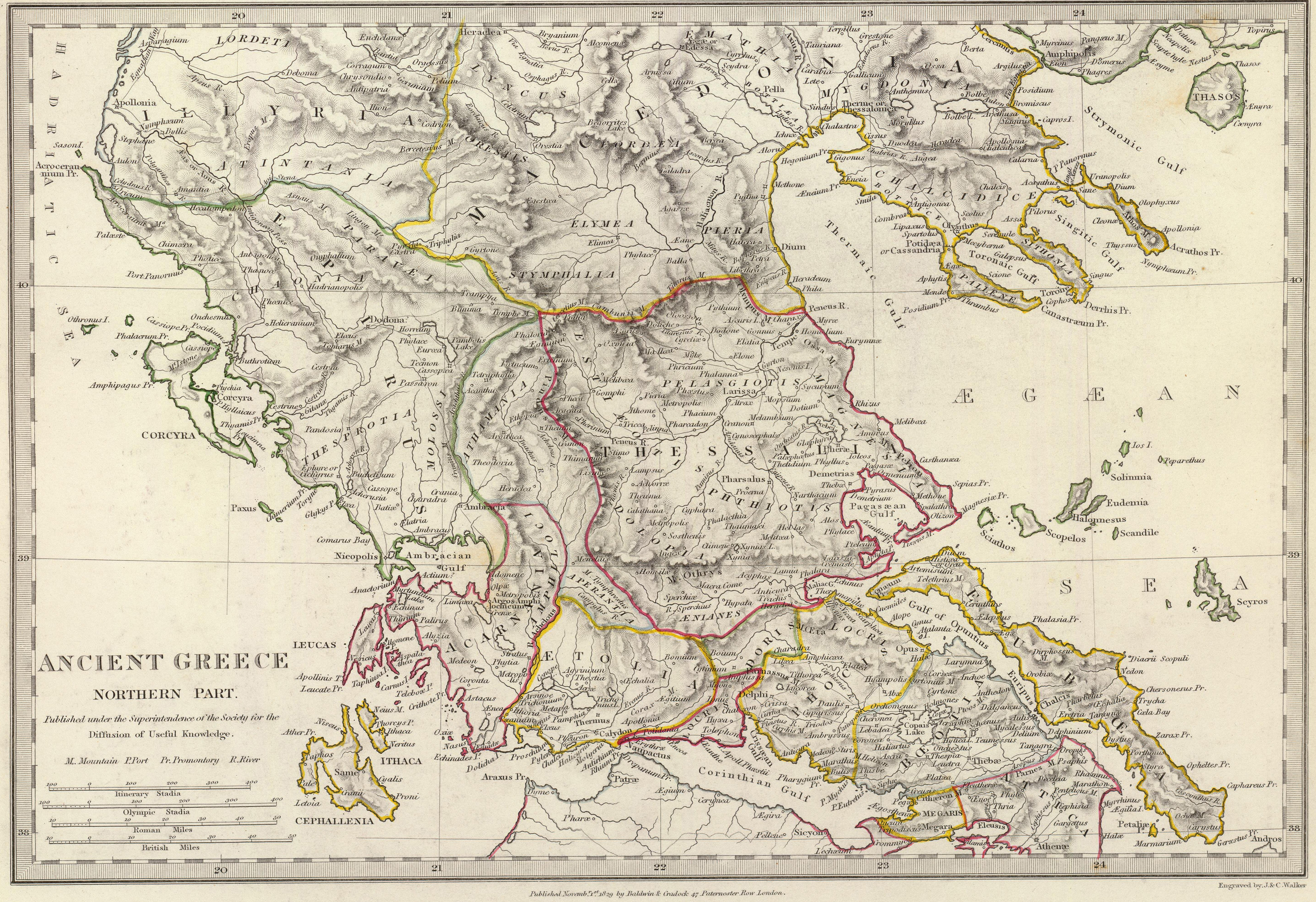
|
Oreus
Oreus or Oreos ( grc, Ὠρεός, Ōreos), prior to the 5th century BC called Histiaea or Histiaia (Ἱστίαια), also Hestiaea or Hestiaia (Ἑστίαια), was a town near the north coast of ancient Euboea, situated upon the river Callas, at the foot of Mount Telethrium, and opposite Antron on the Thessalian coast. From this town the whole northern extremity of Euboea was named Histiaeotis (Ἱστιαιῶτις, ) According to some it was a colony from the Attic deme of Histiaea; according to others it was founded by the Thessalian Perrhaebi. Another foundation story had it that the name Histiaea is said to derive from the mythical figure Histiaea, the daughter of Hyrieus. It was one of the most ancient of the Euboean cities. It occurs in the Catalogue of Ships in the ''Iliad'', where Homer gives it the epithet of πολυστάφυλος (rich in grapes); and the ''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' mentions it as one of the four cities of Euboea. It was an important c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Artemisium
The Battle of Artemisium or Artemision was a series of naval engagements over three days during the second Persian invasion of Greece. The battle took place simultaneously with the land battle at Thermopylae, in August or September 480 BC, off the coast of Euboea and was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and others, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. The Persian invasion was a delayed response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece, which had been ended by the Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon. King Xerxes had amassed a huge army and navy, and set out to conquer all of Greece. The Athenian general Themistocles proposed that the Allied Greeks block the advance of the Persian army at the pass of Thermopylae and simultaneously block the Persian navy at the Straits of Artemisium. An Allied naval force of 271 triremes was thus dispatched to await the arrival of the Persians. Approaching Artemisium to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, wikt:Περικλῆς, Περικλῆς; c. 495 – 429 BC) was a Greeks, Greek politician and general during the Fifth-century Athens, Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athens, Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed by Thucydides, a contemporary historian, as "the first citizen of Athens".Thucydides, s:History of the Peloponnesian War/Book 2#2:65, 2.65 Pericles turned the Delian League into an Athenian empire and led his countrymen during the first two years of the Peloponnesian War. The period during which he led Athens, roughly from 461 to 429 BC, is sometimes known as the "Age of Pericles", but the period thus denoted can include times as early as the Persian Wars or as late as the following century. Pericles promoted the arts and literature, and it is principally through his efforts that Athens acquired the reputation of being the educational and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalogue Of Ships
The Catalogue of Ships ( grc, νεῶν κατάλογος, ''neōn katálogos'') is an epic catalogue in Book 2 of Homer's ''Iliad'' (2.494–759), which lists the contingents of the Achaean army that sailed to Troy. The catalogue gives the names of the leaders of each contingent, lists the settlements in the kingdom represented by the contingent, sometimes with a descriptive epithet that fills out a half-verse or articulates the flow of names and parentage and place, and gives the number of ships required to transport the men to Troy, offering further differentiations of weightiness. A similar, though shorter, Catalogue of the Trojans and their allies follows (2.816–877). A similar catalogue appears in the Pseudo-Apollodoran ''Bibliotheca''. Historical background In the debate since antiquity over the Catalogue of Ships, the core questions have concerned the extent of historical credibility of the account, whether it was composed by Homer himself, to what extent it reflect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histiaea (mythology) , a district of ancient Thessaly
{{dab, geo ...
Histiaea or Histiaia ( grc, Ἱστίαια) may refer to: * Histiaea (mythology), a daughter of Hyrieus, from whom the town of Histiaea, in Northern Euboea, was said to have derived its name *Oreus or Histiaea, an ancient city on the northwest coast of Euboea * Hestiaea (Attica), a deme/township of ancient Attica See also *Histiaeotis Histiaeotis ( grc, Ἱστιαιῶτις, Histiaiōtis) or ''Hestiaeotis'' (Ἑστιαιῶτις - Hestiaiōtis) was a northwest district of ancient Thessaly, part of the Thessalian tetrarchy, roughly corresponding to modern Trikala region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antron
Antron ( grc, Ἀντρών) or Antrones (Ἀντρῶνες) Demosthenes ''Phil.'' iv. p. 133, Reiske. was a town and polis (city-state) of ancient Thessaly in the district Achaea Phthiotis, at the entrance of the Maliac Gulf, and opposite Oreus in Euboea. It is mentioned in the Catalogue of Ships in the Iliad as one of the cities of Protesilaus, and also in the Homeric hymn to Demeter In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ... as under the protection of that goddess. It was purchased by Philip II of Macedon, and was taken by the Romans in their war with Perseus of Macedon. It probably owed its long existence to the composition of its rocks, which furnished some of the best millstones in Greece; hence the epithet of πετρήεις ("maritime") given to it in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callas (river)
The Xerias ( el, Ξερίας, from ξερός, "dry") is a river of northern Euboea, Greece. Anciently, it was known as the Callas or Kallas ( grc, Κάλλας) which flowed into the sea near Oreus. The is on this river near the village of Milies Milies ( el, Μηλιές) is a village and a former municipality in Magnesia, Thessaly, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality South Pelion, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an ar .... References Geography of Euboea (regional unit) Rivers of Greece {{Greece-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathius Of Thessalonica
Eustathius of Thessalonica (or Eustathios of Thessalonike; el, Εὐστάθιος Θεσσαλονίκης; c. 1115 – 1195/6) was a Byzantine Greek scholar and Archbishop of Thessalonica. He is most noted for his contemporary account of the sack of Thessalonica by the Normans in 1185, for his orations and for his commentaries on Homer, which incorporate many remarks by much earlier researchers. He was officially canonized on June 10, 1988, and his feast day is on September 20.Great Synaxaristes: Ὁ Ἅγιος Εὐστάθιος ὁ Κατάφλωρος Ἀρχιεπίσκοπος Θεσσαλονίκης'' 20 Σεπτεμβρίου. ΜΕΓΑΣ ΣΥΝΑΞΑΡΙΣΤΗΣ. Life A pupil of Nicholas Kataphloron, Eustathius was appointed to the offices of superintendent of petitions (, '' epi ton deeseon''), professor of rhetoric (), and was ordained a deacon in Constantinople. He was ordained bishop of Myra. Around the year 1178, he was appointed to the archbishopric of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the '' Iliad'' and the '' Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. Homer's ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language which shows a mixture of features of the Ionic and Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems were originally transmitted orally. Homer's epic poems shaped aspects of ancient Greek culture and education, fostering ideals of heroism, glory, and honor. To Plato, Homer was simply t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periplus Of Pseudo-Scylax
The ''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' is an ancient Greek periplus (περίπλους ''períplous'', 'circumnavigation') describing the sea route around the Mediterranean and Black Sea. It probably dates from the mid-4th century BC, specifically the 330s, and was probably written at or near Athens. Its author is often included among the ranks of 'minor' Greek geographers. There is only one manuscript available, which postdates the original work by over 1500 years. The author's name is written Pseudo-Scylax or Pseudo-Skylax, often abbreviated as Ps.-Scylax or Ps.-Skylax. Author The only extant, medieval manuscript names the author as "Scylax"' (or "Skylax"), but scholars have proven that this attribution is to be treated as a so-called " pseudepigraphical appeal to authority": Herodotus mentions a Scylax of Caryanda, a Greek navigator who in the late sixth century BC explored the coast of the Indian Ocean on behalf of the Persians.Herodotus. ''Histories'', 4.44. Many details in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and contains 15,693 lines in its most widely accepted version, and was written in dactylic hexameter. Set towards the end of the Trojan War, a ten-year siege of the city of Troy by a coalition of Mycenaean Greek states, the poem depicts significant events in the siege's final weeks. In particular, it depicts a fierce quarrel between King Agamemnon and a celebrated warrior, Achilles. It is a central part of the Epic Cycle. The ''Iliad'' is often regarded as the first substantial piece of European literature. The ''Iliad'', and the ''Odyssey'', were likely written down in Homeric Greek, a literary amalgam of Ionic Greek and other dialects, probably around the late 8th or early 7th century BC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perrhaebi
The Perrhaebi () were an ancient Greek people who lived on the western slopes of Olympus, on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia. They took part in the Trojan War under Guneus and also fought in the Battle of Thermopylae. History Still independent at the time of the ''Iliad'', they were tributary ''períoikoi'' to the neighbouring Thessali in the 5th century BC, with a special dependence upon the city of Larisa. They could, however, enjoy some degree of autonomy whenever the Thessalian League was weaker, and they had retained from their independence two votes in the Delphic Amphictyonic League (''Amphiktyonía''), until Philip II of Macedon took one vote from them. They were part of the Macedonian Kingdom until the Roman conquest by Titus Quinctius Flamininus in 196 BC. They were listed in Xerxes' vast army by Herodotus. A coin of the Perrhaebi depicted a man restraining a bull on one side and a horse on the other. The inscription was "Περραιβών".Handboo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Homer_and_his_Guide_(1874).jpg)