|
Parallelogram
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a simple polygon, simple (non-list of self-intersecting polygons, self-intersecting) quadrilateral with two pairs of Parallel (geometry), parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure. The congruence (geometry), congruence of opposite sides and opposite angles is a direct consequence of the Euclidean parallel postulate and neither condition can be proven without appealing to the Euclidean parallel postulate or one of its equivalent formulations. By comparison, a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is a trapezoid in American English or a trapezium in British English. The three-dimensional counterpart of a parallelogram is a parallelepiped. The word "parallelogram" comes from the Greek παραλληλό-γραμμον, ''parallēló-grammon'', which means "a shape of parallel lines". Special cases *Rectangle – A par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four Edge (geometry), edges (sides) and four Vertex (geometry), corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons (e.g. pentagon). Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices A, B, C and D is sometimes denoted as \square ABCD. Quadrilaterals are either simple polygon, simple (not self-intersecting), or complex polygon, complex (self-intersecting, or crossed). Simple quadrilaterals are either convex polygon, convex or concave polygon, concave. The Internal and external angle, interior angles of a simple (and Plane (geometry), planar) quadrilateral ''ABCD'' add up to 360 Degree (angle), degrees, that is :\angle A+\angle B+\angle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallelogram Law
In mathematics, the simplest form of the parallelogram law (also called the parallelogram identity) belongs to elementary geometry. It states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the four sides of a parallelogram equals the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two diagonals. We use these notations for the sides: ''AB'', ''BC'', ''CD'', ''DA''. But since in Euclidean geometry a parallelogram necessarily has opposite sides equal, that is, ''AB'' = ''CD'' and ''BC'' = ''DA'', the law can be stated as 2AB^2 + 2BC^2 = AC^2 + BD^2\, If the parallelogram is a rectangle, the two diagonals are of equal lengths ''AC'' = ''BD'', so 2AB^2 + 2BC^2 = 2AC^2 and the statement reduces to the Pythagorean theorem. For the general quadrilateral (with four sides not necessarily equal) Euler's quadrilateral theorem states AB^2 + BC^2 + CD^2+DA^2 = AC^2+BD^2 + 4x^2, where x is the length of the line segment joining the midpoints of the diagonals. It can be seen from the diagram that x = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
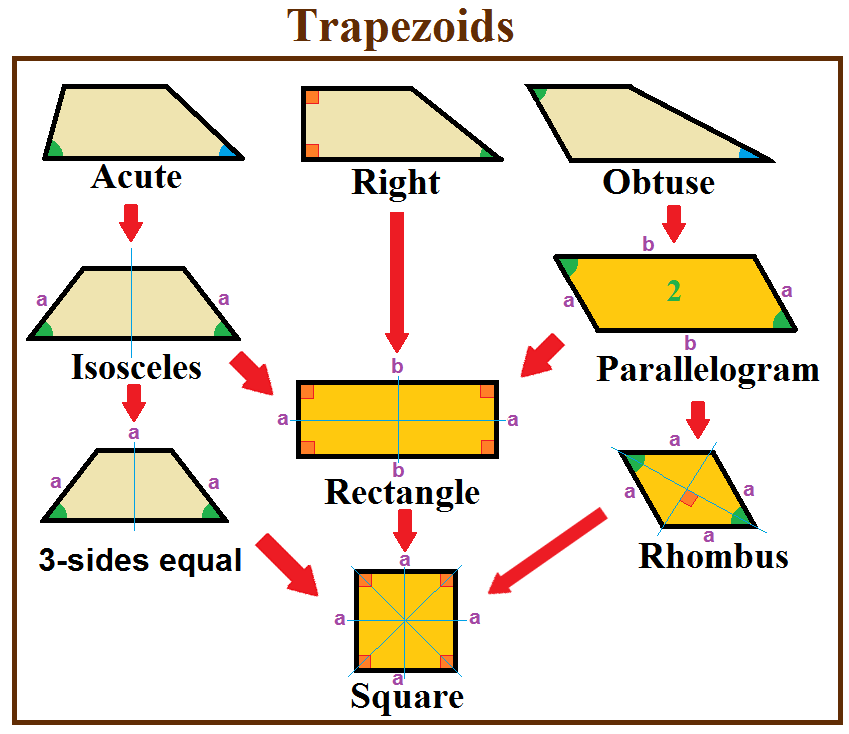
Trapezoid
In geometry, a trapezoid () in North American English, or trapezium () in British English, is a quadrilateral that has at least one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called the ''bases'' of the trapezoid. The other two sides are called the ''legs'' or ''lateral sides''. (If the trapezoid is a parallelogram, then the choice of bases and legs is arbitrary.) A trapezoid is usually considered to be a convex quadrilateral in Euclidean geometry, but there are also crossed cases. If ''ABCD'' is a convex trapezoid, then ''ABDC'' is a crossed trapezoid. The metric formulas in this article apply in convex trapezoids. Definitions ''Trapezoid'' can be defined exclusively or inclusively. Under an exclusive definition a trapezoid is a quadrilateral having pair of parallel sides, with the other pair of opposite sides non-parallel. Parallelograms including rhombi, rectangles, and squares are then not considered to be trapezoids. Under an inclusive definition, a trapezoid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallelepiped
In geometry, a parallelepiped is a three-dimensional figure formed by six parallelograms (the term ''rhomboid'' is also sometimes used with this meaning). By analogy, it relates to a parallelogram just as a cube relates to a square. Three equivalent definitions of ''parallelepiped'' are *a hexahedron with three pairs of parallel faces, *a polyhedron with six faces (hexahedron), each of which is a parallelogram, and *a prism (geometry), prism of which the base is a parallelogram. The rectangular cuboid (six rectangular faces), cube (six square faces), and the rhombohedron (six rhombus faces) are all special cases of parallelepiped. "Parallelepiped" is now usually pronounced or ; traditionally it was because of its etymology in Ancient Greek, Greek παραλληλεπίπεδον ''parallelepipedon'' (with short -i-), a body "having parallel planes". Parallelepipeds are a subclass of the prismatoids. Properties Any of the three pairs of parallel faces can be viewed as the bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (: rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the Diamonds (suit), diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an Octahedron#Orthogonal projections, octahedral diamond, or a lozenge (shape), lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after calisson, the French sweet—also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple polygon, simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a Kite (geometry), kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from , meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomboid
Traditionally, in two-dimensional geometry, a rhomboid is a parallelogram in which adjacent sides are of unequal lengths and angles are non-right angled. The terms "rhomboid" and "parallelogram" are often erroneously conflated with each other (i.e, when most people refer to a "parallelogram" they almost always mean a rhomboid, a specific subtype of parallelogram); however, while all rhomboids are parallelograms, not all parallelograms are rhomboids. A parallelogram with sides of equal length ( equilateral) is called a ''rhombus'' but not a rhomboid. A parallelogram with right angled corners is a ''rectangle'' but not a rhomboid. A parallelogram is a rhomboid if it is neither a rhombus nor a rectangle. History Euclid introduced the term in his '' Elements'' in Book 1, Definition 22, Euclid never used the definition of rhomboid again and introduced the word parallelogram in Proposition 34 of Book 1; ''"In parallelogrammic areas the opposite sides and angles are equal to on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectangle
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a ''square''. The term "wikt:oblong, oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with Vertex (geometry), vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted as . The word rectangle comes from the Latin ''rectangulus'', which is a combination of ''rectus'' (as an adjective, right, proper) and ''angulus'' (angle). A #Crossed rectangles, crossed rectangle is a crossed (self-intersecting) quadrilateral which consists of two opposite sides of a rectangle along with the two diagonals (therefore only two sides are parallel). It is a special case of an antiparallelogram, and its angles are not right angles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Cross Product
In mathematics, the cross product or vector product (occasionally directed area product, to emphasize its geometric significance) is a binary operation on two vectors in a three-dimensional oriented Euclidean vector space (named here E), and is denoted by the symbol \times. Given two linearly independent vectors and , the cross product, (read "a cross b"), is a vector that is perpendicular to both and , and thus normal to the plane containing them. It has many applications in mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer programming. It should not be confused with the dot product (projection product). The magnitude of the cross product equals the area of a parallelogram with the vectors for sides; in particular, the magnitude of the product of two perpendicular vectors is the product of their lengths. The units of the cross-product are the product of the units of each vector. If two vectors are parallel or are anti-parallel (that is, they are linearly dependent), or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square (geometry)
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degrees, or /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for squaring the circle by compass and straightedge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viviani's Theorem
Viviani's theorem, named after Vincenzo Viviani, states that the sum of the shortest distances from ''any'' interior point to the sides of an equilateral triangle equals the length of the triangle's altitude. It is a theorem commonly employed in various math competitions, secondary school mathematics examinations, and has wide applicability to many problems in the real world. Proof This proof depends on the readily-proved proposition that the area of a triangle is half its base times its height—that is, half the product of one side with the altitude from that side.Claudi Alsina, Roger B. Nelsen: ''Charming Proofs: A Journey Into Elegant Mathematics''. MAA 2010, , p. 96 () Let ABC be an equilateral triangle whose height is ''h'' and whose side is ''a''. Let P be any point inside the triangle, and ''s, t, u'' the perpendicular distances of P from the sides. Draw a line from P to each of A, B, and C, forming three triangles PAB, PBC, and PCA. Now, the areas of these tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |