|
Parabiosis
Parabiosis, meaning "living beside", is a laboratory technique to study physiology. It combines two living organisms which are joined surgically to develop a single, shared physiological system. Parabiosis is used in the study of areas such as obesity, biological aging, stem cell research, tissue regeneration, diabetes, organ transplantation, tumor biology, and endocrinology. It can also describe a communal ecology of separate species of ants in colonies. Physiology Parabiotic experiments Parabiosis combines two living organisms which are joined surgically and develop single, shared physiological systems. Researchers can prove that the feedback system in one animal is circulated and affects the second animal via blood and plasma exchange. Parabiotic experiments were pioneered by Paul Bert in the mid-1800s. He postulated that surgically connected animals could share a circulatory system. Bert was awarded the Prize of Experimental Physiology of the French Academy of Science i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, '' pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
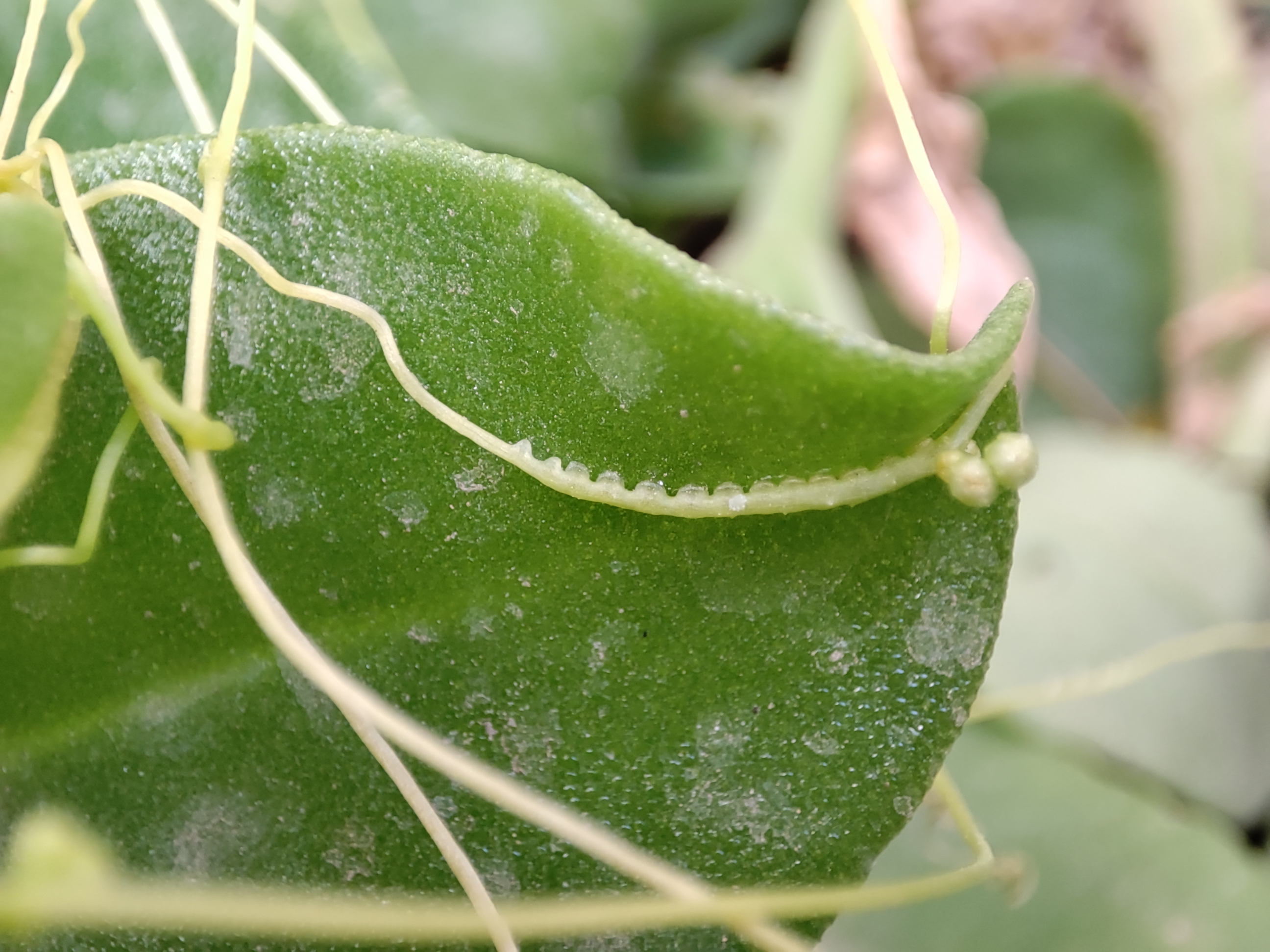
Dodder
''Cuscuta'' (), commonly known as dodder or amarbel, is a genus of over 201 species of yellow, orange, or red (rarely green) parasitic plants. Formerly treated as the only genus in the family Cuscutaceae, it now is accepted as belonging in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae, on the basis of the work of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. The genus is found throughout the temperate and tropical regions of the world, with the greatest species diversity in subtropical and tropical regions; the genus becomes rare in cool temperate climates, with only four species native to northern Europe. Folk names include: strangle tare, scaldweed, beggarweed, lady's laces, fireweed, wizard's net, devil's guts, devil's hair, devil's ringlet, goldthread, hailweed, hairweed, hellbine, love vine, pull-down, strangleweed, angel hair, and witch's hair. Description Cuscuta can be identified by its thin stems appearing leafless, with the leaves reduced to minute scales. In these respects it clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistletoe
Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant. The name mistletoe originally referred to the species '' Viscum album'' (European mistletoe, of the family Santalaceae in the order Santalales); it is the only species native to the British Isles and much of Europe. A related species with red rather than white fruits, '' Viscum cruciatum'', occurs in Southwest Spain and Southern Portugal, as well as in Morocco in North Africa and in southern Africa. The genus ''Viscum'' is not native to North America, but ''Viscum album'' was introduced to Northern California in 1900. The eastern mistletoe native to North America, '' Phoradendron leucarpum'', belongs to a distinct genus of the family Santalaceae. European mistletoe has smooth-edged, oval, evergreen leaves borne in pairs along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
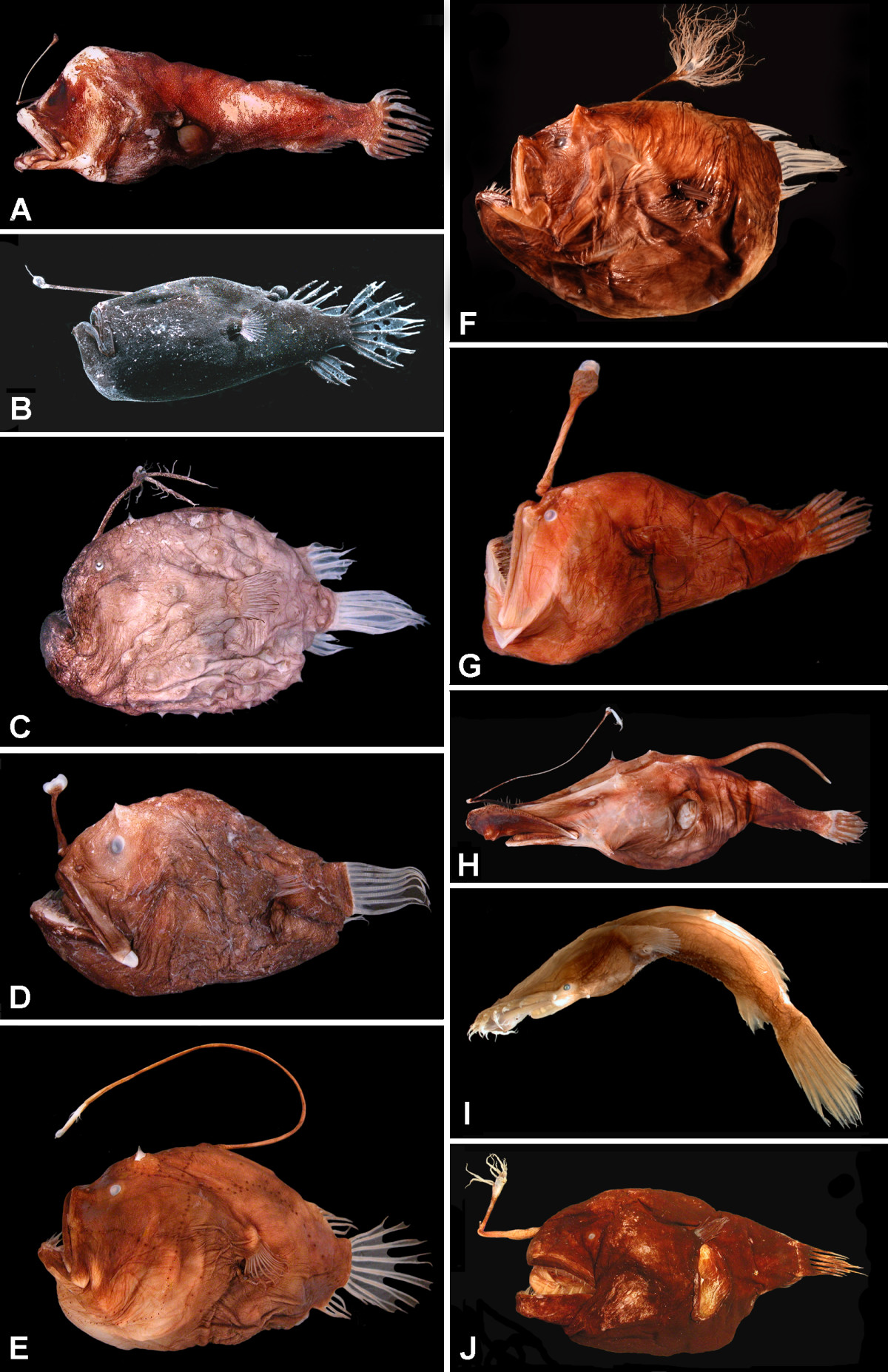
Ceratiidae
Sea devils are the family of deep-sea anglerfish known as the Ceratiidae, from the Greek ''keras'', "horn", referring to the bioluminescent lure that projects from the fishes' forehead. They are among the most widespread of the anglerfishes, found in all oceans from the tropics to the Antarctic. They are large and elongated: females of the largest species, Krøyer's deep sea angler fish, ''Ceratias holboelli'', reach in length. Males, by contrast, are much smaller, reaching , and, like other anglerfishes, spend much of their lives attached to a female after a free-living adolescent stage in which they are very small – at most – and have sharp, beak-like, toothless jaws. One or more males attach themselves permanently to a female, eventually merging circulatory system The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglerfish
The anglerfish are fish of the teleost order Lophiiformes (). They are bony fish named for their characteristic mode of predation, in which a modified luminescent fin ray (the esca or illicium) acts as a lure for other fish. The luminescence comes from symbiotic bacteria, which are thought to be acquired from seawater, that dwell in and around the sea. Some anglerfish are notable for extreme sexual dimorphism and sexual symbiosis of the small male with the much larger female, seen in the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep sea anglerfish. In these species, males may be several orders of magnitude smaller than females. Anglerfish occur worldwide. Some are pelagic (dwelling away from the sea floor), while others are benthic (dwelling close to the sea floor). Some live in the deep sea (such as the Ceratiidae), while others on the continental shelf, such as the frogfishes and the Lophiidae (monkfish or goosefish). Pelagic forms are most often laterally compressed, whereas th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate
{{wiktionary, obligate As an adjective, obligate means "by necessity" (antonym '' facultative'') and is used mainly in biology in phrases such as: * Obligate aerobe, an organism that cannot survive without oxygen * Obligate anaerobe, an organism that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen * Obligate air-breather, a term used in fish physiology to describe those that respire entirely from the atmosphere * Obligate biped, Bipedalism designed to walk on two legs * Obligate carnivore, an organism dependent for survival on a diet of animal flesh. * Obligate