|
Nordihydroguaiaretic Acid
Nordihydroguaiaretic acid, informally abbreviated NDGA in research articles, is a classic lignan, a phenylpropane dimer linked by a bond between positions C8 and C8′, as opposed to a neolignan. It is a natural compound found in the creosote bush (''Larrea tridentata''). Medical properties As a lignan, it is a member of one of the major classes of phytoestrogens. While it is commonly asserted that the biological properties of lignans per sé are void, and that only the enterolignans enterodiol and enterolactone, produced from lignans by intestinal bacteria have interesting biological properties, nordihydroguaiaretic acid has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties in vitro or in animal models. It is a redox-type inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. A 1986 study involved feeding female mosquitos NDGA to test the effect on their average life span. While the usual mosquito life span was 29 days, the NDGA-fed mosquitos lived an average of 45 days—an increase of 50 percent. A 2008 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignan
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores. Biosynthesis and metabolism Lignans and lignin differ in their molecular weight, the former being small and soluble in water, the latter being high polymers that are undigestable. Both are polyphenolic substances derived by oxidative coupling of monolignols. Thus, most lignans feature a C18 cores, resulting from the dimerization of C9 precursors. The coupling of the lignols occurs at C8. Eight classes of lignans are: "furofuran, furan, dibenzylbutane, dibenzylbutyrolactone, aryltetralin, arylnaphthalene, dibenzocyclooctadiene, and dibenzylbutyrolactol." Many lignans are metabolized by mammalian gut microflora, producing so-called enterolignans. Food sources Flax s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolignan
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores. Biosynthesis and metabolism Lignans and lignin differ in their molecular weight, the former being small and soluble in water, the latter being high polymers that are undigestable. Both are polyphenolic substances derived by oxidative coupling of monolignols. Thus, most lignans feature a C18 cores, resulting from the dimerization of C9 precursors. The coupling of the lignols occurs at C8. Eight classes of lignans are: "furofuran, furan, dibenzylbutane, dibenzylbutyrolactone, aryltetralin, arylnaphthalene, dibenzocyclooctadiene, and dibenzylbutyrolactol." Many lignans are metabolized by mammalian gut microflora, producing so-called enterolignans. Food sources Flax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larrea Tridentata
''Larrea tridentata'', called creosote bush and greasewood as a plant, chaparral as a medicinal herb, and ''gobernadora'' (Spanish language, Spanish for "governess") in Mexico, due to its ability to secure more water by inhibiting the growth of nearby plants. In Sonora, it is more commonly called ''hediondilla''; Spanish ''hediondo'' = "smelly". It is a flowering plant in the family Zygophyllaceae. The specific name ''tridentata'' refers to its three-toothed leaves. Distribution ''Larrea tridentata'' is a prominent species in the Mojave Desert, Mojave, Sonoran Desert, Sonoran, and Chihuahuan Desert, Chihuahuan Deserts of western North America, and its range includes those and other regions in portions of southeastern California, Arizona, southern Nevada, southwestern Utah, New Mexico, and Texas in the United States, and Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Sonora, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Zacatecas, Durango and San Luis Potosí, San Luis Potosì in Mexico. The species grows as far east a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
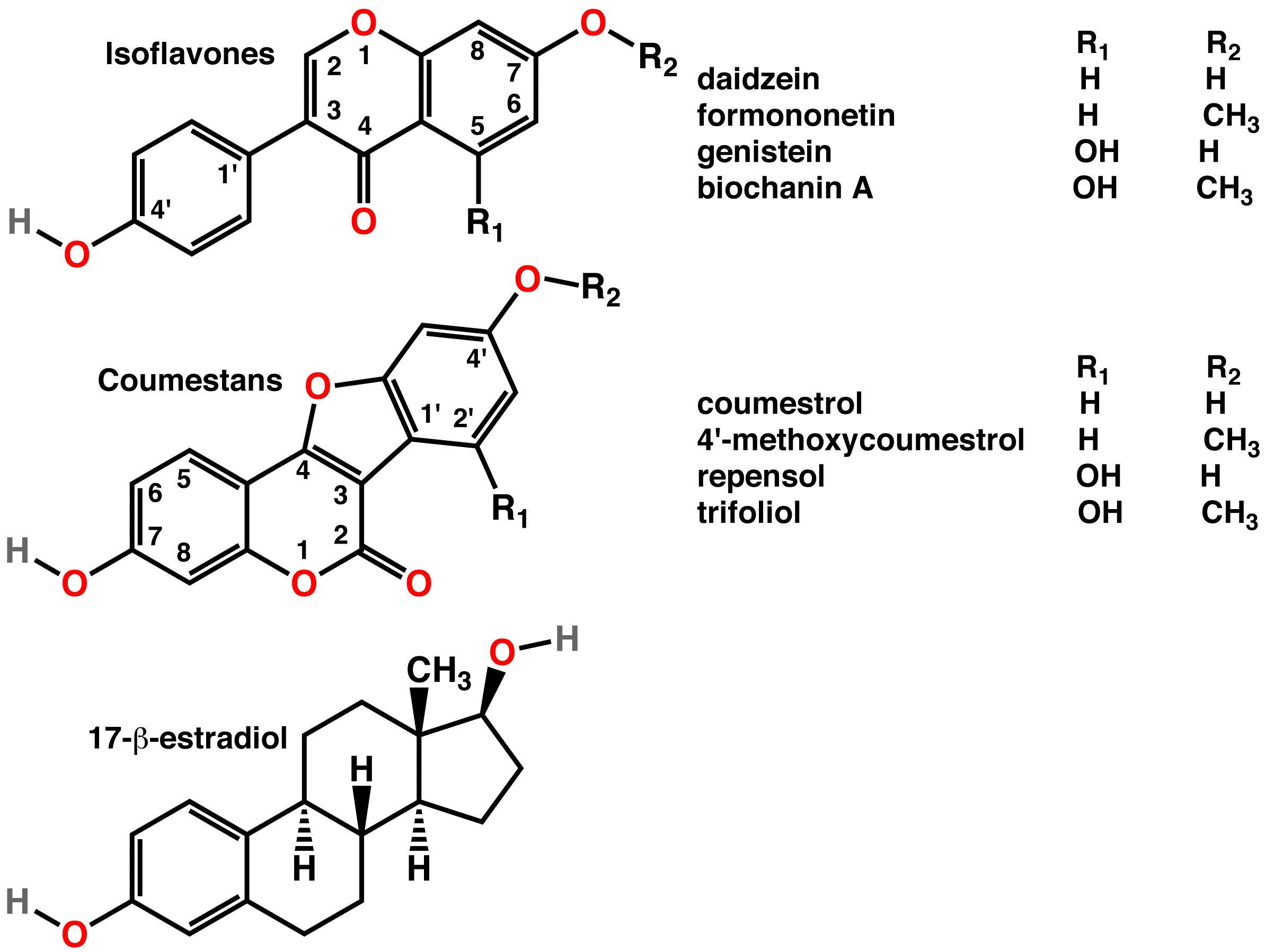
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (see estrogen) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity with estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soy protein, beans, oats, barley, rice, coffee, apples, carrots (see Food Sources section below for bigger list). Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" - Greek οίστρος - means "sexual desire", and "gene" - Greek γόνο - is "to generate". It has been hypothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterolignan
Enterolignans are organic compounds formed by the action of gut microflora on lignans. They are thus the products of the combined action of both plants and of the animal gut. Prominent enterolignans are enterodiol and enterolactone Enterolactone is a organic compound classified as an enterolignan. It is formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on plant lignan precursors present in the diet. Sources Many dietary plant lignan precursors, such as secoisolariciresinol, mat .... Enterolignans are also called "mammalian lignans", although that term is self-contradictory since mammals do not produce lignans. . Enterolignans have attracted intense attention because of their potential beneficial roles in nutrition. Elevated levels of enterodiol in urine are attributed consumption of tea and other lignan-rich foods. References Polyols Lignans Phenols {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterodiol
Enterodiol is an organic compound with the formula OC6H4CH2CH(CH2OH)sub>2. It is formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors. As such it is sometimes classified as a enterolignan Enterolignans are organic compounds formed by the action of gut microflora on lignans. They are thus the products of the combined action of both plants and of the animal gut. Prominent enterolignans are enterodiol and enterolactone Enterolactone ... or mammalian lignan. Elevated levels of enterodiol in urine are attributed consumption of tea and other lignan-rich foods. References Polyols Lignans Phenols {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterolactone
Enterolactone is a organic compound classified as an enterolignan. It is formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on plant lignan precursors present in the diet. Sources Many dietary plant lignan precursors, such as secoisolariciresinol, matairesinol, lariciresinol, pinoresinol, and sesamin, can be metabolized by Gut microbiota, gut microbes to enterolactone. In edible plants lignans are bound to the fiber fraction and therefore fiber-rich food products, such as cereals, vegetables, fruits and berries, are generally good sources of lignans and enterolactone. The richest known dietary sources of enterolactone precursors are flaxseed and sesame seed. Since enterolactone is produced by specific species of gut microbiota, the capacity to produce it varies between people. Antibiotic treatments can abolish the capacity to produce enterolactone. It may take up to a year before enterolactone production is restored. Health effects Enterolactone is suggested to possess beneficial hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Lipoxygenase
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, also known as ALOX5, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, or 5-LO, is a non-heme iron-containing enzyme (EC 1.13.11.34) that in humans is encoded by the ''ALOX5'' gene. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms essential fatty acids (EFA) substrates into leukotrienes as well as a wide range of other biologically active products. ALOX5 is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases. Gene The ''ALOX5'' gene, which occupies 71.9 kilobase pairs (kb) on chromosome 10 (all other human lipoxygenases are clustered together on chromosome 17), is composed of 14 exons divided by 13 introns encoding the mature 78 kilodalton (kD) ALOX5 protein consisting of 673 amino acids. The gene promoter region of ALOX5 contains 8 GC boxes but lacks TATA boxes or CAT boxes and thus resembles the gene promoters of typical housekeeping genes. Five of the 8 GC boxes are arranged in tandem and are recognized by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts. The mosquito life cycle consists of egg, larva, pupa, and adult stages. Eggs are laid on the water surface; they hatch into motile larvae that feed on aquatic algae and organic material. These larvae are important food sources for many freshwater animals, such as dragonfly nymphs, many fish, and some birds such as ducks. The adult females of most species have tube-like mouthparts (called a proboscis) that can pierce the skin of a host and feed on blood, which contains protein and iron needed to produce eggs. Thousands of mosquito species feed on the blood of various hosts � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Average Life Span
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort (all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. In the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, human LEB was 26 years; in 2010, world LEB was 67.2 years. In recent years, LEB in Eswatini (formerly Swaziland) is 49, while LEB in Japan is 83. The combination of high infant m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell ( cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). By extension, the word may be metaphorically used to describe toxic effects on larger and more complex groups, such as the family unit or society at large. Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |