|
Off-flavour
Off-flavours or off-flavors ( see spelling differences) are taints in food products caused by the presence of undesirable compounds. They can originate in raw materials, from chemical changes during food processing and storage, and from micro-organisms. Off-flavours are a recurring issue in drinking water supply and many food products. Water bodies are often affected by geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol, affecting the flavour of water for drinking and of fish growing in that water. Haloanisoles similarly affect water bodies, and are a recognised cause of off-flavour in wine. Cows grazing on weeds such as wild garlic can produce a ‘weedy’ off-flavour in milk.Ridgway, K. (n.d.). Avoiding Customer Complaints: Origins of Food Taints and Off-flavours. RSSL. Many more examples can be seen throughout food production sectors including in oats, coffee, glucose syrup Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coffee Cupping
Coffee cupping, or coffee tasting, is the practice of observing the tastes and aromas of brewed coffee. It is a professional practice but can be done informally by anyone or by professionals known as "Q Graders". A standard coffee cupping procedure involves deeply sniffing the coffee, then slurping the coffee from a spoon so it is aerated and spread across the tongue. The coffee taster attempts to measure aspects of the coffee's taste, specifically the ''body'' (the texture or mouthfeel, such as oiliness), ''sweetness'', ''acidity'' (a sharp and tangy feeling, like when biting into an orange), ''flavour'' (the characters in the cup), and aftertaste. Since coffee beans embody telltale flavours from the region where they were grown, cuppers may attempt to identify the coffee's origin. Aromas Various descriptions are used to note coffee aroma. *Animal-like – This odour descriptor is somewhat reminiscent of the smell of animals. It is not a fragrant aroma like musk but has the cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Syrup
Glucose syrup, also known as confectioner's glucose, is a syrup made from the hydrolysis of starch. Glucose is a sugar. Maize (corn) is commonly used as the source of the starch in the US, in which case the syrup is called "corn syrup", but glucose syrup is also made from potatoes and wheat, and less often from barley, rice and cassava.p. 21 Glucose syrup containing over 90% glucose is used in industrial fermentation, but syrups used in confectionery contain varying amounts of glucose, maltose and higher oligosaccharides, depending on the grade, and can typically contain 10% to 43% glucose. Glucose syrup is used in foods to sweeten, soften texture and add volume. By converting some glucose in corn syrup into fructose (using an enzyme, enzymatic process), a sweeter product, high fructose corn syrup can be produced. Glucose syrup was first made in 1811 in Russia by Gottlieb Kirchhoff using heat and sulfuric acid. Types Depending on the method used to Hydrolysis, hydrolyse th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and #Fermenting, fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with Yeast#Beer, yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer, at home by a homebrewer, or communally. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that emerging civilizations, including ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, brewed beer. Since the nineteenth century the #brewing industry, brewing industry has been part of most western economies. The basic ingredients of beer are water and a Fermentation, fermentable starch source such as malted barley. Most beer is fermented with a brewer's yeast and flavoured with hops. Less widely used starch sources include millet, sorghum and cassava. Secondary sources (adjuncts), such as maize (corn), rice, or sugar, may also be used, sometimes to reduce cost, or to add a feature, such as addin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various List of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the English Language'', first published in 1828. Webster's efforts at spellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking Water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, age, health-related issues, and environmental conditions. This 