hibernation, a state of inactivity in which some organisms survive conditions of insufficiently available resources. * Obligate intracellular parasite, a parasitic microorganism that cannot reproduce without entering a suitable host cell * Obligate parasite An obligate parasite or holoparasite is a parasitic organism that cannot complete its life-cycle without exploiting a suitable host. If an obligate parasite cannot obtain a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjoined Twins
Conjoined twins – sometimes popularly referred to as Siamese twins – are twins joined '' in utero''. A very rare phenomenon, the occurrence is estimated to range from 1 in 49,000 births to 1 in 189,000 births, with a somewhat higher incidence in Southwest Asia and Africa. Approximately half are stillborn, and an additional one-third die within 24 hours. Most live births are female, with a ratio of 3:1. Two theories exist to explain the origins of conjoined twins. The more generally accepted theory is ''fission'', in which the fertilized egg splits partially. The other theory, no longer believed to be the basis of conjoined twinning, is ''fusion'', in which a fertilized egg completely separates, but stem cells (which search for similar cells) find similar stem cells on the other twin and fuse the twins together. Conjoined twins share a single common chorion, placenta, and amniotic sac, although these characteristics are not exclusive to conjoined twins, as there are some monozy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precursors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remyelination
Remyelination is the process of propagating oligodendrocyte precursor cells to form oligodendrocytes to create new myelin sheaths on demyelinated axons in the CNS. This is a process naturally regulated in the body and tends to be very efficient in a healthy CNS. The process creates a thinner myelin sheath than normal, but it helps to protect the axon from further damage, from overall degeneration, and proves to increase conductance once again. The processes underlying remyelination are under investigation in the hope of finding treatments for demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. Function Remyelination is activated and regulated by a variety of factors surrounding lesion sites that control the migration and differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Remyelination looks different from developmental myelination in the structure of the myelin formed. Reasons for this are unclear, but proper function of the axon is restored regardless. Perhaps of most interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelination
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from senso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




.png)
