|
Optical Correlation
An optical correlator is an optical computer for comparing two signals by utilising the Fourier transforming properties of a lens. It is commonly used in optics for target tracking and identification. Introduction The correlator has an input signal which is multiplied by some filter in the Fourier domain. An example filter is the matched filter which uses the cross correlation of the two signals. The cross correlation or correlation plane, c(x,y) of a 2D signal i(x,y) with h(x,y) is : c(x,y)=i(x,y) \otimes h^(-x,-y) This can be re-expressed in Fourier space as : C(\xi,\eta)=I(\xi,\eta) H^(-\xi,-\eta) where the capital letters denote the Fourier transform of what the lower case letter denotes. So the correlation can then be calculated by inverse Fourier transforming the result. Implementation According to Fresnel Diffraction theory a convex lens of focal length f will produce the exact Fourier transform at a distance f behind the lens of an object placed f distance in fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Computer
Optical computing or photonic computing uses light waves produced by lasers or incoherent sources for data processing, data storage or data communication for computing. For decades, photons have shown promise to enable a higher bandwidth than the electrons used in conventional computers (see optical fibers). Most research projects focus on replacing current computer components with optical equivalents, resulting in an optical digital computer system processing binary data. This approach appears to offer the best short-term prospects for commercial optical computing, since optical components could be integrated into traditional computers to produce an optical-electronic hybrid. However, optoelectronic devices consume 30% of their energy converting electronic energy into photons and back; this conversion also slows the transmission of messages. All-optical computers eliminate the need for optical-electrical-optical (OEO) conversions, thus reducing electrical power consumption. Appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Optics
Fourier optics is the study of classical optics using Fourier transforms (FTs), in which the waveform being considered is regarded as made up of a combination, or '' superposition'', of plane waves. It has some parallels to the Huygens–Fresnel principle, in which the wavefront is regarded as being made up of a combination of spherical wavefronts (also called phasefronts) whose sum is the wavefront being studied. A key difference is that Fourier optics considers the plane waves to be natural modes of the propagation medium, as opposed to Huygens–Fresnel, where the spherical waves originate in the physical medium. A curved phasefront may be synthesized from an infinite number of these "natural modes" i.e., from plane wave phasefronts oriented in different directions in space. Far from its sources, an expanding spherical wave is locally tangent to a planar phase front (a single plane wave out of the infinite spectrum), which is transverse to the radial direction of propagation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matched Filter
In signal processing, a matched filter is obtained by correlating a known delayed signal, or ''template'', with an unknown signal to detect the presence of the template in the unknown signal. This is equivalent to convolving the unknown signal with a conjugated time-reversed version of the template. The matched filter is the optimal linear filter for maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in the presence of additive stochastic noise. Matched filters are commonly used in radar, in which a known signal is sent out, and the reflected signal is examined for common elements of the out-going signal. Pulse compression is an example of matched filtering. It is so called because the impulse response is matched to input pulse signals. Two-dimensional matched filters are commonly used in image processing, e.g., to improve the SNR of X-ray observations. Matched filtering is a demodulation technique with LTI (linear time invariant) filters to maximize SNR. It was originally also known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Correlation
In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of two series as a function of the displacement of one relative to the other. This is also known as a ''sliding dot product'' or ''sliding inner-product''. It is commonly used for searching a long signal for a shorter, known feature. It has applications in pattern recognition, single particle analysis, electron tomography, averaging, cryptanalysis, and neurophysiology. The cross-correlation is similar in nature to the convolution of two functions. In an autocorrelation, which is the cross-correlation of a signal with itself, there will always be a peak at a lag of zero, and its size will be the signal energy. In probability and statistics, the term ''cross-correlations'' refers to the correlations between the entries of two random vectors \mathbf and \mathbf, while the ''correlations'' of a random vector \mathbf are the correlations between the entries of \mathbf itself, those forming the correlation matrix of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresnel Diffraction
In optics, the Fresnel diffraction equation for near-field diffraction is an approximation of the Kirchhoff–Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field. It is used to calculate the diffraction pattern created by waves passing through an aperture or around an object, when viewed from relatively close to the object. In contrast the diffraction pattern in the far field region is given by the Fraunhofer diffraction equation. The near field can be specified by the Fresnel number, , of the optical arrangement. When F \gg 1 the diffracted wave is considered to be in the near field. However, the validity of the Fresnel diffraction integral is deduced by the approximations derived below. Specifically, the phase terms of third order and higher must be negligible, a condition that may be written as \frac \ll 1, where \theta is the maximal angle described by \theta \approx a/L, and the same as in the definition of the Fresnel number. The m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convex Lens
A lens is a transmissive optics, optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a #Compound lenses, compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common Optical axis, axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are Grinding (abrasive cutting), ground and Polishing, polished or Molding (process), molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a Prism (optics), prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as Near-sightedness, myopia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Amplitudes
In physics and engineering, a phasor (a portmanteau of phase vector) is a complex number representing a sinusoidal function whose amplitude (''A''), angular frequency (''ω''), and initial phase (''θ'') are time-invariant. It is related to a more general concept called analytic representation,Bracewell, Ron. ''The Fourier Transform and Its Applications''. McGraw-Hill, 1965. p269 which decomposes a sinusoid into the product of a complex constant and a factor depending on time and frequency. The complex constant, which depends on amplitude and phase, is known as a phasor, or complex amplitude, and (in older texts) sinor or even complexor. A common situation in electrical networks powered by time varying current is the existence of multiple sinusoids all with the same frequency, but different amplitudes and phases. The only difference in their analytic representations is the complex amplitude (phasor). A linear combination of such functions can be represented as a linear com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence (physics)
In physics, two wave sources are coherent if their frequency and waveform are identical. Coherence is an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e., temporally or spatially constant) interference. It contains several distinct concepts, which are limiting cases that never quite occur in reality but allow an understanding of the physics of waves, and has become a very important concept in quantum physics. More generally, coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of a single wave, or between several waves or wave packets. Interference is the addition, in the mathematical sense, of wave functions. A single wave can interfere with itself, but this is still an addition of two waves (see Young's slits experiment). Constructive or destructive interference are limit cases, and two waves always interfere, even if the result of the addition is complicated or not remarkable. When interfering, two waves can add together to create a wave of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses of ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
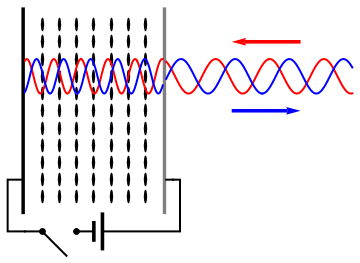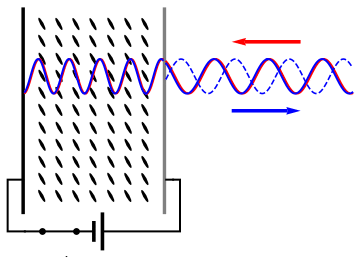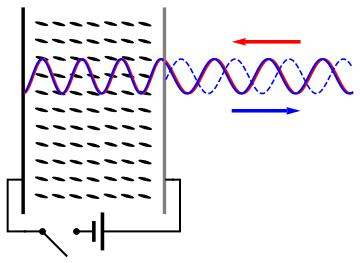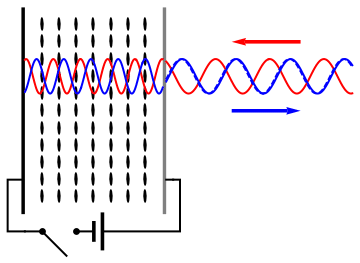
Spatial Light Modulator
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is an object that imposes some form of spatially varying modulation on a beam of light. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. In the 1980s, large SLMs were placed on overhead projectors to project computer monitor contents to the screen. Since then, more modern projectors have been developed where the SLM is built inside the projector. These are commonly used in meetings of all kinds for presentations. Usually, a SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can also be used as part of a holographic display technology. SLMs have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |