|
Occlusal Trauma
Occlusal trauma is the damage to teeth when an excessive force is acted upon them and they do not align properly.Bibb, CA: Occlusal Evaluation and Therapy in the Management of Periodontal Disease. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. pages 698-701. When the jaws close, for instance during chewing or at rest, the relationship between the opposing teeth is referred to as occlusion. When trauma, disease or dental treatment alters occlusion by changing the biting surface of any of the teeth, the teeth will come together differently, and their occlusion will change.Hinrichs, JE: Occlusal The Role of Dental Calculus and Other Predisposing Factors. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carranza, FA; editors: ''Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology'', 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. page 192. When that change has a negative effect on how the teeth occlude, this may cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiograph
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, apoptosis is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates in the surrounding tissue an inflammatory response, which attracts leukocytes and nearby phagocytes which eliminate the dead cells by phagocytosis. However, microbial damaging substances released by leukocytes would crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edentulous
Toothlessness, or edentulism, is the condition of having no teeth. In organisms that naturally have teeth, it is the result of tooth loss. Organisms that never possessed teeth can also be described as edentulous. Examples are the members of the former zoological classification Order (biology), order of ''Xenarthra#Evolutionary relationships, Edentata'', which included anteaters and sloths, as they possess no Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, anterior teeth and no or poorly developed Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, posterior teeth. In naturally dentate species, edentulism is more than just the simple presence or absence of teeth. It is biochemically complex because the teeth, jaws, and oral mucosa are dynamic (changing over time). Processes such as bone remodeling (loss and gain of bone tissue) in the jaws and inflammation of soft tissue in response to the oral microbiota are clinically important for edentulous peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
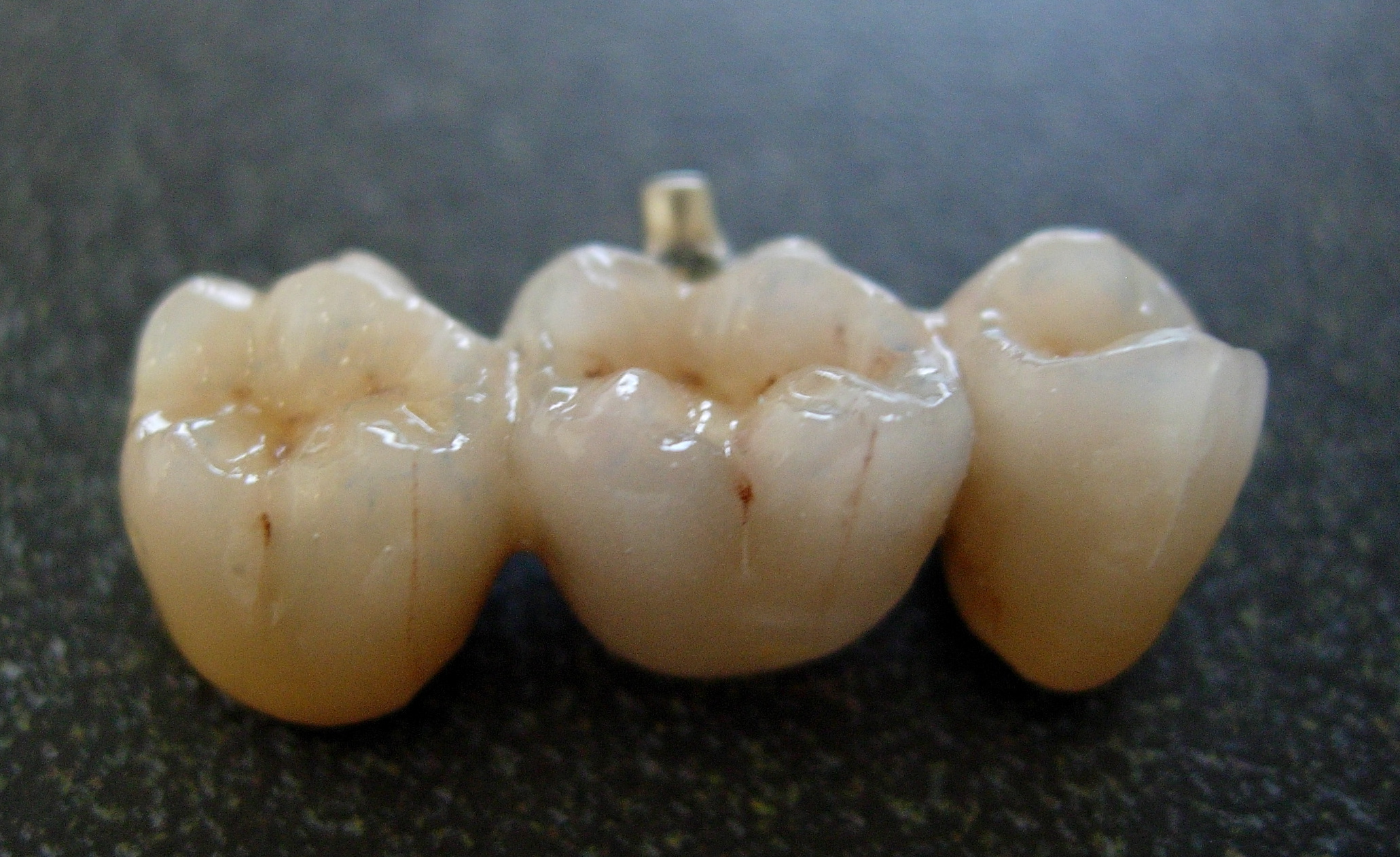
Bridge (dentistry)
A bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants. Definitions Fixed bridge: A dental prosthesis that is definitively attached to natural teeth and replaces missing teeth. Abutment: The tooth that supports and retains a dental prosthesis. Pontic: The artificial tooth that replaces a missing natural tooth. Retainer: The component attached to the abutment for retention of the prosthesis. Retainers can be major or minor. Unit: Pontics and abutment teeth are referred to as units. The total number of units in a bridge is equal to the number of pontics plus the number of abutment teeth. Saddle: The area on the alveolar ridge which is edentulous where at least one missing tooth is to be reinstated. Connector: Joins the pontic to the retainer or two retainers together. Connectors may be fixed or movable. Span: The length of the alveolar rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown (dentistry)
In dentistry, a crown most commonly refers to a dental cap, a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large cavity threatens the health of a tooth. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using ''indirect methods''. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly. The most common method of crowning a tooth involves taking a dental impression of a tooth prepared by a dentist, then fabricating the crown outside of the mouth. The crown can then be inserted at a subsequent dental appointment. This ''indirect method'' of tooth restoration allows use of strong restorative material requiring time-consuming fabrication under intense heat, such as casting metal or firing porcelain, that would not be possib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Implant
A dental implant (also known as an endosseous implant or fixture) is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biologic process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic (a tooth, bridge or denture) is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown. Success or failure of implants depends on the health of the person receiving the treatment, drugs which affect the chances of osseointegration, and the health of the tissues in the mouth. The amount of stress that will be put on the impla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Removable Partial Denture
A removable partial denture (RPD) is a denture for a partially edentulous patient who desires to have replacement teeth for functional or aesthetic reasons and who cannot have a bridge (a fixed partial denture) for any reason, such as a lack of required teeth to serve as support for a bridge (i.e. distal abutments) or financial limitations. This type of prosthesis is referred to as a ''removable partial denture'' because patients can remove and reinsert it when required without professional help. Conversely, a "fixed" prosthesis can and should be removed only by a dental professional. The aim of an RPD is to restore masticatory function, speech, appearance and other anatomical features. Usage RPD may be used when there is a lack of required teeth to serve as support for a bridge (i.e. distal abutments) or financial limitations. A single-tooth RPD known as a "flipper tooth" may be used temporarily after a tooth is extracted, during the several months it takes to complete the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontium
The periodontium is the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. The word comes from the Greek terms περί ''peri''-, meaning "around" and -''odont'', meaning "tooth". Literally taken, it means that which is "around the tooth". Periodontics is the dental specialty that relates specifically to the care and maintenance of these tissues. It provides the support necessary to maintain teeth in function. It consists of four principal components, namely: * Gingiva * Periodontal ligament (PDL) * Cementum * Alveolar bone proper Each of these components is distinct in location, architecture, and biochemical properties, which adapt during the life of the structure. For example, as teeth respond to forces or migrate medially, bone resorbs on the pressure side and is added on the tension side. Cementum similarly adapts to wear on the occlusal surfaces of the teeth by apical deposition. The periodontal ligament in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruxism
Bruxism is excessive teeth grinding or jaw clenching. It is an oral parafunctional activity; i.e., it is unrelated to normal function such as eating or talking. Bruxism is a common behavior; reports of prevalence range from 8% to 31% in the general population. Several symptoms are commonly associated with bruxism, including aching jaw muscles, headaches, hypersensitive teeth, tooth wear, and damage to dental restorations (e.g. crowns and fillings). Symptoms may be minimal, without patient awareness of the condition. If nothing is done, after a while many teeth start wearing down until the whole tooth is gone. There are two main types of bruxism: one occurs during sleep (nocturnal bruxism) and one during wakefulness (awake bruxism). Dental damage may be similar in both types, but the symptoms of sleep bruxism tend to be worse on waking and improve during the course of the day, and the symptoms of awake bruxism may not be present at all on waking, and then worsen over the day. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cementum
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy, Bath-Balogh and Fehrenbach, Elsevier, 2011, page 170. Structure The cells of cementum are the entrapped cementoblasts, the cementocytes. Each cementocyte lies in its lacuna, similar to the pattern noted in bone. These lacunae also have canaliculi or canals. Unlike those in bone, however, these canals in cementum do not contain nerves, nor do they radiate outward. Instead, the canals are oriented toward the periodontal ligament and contain cementocytic processes that exist to diffuse nutrients from the ligament because it is vascularized. After the apposition of cementum in layers, the cementoblasts that do not become entrapped in cementum line up along the cemental surface along the length of the outer covering of the perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Bone
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity. The synonymous terms ''alveolar ridge'' and ''alveolar margin'' are also sometimes used more specifically to refer to the ridges on the inside of the mouth which can be felt with the tongue, either on roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the lower teeth. Terminology The term ''alveolar'' () ('hollow') refers to the cavities of the tooth sockets, known as dental alveoli. The alveolar process is also called the ''alveolar bone'' or ''alveolar ridge''. The curved portion is referred to as the alveolar arch. The alveolar bone proper, also called bundle bone, directly surrounds the teeth. The term alveolar crest describes the extreme rim of the bone nearest to the crowns of the teeth. The portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
