|
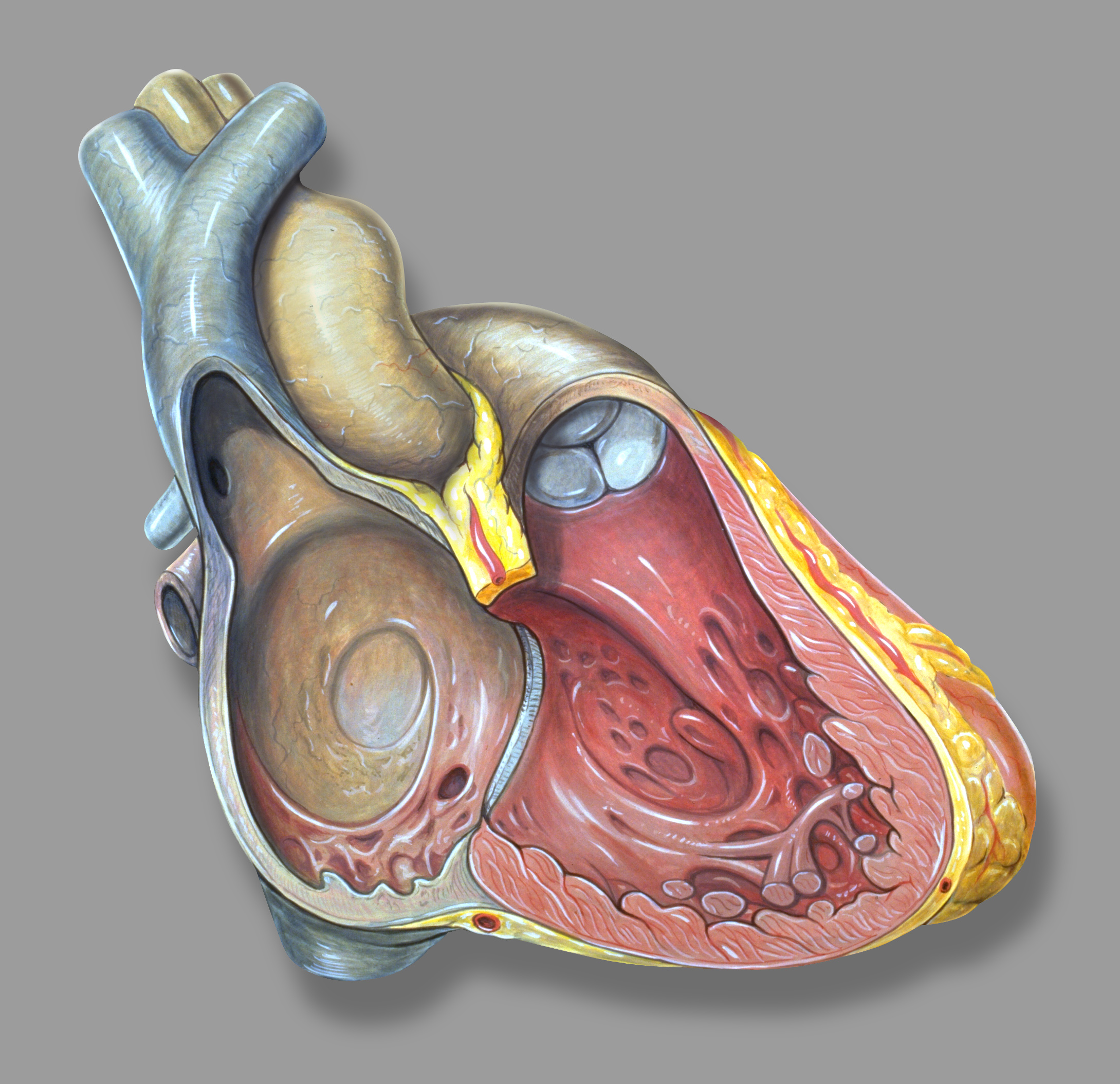
Oblique Vein
The oblique vein of the left atrium (oblique vein of Marshall) is a small vessel which descends obliquely on the back of the left atrium and ends in the coronary sinus near its left extremity; it is continuous above with the ligament of the left vena cava (lig. venæ cavæ sinistræ vestigial fold of Marshall), and the two structures form the remnant of the left Cuvierian duct The common cardinal veins, also known as the ducts of Cuvier, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior venae cavae. It is present in all mammals, including humans. The coronary sinus drains into the right atrium, at the coronary sinus orifice, an opening between the inferior vena cava and the right atrioventricular orifice or tricuspid valve. It returns blood from the heart muscle, and is protected by a semicircular fold of the lining membrane of the auricle, the valve of coronary sinus (or valve of Thebesius). The sinus, before entering the atrium, is considerably dilated - nearly to the size of the end of the little finger. Its wall is partly muscular, and at its junction with the great cardiac vein is somewhat constricted and furnished with a valve, known as the valve of Vieussens consisting of two unequal segments. Structure The coron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament Of The Left Vena Cava
The fold of the left vena cava, ligament of the left vena cava, or vestigial fold of Marshall, is a triangular fold of the serous pericardium that lies between the left pulmonary artery and subjacent pulmonary vein. It is formed by the folding of the serous layer over the remnant of the lower part of the left superior vena cava ( duct of Cuvier), which becomes obliterated during fetal life, and remains as a fibrous band stretching from the highest left intercostal vein to the left atrium, where it is continuous with a small cardiac vein, the vein of the left atrium (oblique vein of Marshall), which opens into the coronary sinus In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle (myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior vena .... References {{Authority control Cardiac anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuvierian Duct
The common cardinal veins, also known as the ducts of Cuvier, are veins that drain into the during prenatal development. These drain an and a |