|
Optical Pyrometer
A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of distant objects. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance determines the temperature of a surface from the amount of the thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry and sometimes radiometry. The word pyrometer comes from the Greek word for fire, "πῦρ" (''pyr''), and ''meter'', meaning to measure. The word pyrometer was originally coined to denote a device capable of measuring the temperature of an object by its incandescence, visible light emitted by a body which is at least red-hot. Modern pyrometers or infrared thermometers also measure the temperature of cooler objects, down to room temperature, by detecting their infrared radiation flux. Principle It is based on the principle that the intensity of light received by the observer depends upon distance of observer from source and temperature of dista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed fuel particles such as coal, cenospheres, charred wood, and petroleum coke that may become airborne during pyrolysis and that are more properly identified as cokes or char. Soot causes various types of cancer and lung disease. Sources Soot as an airborne contaminant in the environment has many different sources, all of which are results of some form of pyrolysis. They include soot from coal burning, internal-combustion engines, power-plant boilers, hog-fuel boilers, ship boilers, central steam-heat boilers, waste incineration, local field burning, house fires, forest fires, fireplaces, and furnaces. These exterior sources also contribute to the indoor environment sources such as smoking of plant matter, cooking, oil lamps, candles, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgical Furnace
A metallurgical furnace, more commonly referred to as a furnace, is a device used to heat and melt metal ore to remove gangue, primarily in Metal, iron and steel production. The heat energy to fuel a furnace may be supplied directly by fuel combustion, by electricity such as the electric arc furnace, or through induction heating in induction furnaces. There are several different types of furnaces used in metallurgy to work with specific metal and ores. Smelting furnaces Smelting furnaces are used in smelting to extract metal from ore. Smelting furnaces include: * The blast furnace, used to Redox, reduce iron ore to pig iron ** Cold blast ** Hot blast * Steelmaking furnaces, including: ** Puddling furnace ** Reverberatory furnace ** ** Open hearth furnace ** Basic oxygen furnace ** Electric arc furnace ** Electric induction furnace Other furnaces * Furnaces used to remelt metal in Foundry, foundries. * Furnaces used to reheat and Heat treatment, heat treat metal for use in: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals; that is, the way in which science is applied to the production of metals, and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planck's Law
In physics, Planck's law describes the spectral density of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature , when there is no net flow of matter or energy between the body and its environment. At the end of the 19th century, physicists were unable to explain why the observed spectrum of black-body radiation, which by then had been accurately measured, diverged significantly at higher frequencies from that predicted by existing theories. In 1900, German physicist Max Planck heuristically derived a formula for the observed spectrum by assuming that a hypothetical electrically charged oscillator in a cavity that contained black-body radiation could only change its energy in a minimal increment, , that was proportional to the frequency of its associated electromagnetic wave. This resolved the problem of the ultraviolet catastrophe predicted by classical physics. This discovery was a pioneering insight of modern physics and is of fundam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
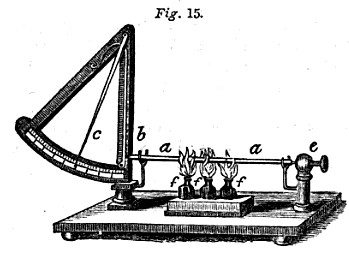
Disappearing-filament Pyrometer
The disappearing-filament pyrometer is an optical pyrometer, in which the temperature of a glowing incandescent object is measured by comparing it to the light of a heated filament. Invented independently in 1901 by Ludwig Holborn and Ferdinand Kurlbaum in Germany and Everett Fleet Morse in the United States, it was the first device which could measure temperatures above 1000 °C. Disappearing filament pyrometers have been used to measure temperatures between about 600 °C and 3000 °C. Like other optical pyrometers they are used to measure the temperature of objects too hot for contact thermometers, such as molten metals. Widely used in the steel and ceramics industries as well as for research, they have been almost totally superseded by electronic spectral-band pyrometers. The simplest design has optics like a Keplerian telescope. A thin wire ( filament), placed at the focal plane of the objective lens, is heated by electric current. When seen through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Grown By Czochralski Process 1956
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance Thermometer
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum (Pt), nickel (Ni), or copper (Cu). The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature. As RTD elements are fragile, they are often housed in protective probes. RTDs, which have higher accuracy and repeatability, are slowly replacing thermocouples in industrial applications below 600 ° C. Resistance/temperature relationship of metals Common RTD sensing elements for biomedical application constructed of platinum (Pt), nickel (Ni), or copper (Cu) have a repeatable resistance versus temperature relationship (''R'' vs ''T'') and operating temperature range. The ''R'' vs ''T'' relationship is defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedgwood Museum
Wedgwood is an English fine china, porcelain and luxury accessories manufacturer that was founded on 1 May 1759 by the potter and entrepreneur Josiah Wedgwood and was first incorporated in 1895 as Josiah Wedgwood and Sons Ltd. It was rapidly successful and was soon one of the largest manufacturers of Staffordshire pottery, "a firm that has done more to spread the knowledge and enhance the reputation of British ceramic art than any other manufacturer", exporting across Europe as far as Russia, and to the Americas. It was especially successful at producing fine earthenware and stoneware that were accepted as equivalent in quality to porcelain (which Wedgwood only made later) but were considerably cheaper. Wedgwood is especially associated with the "dry-bodied" (unglazed) stoneware Jasperware in contrasting colours, and in particular that in "Wedgwood blue" and white, always much the most popular colours, though there are several others. Jasperware has been made continuously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josiah Wedgwood
Josiah Wedgwood (12 July 1730 – 3 January 1795) was an English potter, entrepreneur and abolitionist. Founding the Wedgwood company in 1759, he developed improved pottery bodies by systematic experimentation, and was the leader in the industrialisation of the manufacture of European pottery. The renewed classical enthusiasms of the late 1760s and early 1770s were of major importance to his sales promotion. His expensive goods were in much demand from the upper classes, while he used emulation effects to market cheaper sets to the rest of society. Every new invention that Wedgwood produced – green glaze, creamware, black basalt, and jasperware – was quickly copied. Having once achieved efficiency in production, he obtained efficiencies in sales and distribution. His showrooms in London gave the public the chance to see his complete range of tableware. Wedgwood's company never made porcelain during his lifetime, but specialised in fine earthenwares and stonewares that had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |