|
Omnigeneity
Omnigeneity (sometimes also called omnigenity) is a property of a magnetic field inside a magnetic confinement fusion reactor. Such a magnetic field is called omnigenous if the path a single particle takes does not drift radially inwards or outwards on average. A particle is then confined to stay on a flux surface. All tokamaks are exactly omnigenous by virtue of their axisymmetry, and conversely an unoptimized stellarator is generally ''not'' omnigenous. Because an exactly omnigenous reactor has no neoclassical transport (in the collisionless limit), stellarators are usually optimized in a way such that this criterion is met. One way to achieve this is by making the magnetic field quasi-symmetric, and the Helically Symmetric eXperiment takes this approach. One can also achieve this property without quasi-symmetry, and Wendelstein 7-X is an example of a device which is close to omnigeneity without being quasi-symmetric. Theory The drifting of particles across flux surfaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellarator
A stellarator confines Plasma (physics), plasma using external magnets. Scientists aim to use stellarators to generate fusion power. It is one of many types of magnetic confinement fusion devices. The name "stellarator" refers to stars because fusion mostly occurs in stars such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest human-designed fusion power devices. The stellarator was invented by American scientist Lyman Spitzer in 1951. Much of its early development was carried out by Spitzer's team at what became the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). Spitzer's Model A began operation in 1953 and demonstrated plasma confinement. Larger models followed, but demonstrated poor performance, losing plasma at rates far worse than theoretical predictions. By the early 1960s, hopes of producing a commercial machine faded, and attention turned to studying fundamental theory. By the mid-1960s, Spitzer was convinced that the stellarator was matching the Bohm diffusion rate, which suggested i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasisymmetry
In magnetic confinement fusion, quasisymmetry (sometimes hyphenated as quasi-symmetry) is a type of continuous symmetry in the magnetic field strength of a stellarator. Quasisymmetry is desired, as Noether's theorem implies that there exists a conserved quantity in such cases. This conserved quantity ensures that particles stick to the flux surface, resulting in better confinement and neoclassical transport. It is currently unknown if it is mathematically possible to construct a quasi-symmetric magnetic field which upholds magnetohydrodynamic force balance, which is required for stability. There are stellarator designs which are very close to being quasisymmetric, and it is possible to find solutions by generalizing the magnetohydrodynamic force balance equation. Quasisymmetric systems are a subset In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Confinement Fusion
Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma (physics), plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion. Deuterium–tritium fusion, Fusion reactions for reactors usually combine light Atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei of deuterium and tritium to form an alpha particle (helium-4 nucleus) and a neutron, where the energy is released in the form of the kinetic energy of the reaction products. In order to overcome the Coulomb barrier, electrostatic repulsion between the nuclei, the fuel must have a temperature of hundreds of millions of kelvin, at which the fuel is fully Ionization, ionized and becomes a Plasma (physics), plasma. In addition, the plasma must be at a sufficient density, and the energy must remain in the reacting region for a sufficient time, as specified by the Lawson criterion (tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
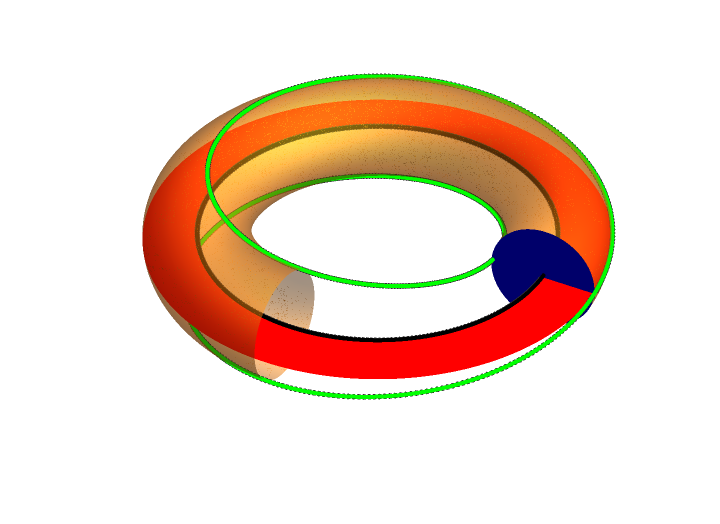
Flux Surface
In magnetic confinement fusion, a flux surface is a surface on which magnetic field lines lie. Since the magnetic field is divergence-free (and magnetic nulls are undesirable), the Poincare-Hopf theorem implies that such a surface must be either a torus, or a knot. In the tokamak and the stellarator flux surfaces have toroidal shapes, whereas the more exotic knotatron has a knotted flux surface. Flux surfaces are typically characterized by the poloidal magnetic flux In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the we ... or the toroidal magnetic flux. The poloidal flux is the magnetic flux passing through a ribbon going from the magnetic axis (the centre of the device) to the flux surface, and the toroidal flux is the magnetic flux passing through a circle which encloses the magnetic axi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational Symmetry
Rotational symmetry, also known as radial symmetry in geometry, is the property a shape (geometry), shape has when it looks the same after some rotation (mathematics), rotation by a partial turn (angle), turn. An object's degree of rotational symmetry is the number of distinct Orientation (geometry), orientations in which it looks exactly the same for each rotation. Certain geometric objects are partially symmetrical when rotated at certain angles such as squares rotated 90°, however the only geometric objects that are fully rotationally symmetric at any angle are spheres, circles and other spheroids. Formal treatment Formally the rotational symmetry is symmetry with respect to some or all rotations in -dimensional Euclidean space. Rotations are Euclidean group#Direct and indirect isometries, direct isometries, i.e., Isometry, isometries preserving Orientation (mathematics), orientation. Therefore, a symmetry group of rotational symmetry is a subgroup of (see Euclidean g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfields: discrete optimization and continuous optimization. Optimization problems arise in all quantitative disciplines from computer science and engineering to operations research and economics, and the development of solution methods has been of interest in mathematics for centuries. In the more general approach, an optimization problem consists of maxima and minima, maximizing or minimizing a Function of a real variable, real function by systematically choosing Argument of a function, input values from within an allowed set and computing the Value (mathematics), value of the function. The generalization of optimization theory and techniques to other formulations constitutes a large area of applied mathematics. Optimization problems Opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Transport
In Plasma (physics), plasma physics and magnetic confinement fusion, neoclassical transport or neoclassical diffusion is a theoretical description of collisional Transport phenomena, transport in toroidal plasmas, usually found in Tokamak, tokamaks or Stellarator, stellarators. It is a modification of classical diffusion adding in effects of non-uniform magnetic fields due to the toroidal geometry, which give rise to new diffusion effects. Description Classical transport models a plasma (physics), plasma in a magnetic field as a large number of particles traveling in helical paths around a Field line, line of force. In typical reactor designs, the lines are roughly parallel, so particles orbiting adjacent lines may collide and Scattering, scatter. This results in a random walk process which eventually leads to the particles finding themselves outside the magnetic field. Neoclassical transport adds the effects of the geometry of the fields. In particular, it considers the field ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendelstein 7-X
The Wendelstein 7-X (abbreviated W7-X) reactor is an experimental stellarator built in Greifswald, Germany, by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP), and completed in October 2015.Introduction – the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator Retrieved 5 November 2014. Its purpose is to advance stellarator technology: though this experimental reactor will not produce electricity, it is used to evaluate the main components of a future plant; it was developed based on the predecessor Wendelstein 7-AS experimental reactor. , the Wendelstein 7-X reactor is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Mirror
A magnetic mirror, also known as a magnetic trap or sometimes as a pyrotron, is a type of magnetic confinement fusion device used in fusion power to trap high temperature Plasma (physics), plasma using magnetic fields. The mirror was one of the earliest major approaches to fusion power, along with the stellarator and z-pinch machines. In a classic magnetic mirror, a configuration of electromagnets is used to create an area with an increasing density of magnetic field lines at either end of a confinement volume. Particles approaching the ends experience an increasing force that eventually causes them to reverse direction and return to the confinement area. This mirror effect will occur only for particles within a limited range of velocities and angles of approach, while those outside the limits will escape, making mirrors inherently "leaky". An analysis of early fusion devices by Edward Teller pointed out that the basic mirror concept is inherently unstable. In 1960, Soviet resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |