: # Claims made within the domain of discourse are taken to be truth-apt; that is, true or false # The domain of discourse is to be interpreted at face value—not reduced to meaning something else # The aim of discourse in any given domain is not truth, but some other virtue(s) (e.g., simplicity, explanatory scope). Two important strands of fictionalism are modal fictionalism developed by Gideon Rosen, which states that possible worlds, regardless of whether they exist or not, may be a part of a useful discourse, and mathematical fictionalism advocated by Hartry Field. Modal fictionalism is recognized as further refinement to the basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Television
Color television or Colour television is a television transmission technology that includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improves on the monochrome or black-and-white television technology, which displays the image in shades of gray (grayscale). Television broadcasting stations and networks in most parts of the world upgraded from black-and-white to color transmission between the 1960s and the 1980s. The invention of color television standards was an important part of the history and technology of television. Transmission of color images using mechanical scanners had been conceived as early as the 1880s. A demonstration of mechanically scanned color television was given by John Logie Baird in 1928, but its limitations were apparent even then. Development of electronic scanning and display made a practical system possible. Monochrome transmission standards were developed prior to World War II, but civili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that studies nervous system function rather than nervous system architecture. This area aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Historically, it has been dominated by electrophysiology—the electrical recording of neural activity ranging from the molar (the electroencephalogram, EEG) to the cellular (intracellular recording of the properties of single neurons), such as patch clamp, voltage clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials. However, since the neurone is an electrochemical machine, it is difficult to isolate electrical events from the metabolic and molecular processes that cause them. Thus, neurophysiologists currently utilise tools from chemistry (calcium imaging), physics (functional magnetic resonance imaging, Functional magnetic resonance imaging, fMRI), and molecular biology (site directed mutations) to examine brain activity. The word originates f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
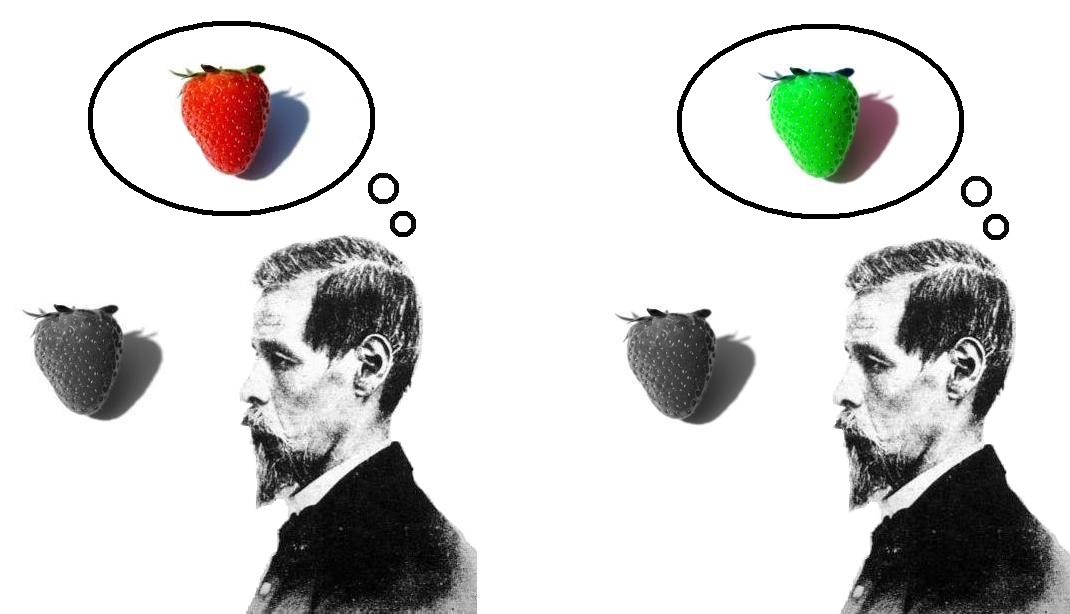
Knowledge Argument
The knowledge argument (also known as Mary's room or Mary the super-scientist) is a philosophical thought experiment proposed by Frank Jackson in his article "Epiphenomenal Qualia" (1982) and extended in "What Mary Didn't Know" (1986). The experiment describes Mary, a scientist who exists in a black and white world where she has extensive access to physical descriptions of color, but no actual human perceptual experience of color. The central question of the thought experiment is whether Mary will gain new knowledge when she goes outside the black and white world and experiences seeing in color. The experiment is intended to argue against physicalism—the view that the universe, including all that is mental, is entirely physical. The debate that emerged following its publication became the subject of an edited volume—''There's Something About Mary'' (2004)—which includes replies from such philosophers as Daniel Dennett, David Lewis, and Paul Churchland. Thought experiment Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Colour Scientist
Mary may refer to: People * Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name) Religious contexts * New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below * Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blessed Virgin Mary * Mary Magdalene, devoted follower of Jesus * Mary of Bethany, follower of Jesus, considered by Western medieval tradition to be the same person as Mary Magdalene * Mary, mother of James * Mary of Clopas, follower of Jesus * Mary, mother of John Mark * Mary of Egypt, patron saint of penitents * Mary of Rome, a New Testament woman * Mary, mother of Zechariah and sister of Moses and Aaron; mostly known by the Hebrew name: Miriam * Mary the Jewess one of the reputed founders of alchemy, referred to by Zosimus. * Mary 2.0, Roman Catholic women's movement * Maryam (surah) "Mary", 19th surah (chapter) of the Qur'an Royalty * Mary, Countess of Blois (1200–1241), daughter of Walter of Avesnes and Margaret of Blois * Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualia
In philosophy of mind, qualia ( or ; singular form: quale) are defined as individual instances of subjective, conscious experience. The term ''qualia'' derives from the Latin neuter plural form (''qualia'') of the Latin adjective '' quālis'' () meaning "of what sort" or "of what kind" in a specific instance, such as "what it is like to taste a specific this particular apple now". Examples of qualia include the perceived sensation of ''pain'' of a headache, the ''taste'' of wine, as well as the ''redness'' of an evening sky. As qualitative characters of sensation, qualia stand in contrast to propositional attitudes, where the focus is on beliefs about experience rather than what it is directly like to be experiencing. Philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel Dennett once suggested that ''qualia'' was "an unfamiliar term for something that could not be more familiar to each of us: the ways things seem to us". Much of the debate over their importance hinges on the definition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |