|
Nanoshell
A nanoshell, or rather a nanoshell plasmon, is a type of spherical nanoparticle consisting of a dielectric core which is covered by a thin metallic shell (usually gold). These nanoshells involve a quasiparticle called a plasmon which is a collective excitation or quantum plasma oscillation where the electrons simultaneously oscillate with respect to all the ions. The simultaneous oscillation can be called plasmon hybridization where the tunability of the oscillation is associated with mixture of the inner and outer shell where they hybridize to give a lower energy or higher energy. This lower energy couples strongly to incident light, whereas the higher energy is an anti-bonding and weakly combines to incident light. The hybridization interaction is stronger for thinner shell layers, hence, the thickness of the shell and overall particle radius determines which wavelength of light it couples with. Nanoshells can be varied across a broad range of the light spectrum that spans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photothermal Therapy
Photothermal therapy (PTT) refers to efforts to use electromagnetic radiation (most often in infrared wavelengths) for the treatment of various medical conditions, including cancer. This approach is an extension of photodynamic therapy, in which a photosensitizer is excited with specific band light. This activation brings the sensitizer to an excited state where it then releases vibrational energy (heat), which is what kills the targeted cells. Unlike photodynamic therapy, photothermal therapy does not require oxygen to interact with the target cells or tissues. Current studies also show that photothermal therapy is able to use longer wavelength light, which is less energetic and therefore less harmful to other cells and tissues. Nanoscale materials Most materials of interest currently being investigated for photothermal therapy are on the nanoscale. One of the key reasons behind this is the enhanced permeability and retention effect observed with particles in a certain size range ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization
Polarization or polarisation may refer to: Mathematics *Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds *Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by adjoining more variables *Polarization identity, expresses an inner product in terms of its associated norm *Polarization (Lie algebra) Physical sciences *Polarization (waves), the ability of waves to oscillate in more than one direction, in particular polarization of light, responsible for example for the glare-reducing effect of polarized sunglasses **Polarization (antenna), the state of polarization (in the above sense) of electromagnetic waves transmitted by or received by a radio antenna *Dielectric polarization, charge separation in insulating materials: **Polarization density, volume dielectric polarization **Dipolar polarization, orientation of permanent dipoles **Ionic polarization, displacement of ions in a crystal **Maxwell–W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoparticles
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At the lowest range, metal particles smaller than 1 nm are usually called atom clusters instead. Nanoparticles are usually distinguished from microparticles (1-1000 µm), "fine particles" (sized between 100 and 2500 nm), and "coarse particles" (ranging from 2500 to 10,000 nm), because their smaller size drives very different physical or chemical properties, like colloidal properties and ultrafast optical effects or electric properties. Being more subject to the brownian motion, they usually do not sediment, like colloidal particles that conversely are usually understood to range from 1 to 1000 nm. Being much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light (400-700 nm), nano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precursors ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Cells
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
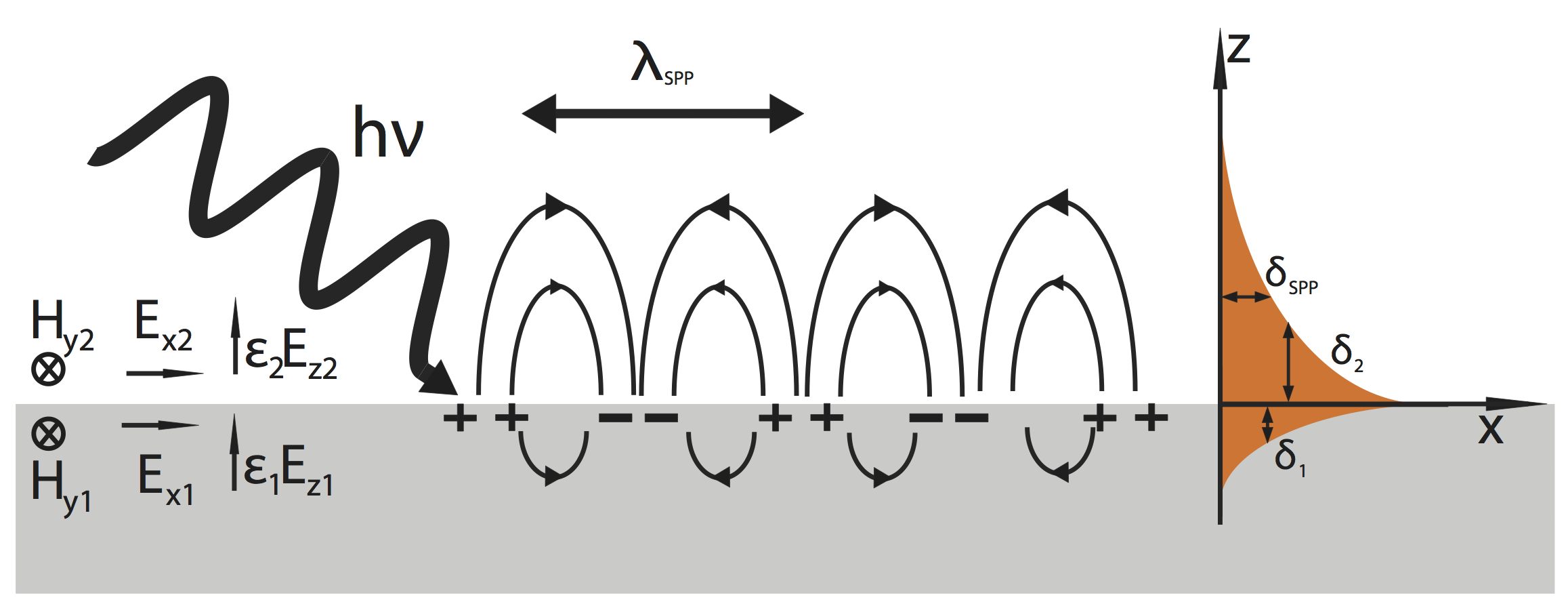
Surface Plasmon
Surface plasmons (SPs) are coherent delocalized electron oscillations that exist at the interface between any two materials where the real part of the dielectric function changes sign across the interface (e.g. a metal-dielectric interface, such as a metal sheet in air). SPs have lower energy than bulk (or volume) plasmons which quantise the longitudinal electron oscillations about positive ion cores within the bulk of an electron gas (or plasma). The charge motion in a surface plasmon always creates electromagnetic fields outside (as well as inside) the metal. The ''total'' excitation, including both the charge motion and associated electromagnetic field, is called either a surface plasmon polariton at a planar interface, or a localized surface plasmon for the closed surface of a small particle. The existence of surface plasmons was first predicted in 1957 by Rufus Ritchie. In the following two decades, surface plasmons were extensively studied by many scientists, the foremost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
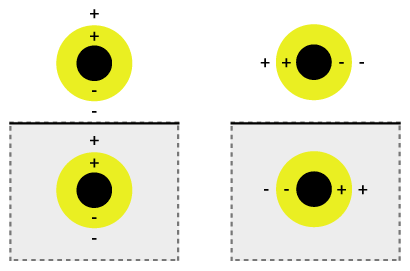
Plasmon
In physics, a plasmon is a quantum of plasma oscillation. Just as light (an optical oscillation) consists of photons, the plasma oscillation consists of plasmons. The plasmon can be considered as a quasiparticle since it arises from the quantization of plasma oscillations, just like phonons are quantizations of mechanical vibrations. Thus, plasmons are collective (a discrete number) oscillations of the free electron gas density. For example, at optical frequencies, plasmons can couple with a photon to create another quasiparticle called a plasmon polariton. Derivation The plasmon was initially proposed in 1952 by David Pines and David Bohm and was shown to arise from a Hamiltonian for the long-range electron-electron correlations. Since plasmons are the quantization of classical plasma oscillations, most of their properties can be derived directly from Maxwell's equations. Explanation Plasmons can be described in the classical picture as an oscillation of electron densit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine or nucleology is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors (gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)