|
Noise Figure
Noise figure (NF) and noise factor (''F'') are figures of merit that indicate degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) that is caused by components in a signal chain. These figures of merit are used to evaluate the performance of an amplifier or a radio receiver, with lower values indicating better performance. The noise factor is defined as the ratio of the output noise power of a device to the portion thereof attributable to thermal noise in the input termination at standard noise temperature ''T''0 (usually 290 K). The noise factor is thus the ratio of actual output noise to that which would remain if the device itself did not introduce noise, or the ratio of input SNR to output SNR. The noise ''factor'' and noise ''figure'' are related, with the former being a unitless ratio and the latter being the same ratio but expressed in units of decibels (dB). General The noise figure is the difference in decibels (dB) between the noise output of the actual receiver to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
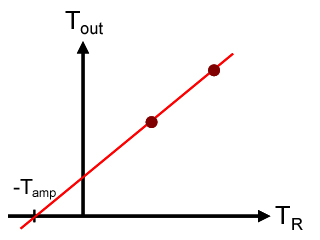
Y-factor
The Y-factor method is a widely used technique for measuring the gain and noise temperature of an amplifier. It is based on the Johnson–Nyquist noise of a resistor at two different, known temperatures. Consider a microwave amplifier with a 50-ohm impedance with a 50-ohm resistor connected to the amplifier input. If the resistor is at a physical temperature ''T''R, then the Johnson–Nyquist noise power coupled to the amplifier input is ''P''J = ''k''B''T''R''B'', where ''k''B is Boltzmann’s constant, and ''B'' is the bandwidth. The noise power at the output of the amplifier (i.e. the noise power coupled to an impedance-matched load that is connected to the amplifier output) is ''P''out = ''Gk''B(''T''R + ''T''amp)''B'', where ''G'' is the amplifier power gain, and ''T''amp is the amplifier noise temperature. In the Y-factor technique, ''P''out is measured for two different, known values of ''T''R. ''P''out is then converted to an effective temperature ''T''out (in unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Noise
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example of convection, specifically atmospheric convection. Thermals on Earth The Sun warms the ground, which in turn warms the air directly above. The warm air near the surface expands, becoming less dense than the surrounding air. The lighter air rises and cools due to its expansion in the lower pressure at higher altitudes. It stops rising when it has cooled to the same temperature, thus density, as the surrounding air. Associated with a thermal is a downward flow surrounding the thermal column. The downward-moving exterior is caused by colder air being displaced at the top of the thermal. The size and strength of thermals are influenced by the properties of the lower atmosphere (the ''troposphere''). When the air is cold, bubbles of warm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise (electronics)
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects. In particular, noise is inherent in physics, and central to thermodynamics. Any conductor with electrical resistance will generate thermal noise inherently. The final elimination of thermal noise in electronics can only be achieved cryogenically, and even then quantum noise would remain inherent. Electronic noise is a common component of noise in signal processing. In communication systems, noise is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal in a communication channel. The noise is a summation of unwanted or disturbing energy from natural and sometimes man-made sources. Noise is, however, typically distinguished from interference, for example in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and signal-to-noise plus interference ratio (SNIR) measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise Figure Meter
A noise-figure meter is an instrument for measuring the noise figure of an amplifier, mixer, or similar device. An example instrument is the 1983-era Agilent 8970A8970A Noise Figure Meteris a Keysight product numbers that were formerly part of Agilent. Measurement methods One way to perform the measurement is described on the Y-factor page. A noise-figure meter could automate that procedure as follows: A gated broadband noise source (such as an avalanche diode) drives the device under test. A measurement is made with the noise source on; another measurement with the noise source off. From those measurements and the characteristics of the noise source, the noise figure can be calculated. Noise source Some noise figure meters need a calibrated broadband noise source—a noise generator. Several methods are used to generate broadband noise. Some methods require two sources: a "hot" and "cold" source. For high frequency measurements, the noise source will be embedded in a transmissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise (electronic)
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects. In particular, noise is inherent in physics, and central to thermodynamics. Any conductor with electrical resistance will generate thermal noise inherently. The final elimination of thermal noise in electronics can only be achieved cryogenically, and even then quantum noise would remain inherent. Electronic noise is a common component of noise in signal processing. In communication systems, noise is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal in a communication channel. The noise is a summation of unwanted or disturbing energy from natural and sometimes man-made sources. Noise is, however, typically distinguished from interference, for example in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and signal-to-noise plus interference ratio (SNIR) meas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference arises when the brain receives and perceives a sound. Acoustic noise is any sound in the acoustic domain, either deliberate (e.g., music or speech) or unintended. In contrast, Noise (electronics), noise in electronics may not be audible to the human ear and may require instruments for detection. In audio engineering, noise can refer to the unwanted residual electronic noise signal that gives rise to acoustic noise heard as a Hiss (electromagnetic), hiss. This signal noise is commonly measured using A-weighting or ITU-R 468 noise weighting, ITU-R 468 weighting. In experimental sciences, noise can refer to any random fluctuations of data that hinders perception of a signal. Measurement Sound is measured based on the amplitude and frequency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Gain
The power gain of an electrical network is the ratio of an output power to an input power. Unlike other signal gains, such as voltage and current gain, "power gain" may be ambiguous as the meaning of terms "input power" and "output power" is not always clear. Three important power gains are operating power gain, transducer power gain and available power gain. Note that all these definitions of power gains employ the use of average (as opposed to instantaneous) power quantities and therefore the term "average" is often suppressed, which can be confusing at occasions. Operating power gain The operating power gain of a two-port network, GP, is defined as: :G_P = \frac where *Pload is the maximum time averaged power delivered to the load, where the maximization is over the load impedance, i.e., we desire the load impedance which maximizes the time averaged power delivered to the load. *Pinput is the time averaged power entering the network. If the time averaged input power depends on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friis Formulas For Noise
Friis formula or Friis's formula (sometimes Friis' formula), named after Danish-American electrical engineer Harald T. Friis, is either of two formulas used in telecommunications engineering to calculate the signal-to-noise ratio of a multistage amplifier. One relates to noise factor while the other relates to noise temperature. The Friis formula for noise factor Friis's formula is used to calculate the total noise factor of a cascade of stages, each with its own noise factor and power gain (assuming that the impedances are matched at each stage). The total noise factor can then be used to calculate the total noise figure. The total noise factor is given as where F_i and G_i are the noise factor and available power gain, respectively, of the ''i''-th stage, and ''n'' is the number of stages. Both magnitudes are expressed as ratios, not in decibels. Consequences An important consequence of this formula is that the overall noise figure of a radio receiver is primarily establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |