|
Optical Dilatometer
An optical dilatometer is a non-contact device able to measure thermal expansions or sintering kinetics of any kind of materials, unlike traditional push rod dilatometer, it can push up to the dilatometric softening of the specimen. It is a device for measuring changes in the dimensions of a specimen, optically, the achieved resolution can result in greater values than those of a conventional pushrod dilatometer. A monochromatic light source, such as a laser, illuminates the specimen. Some of the light is reflected by the specimen and interferes with the incoming light, creating optical interference fringes. As the specimen contracts or expands, there is a proportional movement of the interference fringes, which can be measured using a camera system. The measurement resolution is determined by the wavelength of the light, and is typically 0.5 μm for blue light. Optical dilatometers are used to measure thermal expansion. The optical dilatometer is in fact complementary to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape, area, volume, and density in response to a change in temperature, usually not including phase transitions. Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. Substances which contract with increasing temperature are unusual, and only occur within limited temperature ranges (see examples below). The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster weakening the intermolecular forces between them, therefore expanding the substance. Overview Predicting expansion If an equation of state is available, it can be used to predict the values of the thermal expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "'' ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilatometer
A dilatometer is a scientific instrument that measures volume changes caused by a physical or chemical process. A familiar application of a dilatometer is the mercury-in-glass thermometer, in which the change in volume of the liquid column is read from a graduated scale. Because mercury has a fairly constant rate of expansion over ambient temperature ranges, the volume changes are directly related to temperature. Applications Dilatometers have been used in the fabrication of metallic alloys, study of martensite transformation, compressed and sintered refractory compounds, glasses, ceramic products, composite materials, and plastics.Hans Lehmann, refuge Gatzke '' Dilatometry and differential thermal analysis for the evaluation of processes ''? ? , 1956. Dilatometry is also used to monitor the progress of chemical reactions, particularly those displaying a substantial molar volume change (e.g., polymerisation). A specific example is the rate of phase changes. In food scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Transition Temperature
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle "glassy" state into a viscous or rubbery state as the temperature is increased. ISO 11357-2: Plastics – Differential scanning calorimetry – Part 2: Determination of glass transition temperature (1999). An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. The reverse transition, achieved by supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state, is called vitrification. The glass-transition temperature ''T''g of a material characterizes the range of temperatures over which this glass transition occurs (as an experimental definition, typically marked as 100 s of relaxation time). It is always lower than the melting temperature, ''T''m, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists. Hard plastics like polystyrene and poly(methyl methacrylate) are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiles
Tiles are usually thin, square or rectangular coverings manufactured from hard-wearing material such as ceramic, stone, metal, baked clay, or even glass. They are generally fixed in place in an array to cover roofs, floors, walls, edges, or other objects such as tabletops. Alternatively, tile can sometimes refer to similar units made from lightweight materials such as perlite, wood, and mineral wool, typically used for wall and ceiling applications. In another sense, a tile is a construction tile or similar object, such as rectangular counters used in playing games (see tile-based game). The word is derived from the French word ''tuile'', which is, in turn, from the Latin word ''tegula'', meaning a roof tile composed of fired clay. Tiles are often used to form wall and floor coverings, and can range from simple square tiles to complex or mosaics. Tiles are most often made of ceramic, typically glazed for internal uses and unglazed for roofing, but other materials are also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frit
A frit is a ceramic composition that has been fused, quenched, and granulated. Frits form an important part of the batches used in compounding enamels and ceramic glazes; the purpose of this pre-fusion is to render any soluble and/or toxic components insoluble by causing them to combine with silica and other added oxides.''Dictionary of Ceramics'' (3rd Edition) Edited by Dodd, A. Murfin, D. Institute of Materials. 1994. However, not all glass that is fused and quenched in water is frit, as this method of cooling down very hot glass is also widely used in glass manufacture. According to the ''OED'', the origin of the word "frit" dates back to 1662 and is "a calcinated mixture of sand and fluxes ready to be melted in a crucible to make glass". Nowadays, the unheated raw materials of glass making are more commonly called "glass batch". In antiquity, frit could be crushed to make pigments or shaped to create objects. It may also have served as an intermediate material in the manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Analysis
Thermal analysis is a branch of materials science where the properties of materials are studied as they change with temperature. Several methods are commonly used – these are distinguished from one another by the property which is measured: * Dielectric thermal analysis: dielectric permittivity and loss factor * Differential thermal analysis: temperature difference versus temperature or time * Differential scanning calorimetry: heat flow changes versus temperature or time * Dilatometer, Dilatometry: volume changes with temperature change * Dynamic mechanical analysis: measures storage modulus (stiffness) and loss modulus (damping) versus temperature, time and frequency * Evolved gas analysis: analysis of gases evolved during heating of a material, usually decomposition products * Isothermal titration calorimetry * Isothermal microcalorimetry * Laser flash analysis: thermal diffusivity and thermal conductivity * Thermogravimetric analysis: mass change versus temperature or time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, inorganic, non-metallic, porous, and heterogeneous. They are typically composed of oxides or carbides, nitrides etc. of the following materials: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. ASTM C71 defines refractories as "...non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, or as components of systems, that are exposed to environments above ." Refractory materials are used in furnaces, kilns, incinerators, and reactors. Refractories are also used to make crucibles and moulds for casting glass and metals and for surfacing flame deflector systems for rocket launch structures. Today, the iron- and steel-industry and metal casting sectors use appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
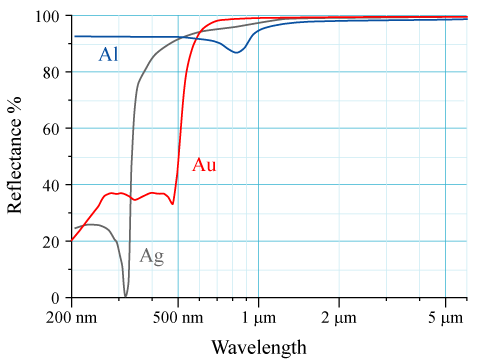
Reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)