|
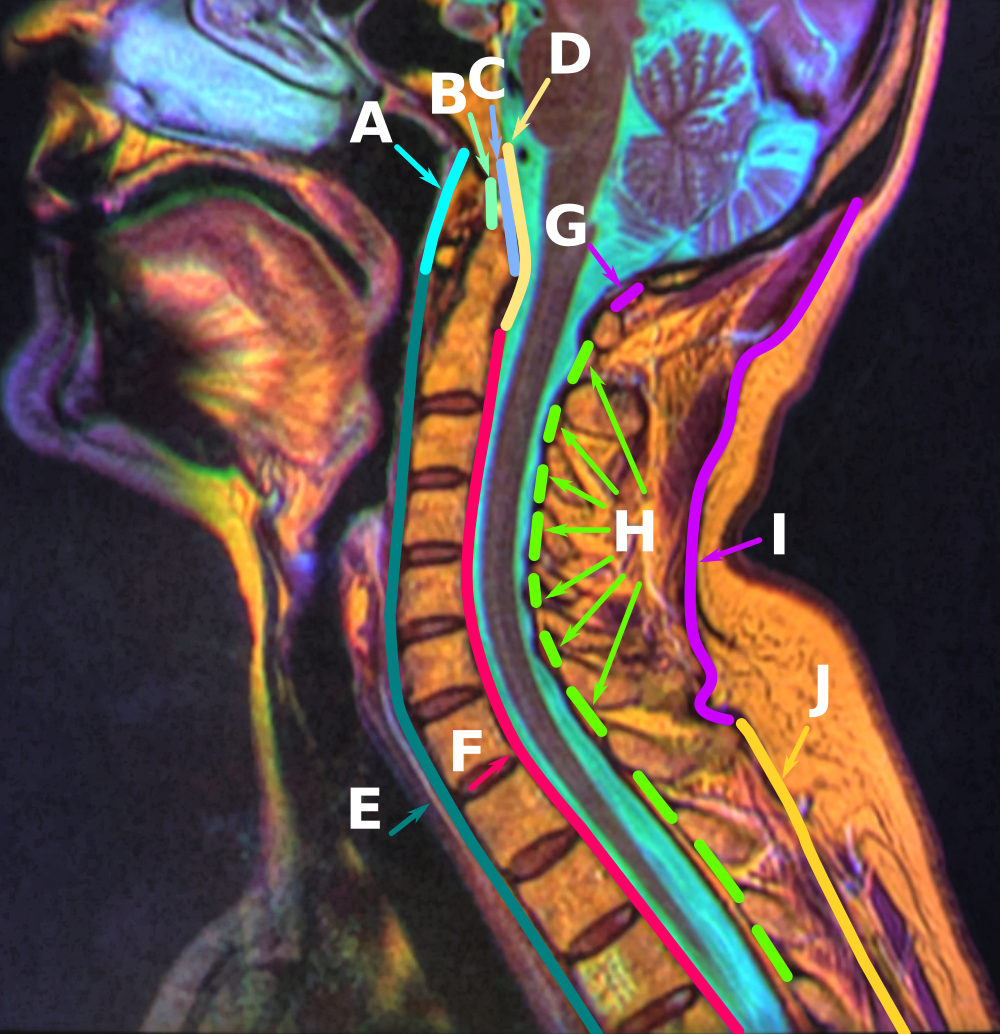
Odontoid
In anatomy, the axis (from Latin ''axis'', "axle") or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The axis' defining feature is its strong odontoid process (bony protrusion) known as the dens, which rises dorsally from the rest of the bone. Structure The body is deeper in front or in the back and is prolonged downward anteriorly to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra. It presents a median longitudinal ridge in front, separating two lateral depressions for the attachment of the longus colli muscles. Odontoid Process of Axis (Dens) The dens, also called the odontoid process or the peg, is the most pronounced projecting feature of the axis. The dens exhibits a slight constriction where it joins the main body of the vertebra. The condition where the dens is separated from the body of the axis is called ''os odontoideum'' and may cause nerve and circulation compression syndro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Atlantal Ligament
In anatomy, the transverse ligament of the atlas is a ligament which arches across the ring of the Atlas (anatomy), atlas (the topmost Cervical vertebrae, cervical vertebra, which directly supports the skull), and keeps the odontoid process in contact with the atlas. Anatomy It is concave in front, convex behind, broader and thicker in the middle than at the ends, and firmly attached on either side to a small tubercle on the medial surface of the lateral mass of the atlas.Gray's anatomy, 1918 As it crosses the odontoid process, a small fasciculus (''crus superius'') is prolonged upward, and another (''crus inferius'') downward, from the superficial or posterior fibers of the ligament. The former is attached to the basilar part of the occipital bone, in close relation with the membrana tectoria; the latter is fixed to the posterior surface of the body of the axis; hence, the whole ligament is named the cruciate ligament of the atlas. The transverse ligament divides the ring of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Odontoid Ligament
The ligament of apex dentis (or apical odontoid ligament) is a ligament that spans between the axis (anatomy), second cervical vertebra in the neck and the skull. It lies as a fibrous cord in the triangular interval between the alar ligaments, which extends from the tip of the odontoid process on the axis (anatomy), axis to the anterior margin of the foramen magnum, being intimately blended with the deep portion of the anterior atlantooccipital membrane and superior wiktionary:crus, crus of the Transverse ligament of atlas, transverse ligament of the atlas. It is regarded as a rudimentary intervertebral fibrocartilage, and in it traces of the notochord may persist. References External links * Ligaments of the head and neck Bones of the vertebral column {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apical Ligament Of Dens
The ligament of apex dentis (or apical odontoid ligament) is a ligament that spans between the second cervical vertebra in the neck and the skull. It lies as a fibrous cord in the triangular interval between the alar ligaments, which extends from the tip of the odontoid process on the axis to the anterior margin of the foramen magnum, being intimately blended with the deep portion of the anterior atlantooccipital membrane and superior crus of the transverse ligament of the atlas. It is regarded as a rudimentary intervertebral fibrocartilage An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold ..., and in it traces of the notochord may persist. References External links * Ligaments of the head and neck Bones of the vertebral column {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Arch Of The Atlas
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as Lumbar puncture, lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alar Ligament
In anatomy, the alar ligaments are ligaments which connect the dens (a bony protrusion on the second cervical vertebra) to tubercles on the medial side of the occipital condyle. They are short, tough, fibrous cords that attach on the skull and on the axis, and function to check side-to-side movements of the head when it is turned. Because of their function, the alar ligaments are also known as the "check ligaments of the odontoid". Structure The alar ligaments are two strong, rounded cords of about 0.5 cm in diameter that run from the sides of the foramen magnum of the skull to the dens of the axis, the second cervical vertebra. They span almost horizontally, creating an angle between them of at least 140°. Development The alar ligaments, along with the transverse ligament of the atlas, derive from the axial component of the first cervical sclerotome. Function The function of the alar ligaments is to limit the amount of rotation of the head, and by their action on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Processes
The articular processes or zygapophyses (Greek ζυγον = "yoke" (because it links two vertebrae) + απο = "away" + φυσις = "process") of a vertebra are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 Articular processes spring from the junctions of the pedicles and laminæ, and there are two right and left, and two superior and inferior. These stick out of an end of a vertebra to lock with a zygapophysis on the next vertebra, to make the backbone more stable. * The superior processes or prezygapophysis project upward from a lower vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less backward (oblique coronal plane). * The inferior processes or postzygapophysis project downward from a higher vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less forward and outwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Sport
Contact sports are sports that emphasize or require physical contact between players. Some sports, such as mixed martial arts, are scored on impacting an opponent, while others, including rugby football, gridiron football and Australian rules football, require tackling of players. These sports are often known as full-contact, as the sport cannot be undertaken without contact. Some sports, such as baseball and kho-kho, only allow physical contact in the form of tagging (lightly touching) opponents. Some contact sports have non-contact variations (such as flag football for American football) which replace tackling and other forms of contact with alternative methods of interacting with an opponent, such as removing a flag from a belt worn by the opponent. Other sports may have contact, but such events are illegal under the rules of the game and are incidental or accidental and do not form part of the sport. It can also include impact via a piece of sporting equipment, such as bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. ''Absolute contraindications'' are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action. For example, children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome, and a person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. Similarly, a person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. ''Relative contraindications'' are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at higher risk of complications from treatment, but these risks may be outweighed by other considerations or mitigated by other measures. For example, a pregnant woman should normally avoid gett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)