2004 article focuses on the USA context and uses data collected from the US military. Recent work showed that the most important driver of water turnover which is closely linked to water requirements is energy expenditure. For those who work in a hot climate, up to a day may be required. Typically in developed countries, tap water meets drinking water quality standards, even though only a small proportion is actually consumed or used in food preparation. Other typical uses for tap water include washing, toilets, and irrigation. Greywater may also be used for toilets or irrigation. Its use for irrigation however may be associated with risks. Water may also be unacceptable due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their unique metabolisms, often evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtain food in many different ecosystems. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food with intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food and agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosmin
Geosmin ( ) is an irregular sesquiterpenoid, produced from the universal sesquiterpene precursor farnesyl pyrophosphate (also known as farnesyl diphosphate), in a two-step -dependent reaction. Geosmin, along with the irregular monoterpene 2-methylisoborneol, together account for the majority of biologically-caused taste and odor outbreaks in drinking water worldwide. Geosmin has a distinct earthy or musty odor, which most people can easily smell. The geosmin odor detection threshold in humans is very low, ranging from 0.006 to 0.01 micrograms per liter in water. Geosmin is also responsible for the earthy taste of beetroots and a contributor to the strong scent (petrichor) that occurs in the air when rain falls after a spell of dry weather or when soil is disturbed. In chemical terms, geosmin is a bicyclic alcohol with formula , a derivative of decalin. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek words (), meaning "earth", and (), meaning "smell". The word was coined in 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation, the grape's growing environment (terroir), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellations intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wines not made from grapes involve fermentation of other crops including rice wine and other fruit wines such as plum, cherry, pomegranate, currant and elderberry. Wine has been produced for thousands of years. The earliest evidence of wine is from the Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. This introduces the concept of humans and their goals in a particular setting.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media. The concept of weeds is particularly significant in agriculture, where the aim is growing crops or pastures of a single species, or a mixture of a few desired species. In such environments, other plant species are considered undesirable and therefore a weed. Besides, some weeds have undesirable characteristics making them a plant pest in most human settings.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Spri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
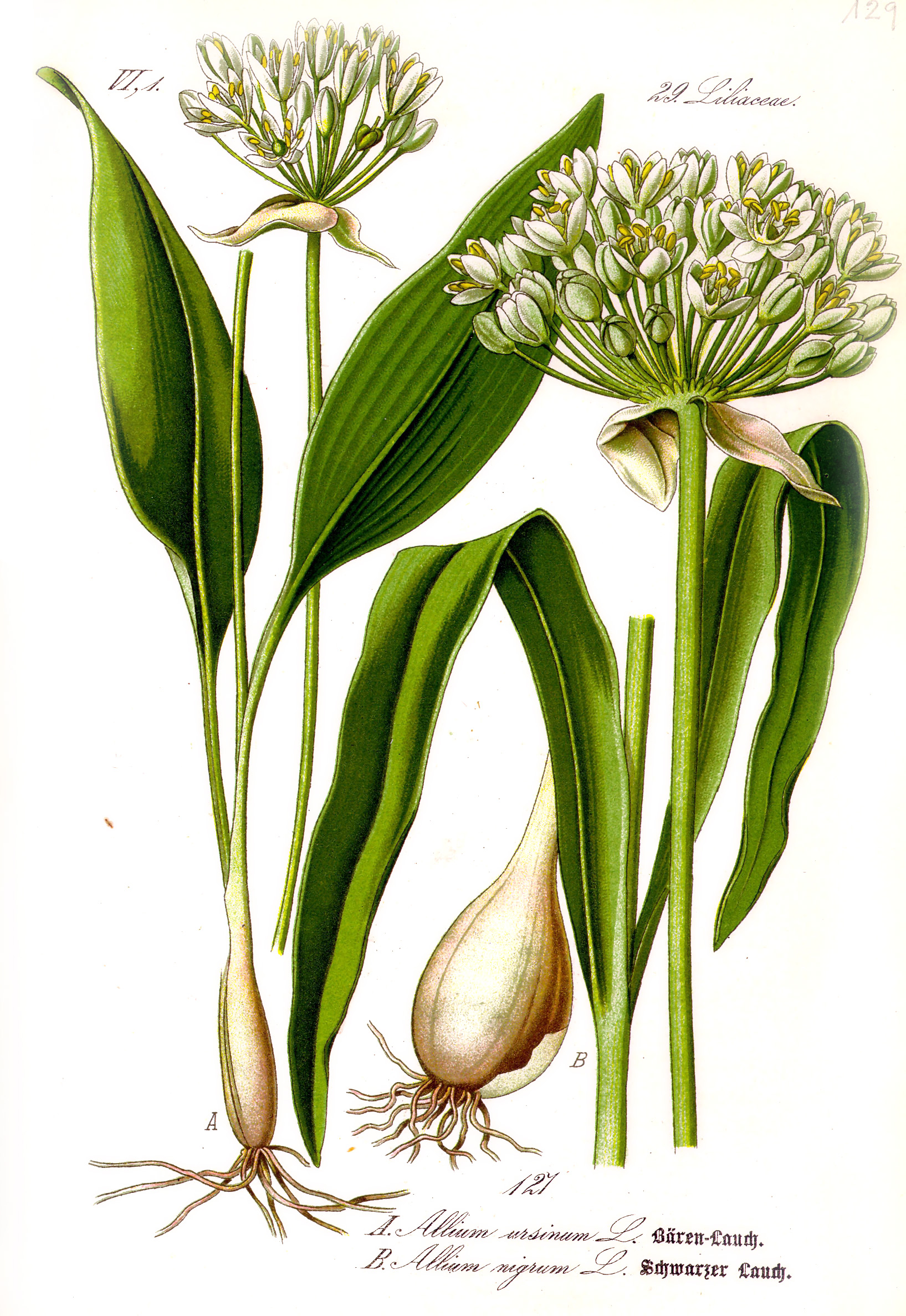
Ramsons
''Allium ursinum'', known as wild garlic, ramsons, cowleekes, cows's leek, cowleek, buckrams, broad-leaved garlic, wood garlic, bear leek, Eurasian wild garlic or bear's garlic, is a bulbous perennial flowering plant in the amaryllis family Amaryllidaceae. It is native to Europe and Asia, where it grows in moist woodland. It is a wild relative of onion and garlic, all belonging to the same genus, ''Allium''. There are two recognized subspecies: ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ursinum'' and ''A. ursinum'' subsp. ''ucrainicum''. Etymology The Latin specific name ''ursinum'' translates to 'bear' and refers to the supposed fondness of the brown bear for the bulbs; folk tales describe the bears consuming them after awakening from hibernation. Another theory is that the "''ursinum''" may refer to Ursa Major, as ''A. ursinum'' was perhaps one of the most northerly distributed ''Allium'' species known to the ancient Greeks, though this hypothesis is disputed. Common names for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |