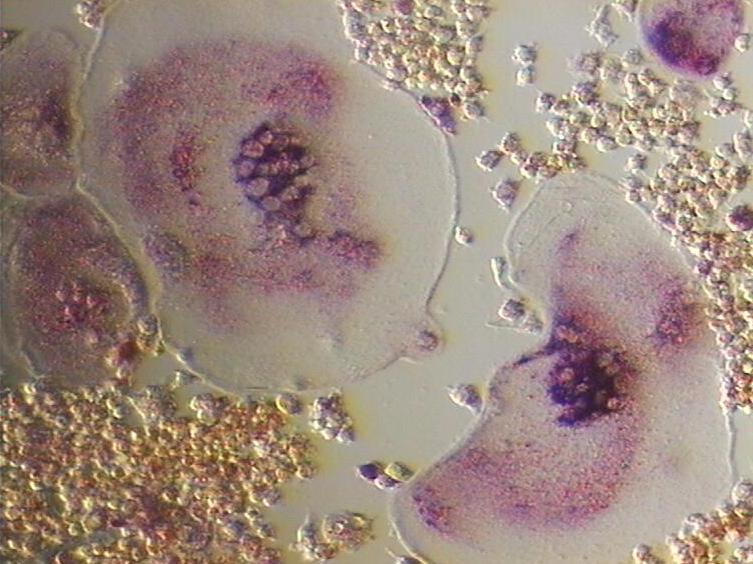
|
Osteoclast Cell
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as ''bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a resorption bay. The peripher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathepsin K
Cathepsin K, abbreviated CTSK, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CTSK'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a cysteine cathepsin, a lysosomal cysteine protease involved in bone remodeling and resorption. This protein, which is a member of the peptidase C1 protein family, is expressed predominantly in osteoclasts. Cathepsin K is a protease, which is defined by its high specificity for kinins, that is involved in bone resorption. The enzyme's ability to catabolize elastin, collagen, and gelatin allows it to break down bone and cartilage. This catabolic activity is also partially responsible for the loss of lung elasticity and recoil in emphysema. Cathepsin K inhibitors show great potential in the treatment of osteoporosis. Cathepsin K is degraded by Cathepsin S, in a process referred to as Controlled Cathepsin Cannibalism. Cathepsin K expression is stimulated by inflammatory cytokines that are released after tissue injury. Clinical significance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Phosphatase
Acid phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.2, acid phosphomonoesterase', phosphomonoesterase, glycerophosphatase, acid monophosphatase, acid phosphohydrolase, acid phosphomonoester hydrolase, uteroferrin, acid nucleoside diphosphate phosphatase, orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum), systematic name phosphate-monoester phosphohydrolase (acid optimum)) is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphomonoesterase. It is stored in lysosomes and functions when these fuse with endosomes, which are acidified while they function; therefore, it has an acid pH optimum. This enzyme is present in many animal and plant species. Different forms of acid phosphatase are found in different organs, and their serum levels are used to evaluate the success of the surgical treatment of prostate cancer. In the past, they were also used to diagnose this type of cancer. It's also used as a cytogenetic marker to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuoles
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function and significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle (biology)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, the vesicles are called ''unilamellar liposomes''; otherwise they are called ''multilamellar liposomes''. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle. Vesicles perform a variety of functions. Because it is separated from the cytosol, the inside of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (histology)
In histology, a lacuna is a small space, containing an osteocyte in bone, or chondrocyte in cartilage. Bone The lacunae are situated between the lamellae, and consist of a number of oblong spaces. In an ordinary microscopic section, viewed by transmitted light, they appear as fusiform opaque spots. Each lacuna is occupied during life by a branched cell, termed an osteocyte, bone-cell or bone-corpuscle. Lacunae are connected to one another by small canals called canaliculi. A lacuna never contains more than one osteocyte. Sinuses are an example of lacuna. Cartilage The cartilage cells or chondrocytes are contained in cavities in the matrix, called cartilage lacunae; around these, the matrix is arranged in concentric lines as if it had been formed in successive portions around the cartilage cells. This constitutes the so-called capsule of the space. Each lacuna is generally occupied by a single cell, but during the division of the cells, it may contain two, four, or eight cells. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Howship
John Howship FRS (1781 – 22 January 1841) was an English surgeon remembered for describing the Howship–Romberg sign. He was an assistant surgeon at St. George's Infirmary, London and lecturer at St. George's Hospital Medical School. He was a member of the council of the Royal College of Surgeons at the time of his death from a lower leg abscess An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b .... Howship was an associate of Robert Hooper, working on illustrations for Hooper's books. He also assisted John Heaviside with exhibits for his museum. Notes External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Howship, John English surgeons 1781 births 1841 deaths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells (also known as multinucleated or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus per cell, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordinated, synchronous manner where all nuclei divide simultaneously or asynchronously where individual nuclei divide independently in time and space. Certain organisms may have a multinuclear stage of their life cycle. For example, slime molds have a vegetative, multinucleate life stage called a plasmodium. Although not normally viewed as a case of multinucleation, plant cells share a common cytoplasm by plasmodesmata, and most cells in animal tissues are in communication with their neighbors via gap junctions. Multinucleate cells, depending on the mechanism by which they are formed, can be divided into "syncytia" (formed by cell fusion) or "coenocytes" (formed by nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis). A number of dinoflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |