|
5-lipoxygenase
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, also known as ALOX5, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, or 5-LO, is a non-heme iron-containing enzyme (EC 1.13.11.34) that in humans is encoded by the ''ALOX5'' gene. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms essential fatty acids (EFA) substrates into leukotrienes as well as a wide range of other biologically active products. ALOX5 is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases. Gene The ''ALOX5'' gene, which occupies 71.9 kilobase pairs (kb) on chromosome 10 (all other human lipoxygenases are clustered together on chromosome 17), is composed of 14 exons divided by 13 introns encoding the mature 78 kilodalton (kD) ALOX5 protein consisting of 673 amino acids. The gene promoter region of ALOX5 contains 8 GC boxes but lacks TATA boxes or CAT boxes and thus resembles the gene promoters of typical housekeeping genes. Five of the 8 GC boxes are arranged in tandem and are recognized by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases () are a family of (non-heme) iron-containing enzymes most of which catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene into cell signaling agents that serve diverse roles as autocrine signals that regulate the function of their parent cells, paracrine signals that regulate the function of nearby cells, and endocrine signals that regulate the function of distant cells. The lipoxygenases are related to each other based upon their similar genetic structure and dioxygenation activity. However, one lipoxygenase, ALOXE3, while having a lipoxygenase genetic structure, possesses relatively little dioxygenation activity; rather its primary activity appears to be as an isomerase that catalyzes the conversion of hydroperoxy unsaturated fatty acids to their 1,5-epoxide, hydroxyl derivatives. Lipoxygenases are found in eukaryotes (plants, fungi, animals, protists); while the third domain of terrestrial life, the archaea, pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukotrienes
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase. Leukotrienes use lipid signaling to convey information to either the cell producing them (autocrine signaling) or neighboring cells (paracrine signaling) in order to regulate immune responses. The production of leukotrienes is usually accompanied by the production of histamine and prostaglandins, which also act as inflammatory mediators. One of their roles (specifically, leukotriene D4) is to trigger contractions in the smooth muscles lining the bronchioles; their overproduction is a major cause of inflammation in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Leukotriene antagonists are used to treat these disorders by inhibiting the production or activity of leukotrienes. History and name The name ''leukotriene'', introduced by Swedish biochemist Bengt Samuelss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological functions incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note: food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine. Diagnosis is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
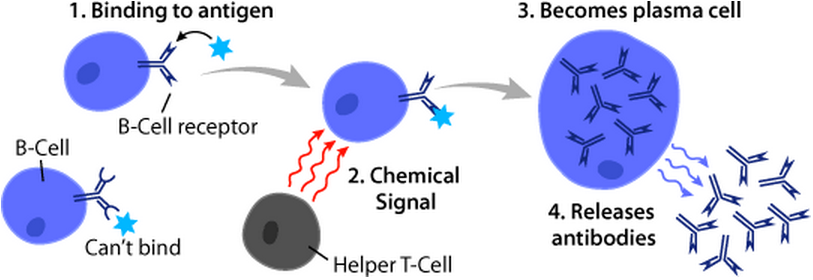
B-lymphocyte
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cells and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mast Cell
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a part of the immune and neuroimmune systems. Mast cells were discovered by Paul Ehrlich in 1877. Although best known for their role in allergy and anaphylaxis, mast cells play an important protective role as well, being intimately involved in wound healing, angiogenesis, immune tolerance, defense against pathogens, and vascular permeability in brain tumours. The mast cell is very similar in both appearance and function to the basophil, another type of white blood cell. Although mast cells were once thought to be tissue-resident basophils, it has been shown that the two cells develop from different hematopoietic lineages and thus cannot be the same cells. Structure Mast cells are very similar to basophil granulocytes (a class of white ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precursors ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.png)