|
Organogold Chemistry
Organogold chemistry is the study of compounds containing gold–carbon bonds. They are studied in academic research, but have not received widespread use otherwise. The dominant oxidation states for organogold compounds are I with coordination number 2 and a linear molecular geometry and III with CN = 4 and a square planar molecular geometry.Elschenbroich, C. and Salzer, A. (1992) ''Organometallics : A Concise Introduction''. Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. Gold(I) Gold(I) complexes are 2-coordinate, linear, diamagnetic, 14 electron species. They typically exist as adducts LAuR with as ligand L for instance a triphenylphosphine or an isocyanide. The ligand prevents reduction of Au(I) to metallic Au(0) with dimerization of the organic residue. Gold(I) can also exist as the aurate M uR2(the ate complex) whereby the cation is usually fitted with a complexing agent to improve stability. The AuR2− anion is also linear just as other M(d10) species such as Hg(Me)2 and Pd(Me)22+. Gold is known to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurophilicity
In chemistry, aurophilicity refers to the tendency of gold complexes to aggregate via formation of weak metallophilic interactions. The main evidence for aurophilicity is from the crystallographic analysis of Au(I) complexes. The aurophilic bond has a length of about 3.0 Å and a strength of about 7–12 kcal/mol, which is comparable to the strength of a hydrogen bond. The effect is greatest for gold as compared with copper or silver—the higher elements in its periodic table group—due to increased relativistic effects. Observations and theory show that, on average, 28% of the binding energy in the aurophilic interaction can be attributed to relativistic expansion of the gold d orbitals. An example of aurophilicity is the propensity of gold centres to aggregate. While both intramolecular and intermolecular aurophilic interactions have been observed, only intramolecular aggregation has been observed at such nucleation sites. Role in self-assembly The similarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dewar–Chatt–Duncanson Model
The Dewar–Chatt–Duncanson model is a model in organometallic chemistry that explains the chemical bonding in transition metal alkene complexes. The model is named after Michael J. S. Dewar, Joseph Chatt and L. A. Duncanson. The alkene donates electron density into a π-acid metal d-orbital from a π-symmetry bonding orbital between the carbon atoms. The metal donates electrons back from a (different) filled d-orbital into the empty π* antibonding orbital. Both of these effects tend to reduce the carbon-carbon bond order, leading to an elongated C−C distance and a lowering of its vibrational frequency. In Zeise's salt K platinum">PtCl3(C2H4).html" ;"title="platinum.html" ;"title="/nowiki>platinum">PtCl3(C2H4)">platinum.html" ;"title="/nowiki>platinum">PtCl3(C2H4)sup>.H2O the C−C bond length has increased to 134 picometres from 133 pm for ethylene. In the nickel compound Ni(C2H4)(PPh3)2 the value is 143 pm. The interaction also causes carbon atoms to "rehybridise" from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloro(triphenylphosphine)gold(I)
Chloro(triphenylphosphine)gold(I) or triphenylphosphinegold(I) chloride is a coordination complex with the formula ( Ph3P)AuCl. This colorless solid is a common reagent for research on gold compounds. Preparation and structure The complex is prepared by reducing chloroauric acid with triphenylphosphine in 95% ethanol: :HAuCl4 + H2O + 2 PPh3 → (Ph3P)AuCl + Ph3PO + 3 HCl Ph3PAuCl can also be prepared by treating a thioether complex of gold like (dimethyl sulfide)gold(I) chloride, Me2S)AuCl with triphenylphosphine. The complex adopts a linear coordination geometry, which is typical of most gold(I) compounds. It crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group ''P''212121 with a = 12.300(4) Å, b = 13.084(4) Å, c = 10.170(3) Å with Z = 4 formula units per unit cell. Reactivity Triphenylphosphinegold(I) chloride is a popular stable precursor for a cationic gold(I) catalyst used in organic synthesis. Typically, it is treated with silver(I) salts of weakly coordinating an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroauric Acid
Chloroauric acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates . Both the trihydrate and tetrahydrate are known. Both are orange-yellow solids consisting of the planar anion. Often chloroauric acid is handled as a solution, such as those obtained by dissolution of gold in aqua regia. These solutions can be converted to other gold complexes or reduced to metallic gold or gold nanoparticles. Properties Structure The tetrahydrate crystallizes as and two water molecules. The oxidation state of gold in and anion is +3. The salts of (tetrachloroauric(III) acid) are tetrachloroaurates(III), containing anions (tetrachloroaurate(III) anions), which have square planar molecular geometry. The Au–Cl distances are around 2.28 Å. Other d8 complexes adopt similar structures, e.g. tetrachloroplatinate(II) . Solute properties Solid chloroauric acid is a hydrophilic ( ionic) protic solute. It is soluble in water and other oxygen-containing solvents, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold(III) Chloride
Gold(III) chloride, traditionally called auric chloride, is a compound of gold and chlorine with the molecular formula . The "III" in the name indicates that the gold has an oxidation state of +3, typical for many gold compounds. Gold(III) chloride is hygroscopic and decomposes in visible light. This compound is a dimer of . This compound has few uses, although it catalyzes various organic reactions. Structure exists as a chloride-bridged dimer both as a solid and vapour, at least at low temperatures. Gold(III) bromide behaves analogously. The structure is similar to that of iodine(III) chloride. Each gold center is square planar in gold(III) chloride, which is typical of a metal complex with a d8 electron count. The bonding in is considered somewhat covalent. Preparation Gold(III) chloride is most often prepared by passing chlorine gas over gold powder at : : The chlorination reaction can be conducted in the presence of tetrabutylammonium chloride, the product bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold(I) Chloride
Gold(I) chloride is a compound of gold and chlorine with the chemical formula AuCl. Preparation Gold(I) chloride is prepared by thermal decomposition of gold(III) chloride. Reactions Although there is a region of stability at higher temperatures at the appropriate chlorine vapor pressures, the compound is metastable at ambient conditions. When heated with water, the compound disporpotionates to metallic gold and gold(III) chloride in an autoredox reaction: : 3 AuCl → 2 Au + AuCl3 At still higher temperatures, around 500 °C, all gold chlorides convert to gold. This conversion is key to the Miller process, which is widely used for the purification of gold. Reaction with potassium bromide yields potassium auric bromide and potassium chloride Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beilstein Journal Of Organic Chemistry
The ''Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal established in 2005. It is published by the Beilstein Institute for the Advancement of Chemical Sciences, a German non-profit foundation. The editor-in-chief is Peter Seeberger (Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.88. Scientific videos are available for selected articles of the journal. References External links * Organic chemistry journals Open access journals Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals Publications established in 2005 English-language journals BioMed Central academic journals {{chem-journal-stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Catalysis
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts. Examples Acid catalysis The proton is a pervasive homogeneous catalyst because water is the most common solvent. Water forms protons by the process of self-ionization of water. In an illustrative case, acids accelerate (catalyze) the hydrolysis of esters: :CH3CO2CH3 + H2O CH3CO2H + CH3OH At neutral pH, aqueous solutions of most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
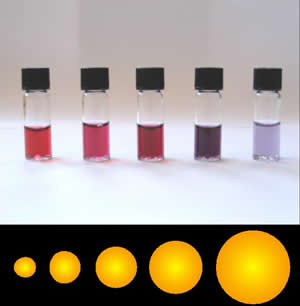
Gold Nanoparticles
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particles or nanorods). Due to their optical, electronic, and molecular-recognition properties, gold nanoparticles are the subject of substantial research, with many potential or promised applications in a wide variety of areas, including electron microscopy, electronics, nanotechnology, materials science, and biomedicine. The properties of colloidal gold nanoparticles, and thus their potential applications, depend strongly upon their size and shape. For example, rodlike particles have both a transverse and longitudinal absorption peak, and anisotropy of the shape affects their self-assembly. History Used since ancient times as a method of staining glass colloidal gold was used in the 4th-century Lycurgus Cup, which changes color depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_chloride_solution.jpg)