|
Nibble
In computing, a nibble, or spelled nybble to match byte, is a unit of information that is an aggregation of four- bits; half of a byte/ octet. The unit is alternatively called nyble, nybl, half-byte or tetrade. In networking or telecommunications, the unit is often called a semi-octet, quadbit, or quartet. As a nibble can represent sixteen () possible values, a nibble value is often shown as a hexadecimal digit (hex digit). A byte is two nibbles, and therefore, a value can be shown as two hex digits. Four-bit computers use nibble-sized data for storage and operations; as the word unit. Such computers were used in early microprocessors, pocket calculators and pocket computers. They continue to be used in some microcontrollers. In this context, 4-bit groups were sometimes also called characters rather than nibbles. History The term ''nibble'' originates from its representing half a byte, with ''byte'' a homophone of the English word ''bite''. In 2014, David B. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as the Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words of 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 48, or 60 bits, corresponding t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Octet (computing)
The octet is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that consists of eight bits. The term is often used when the term '' byte'' might be ambiguous, as the byte has historically been used for storage units of a variety of sizes. The term ''octad(e)'' for eight bits is no longer common. Definition The international standard IEC 60027-2, chapter 3.8.2, states that a byte is an octet of bits. However, the unit byte has historically been platform-dependent and has represented various storage sizes in the history of computing. Due to the influence of several major computer architectures and product lines, the byte became overwhelmingly associated with eight bits. This meaning of ''byte'' is codified in such standards as ISO/IEC 80000-13. While ''byte'' and ''octet'' are often used synonymously, those working with certain legacy systems are careful to avoid ambiguity. Octets can be represented using number systems of varying bases such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
4-bit Computing
4-bit computing is the use of computer architectures in which integer (computer science), integers and other data (computer science), data units are 4 bits wide. 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on processor register, registers or bus (computing), data buses of that size. A group of four bits is also called a nibble and has 24 = 16 possible values, with a range of 0 to 15. 4-bit computation is obsolete, i.e. CPUs supporting 4-bit as the maximum size. However, 4-bit integers (or smaller), and 4-bit floating point is gaining ground for AI, large-language models. 4-bit processors were widely used in electronic calculators and other roles where decimal math was used, like electronic cash registers, microwave oven timers, and so forth. This is because a 4-bit value holds a single binary-coded decimal (BCD) digit, making it a natural size for directly processing decimal values. As a 4-bit value is generally too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unit Of Information
A unit of information is any unit of measure of digital data size. In digital computing, a unit of information is used to describe the capacity of a digital data storage device. In telecommunications, a unit of information is used to describe the throughput of a communication channel. In information theory, a unit of information is used to measure information contained in messages and the entropy of random variables. Due to the need to work with data sizes that range from very small to very large, units of information cover a wide range of data sizes. Units are defined as multiples of a smaller unit except for the smallest unit which is based on convention and hardware design. Multiplier prefixes are used to describe relatively large sizes. For binary hardware, by far the most common hardware today, the smallest unit is the bit, a portmanteau of binary digit, which represents a value that is one of two possible values; typically shown as 0 and 1. The nibble, 4 bits, represents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbols, hexadecimal uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9 and "A"–"F" to represent values from ten to fifteen. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a convenient representation of binary code, binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte is two hexadecimal digits and its value can be written as to in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, several notations denote hexadecimal numbers, usually involving a prefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Binary-coded Decimal
In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications (e.g. error or overflow). In byte-oriented systems (i.e. most modern computers), the term ''unpacked'' BCD usually implies a full byte for each digit (often including a sign), whereas ''packed'' BCD typically encodes two digits within a single byte by taking advantage of the fact that four bits are enough to represent the range 0 to 9. The precise four-bit encoding, however, may vary for technical reasons (e.g. Excess-3). The ten states representing a BCD digit are sometimes called '' tetrades'' (the nibble typically needed to hold them is also known as a tetrade) while the unused, don't care-states are named ''pseudo-tetrad(e)s'', ''pseudo-decimals'', or ''pseudo-decimal digits''. BCD's main virtue, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Center
A data center is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. Since IT operations are crucial for business continuity, it generally includes redundant or backup components and infrastructure for power supply, data communication connections, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices. A large data center is an industrial-scale operation using as much electricity as a medium town. Estimated global data center electricity consumption in 2022 was 240–340 TWh, or roughly 1–1.3% of global electricity demand. This excludes energy used for cryptocurrency mining, which was estimated to be around 110 TWh in 2022, or another 0.4% of global electricity demand. The IEA projects that data center electric use could double between 2022 and 2026. High demand for electricity from data centers, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kilobaud Microcomputing
''Kilobaud Microcomputing'' was a magazine dedicated to the computer homebrew hobbyists from 1977 to 1983. It was one of the three influential computer magazines of the 1970s, along with ''BYTE'' and ''Creative Computing''. It focused mostly on the kit-build market, rather than the pre-assembled home computers that emerged, and as the kit market declined in the early 1980s, ''Kilobaud'' lost relevance and closed in 1983. After this, company continued publishing other magazines dedicated to particular platforms rather than the kit market. Beginnings Wayne Green was the founder and publisher of ''BYTE'' magazine, one of the influential microcomputer magazines of the 1970s. After putting out four issues, in November 1975 Green came to work and found that his ex-wife and the rest of the ''Byte'' magazine staff had moved out of his office and had taken the January issue with them. Consequently, the January 1976 issue had Virginia Green listed as publisher instead of Wayne Green. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ISO 8583
ISO 8583 is an international standard for ''financial transaction card originated'' interchange messaging. It is the International Organization for Standardization standard for systems that exchange electronic transactions initiated by cardholders using payment cards. ISO 8583 defines a message format and a communication flow so that different systems can exchange these transaction requests and responses. The vast majority of transactions made when a customer uses a card to make a payment in a store ( EFTPOS) use ISO 8583 at some point in the communication chain, as do transactions made at ATMs. In particular, the Mastercard, Visa and Verve networks base their authorization communications on the ISO 8583 standard, as do many other institutions and networks. Although ISO 8583 defines a common standard, it is not typically used directly by systems or networks. It defines many standard fields (data elements) which remain the same in all systems or networks, and leaves a few add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cash Machine
An automated teller machine (ATM) is an electronic telecommunications device that enables customers of financial institutions to perform financial transactions, such as cash withdrawals, deposits, funds transfers, balance inquiries or account information inquiries, at any time and without the need for direct interaction with bank staff. ATMs are known by a variety of other names, including automatic teller machines (ATMs) in the United States (sometimes redundantly as "ATM machine"). In Canada, the term automated banking machine (ABM) is also used, although ATM is also very commonly used in Canada, with many Canadian organizations using ATM rather than ABM. In British English, the terms cashpoint, cash machine and hole in the wall are also used. ATMs that are not operated by a financial institution are known as " white-label" ATMs. Using an ATM, customers can access their bank deposit or credit accounts in order to make a variety of financial transactions, most notably cash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
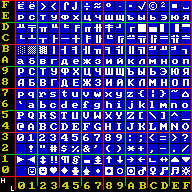
Octets In CP866 Ordered By Nibbles
Octet may refer to: Music * Octet (music), ensemble consisting of eight instruments or voices, or composition written for such an ensemble ** String octet, a piece of music written for eight string instruments *** Octet (Mendelssohn), 1825 composition by Felix Mendelssohn *** Octet (Bruch), 1920 composition by Max Bruch ** Octet (Beethoven), 1793 composition by Ludwig van Beethoven ** Octet (Lachner), 1850 composition by Franz Lachner ** ''Octet'' (Reich), 1979 composition by Steve Reich ** Octet (Reinecke),1892 composition by Carl Reinicke ** Octet (Schubert), 1824 composition by Franz Schubert ** Octet (Stravinsky), 1923 composition by Igor Stravinsky * Violin octet, a family of stringed instruments * ''Octet'' (musical), a musical by Dave Malloy Ballet * ''Octet'' (Christensen), 1958 ballet by Willam Christensen * ''Octet'' (Martins), 2003 ballet by Peter Martins Science and technology * Octet (computing), a grouping of eight bits ** Byte, a unit of digital information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |