|
Nucleophosmin
Nucleophosmin (NPM), also known as nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 or numatrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NPM1'' gene. Function NPM1 is associated with Nucleolus, nucleolar ribonucleoprotein structures and binds single-stranded and double-stranded nucleic acids, but it binds preferentially G-quadruplex forming nucleic acids. It is involved in the biogenesis of ribosomes and may assist small basic proteins in their transport to the nucleolus. Its regulation through SUMOylation (by SENP3 and SENP5) is another facet of the protein's regulation and cellular functions. It is located in the nucleolus, but it can be translocated to the nucleoplasm in case of serum starvation or treatment with anticancer drugs. The protein is phosphorylated. Nucleophosmin has multiple functions: # Histone Chaperone (protein), chaperones # Ribosome biogenesis and transport # Genomic stability and DNA repair # Endoribonuclease activity # Centrosome duplication during cell cycle # Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SENP3
SUMO1/sentrin/SMT3 specific peptidase 3, also known as SENP3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''SENP3'' gene. SENP3 together with SENP5, belongs to the Ulp1 branch in yeast and localize to nucleolus through B23/NPM1. SENP3 is associated and regulated by B23/nucleophosmin/NPM1 and involved in the regulation of ribosome biogenesis Spontaneous generation is a superseded scientific theory that held that living creatures could arise from nonliving matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was hypothesized that certain forms, such as fleas, could arise fr .... SENP3 may be regulated by Arf-Mdm2-p53 pathway. Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * References {{gene-17-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog ''Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the frog e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog ''Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the frog e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Myelogenous Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. Occasionally, spread may occur to the brain, skin, or gums. As an acute leukemia, AML progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated. Risk factors include smoking, previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, and exposure to the chemical benzene. The underlying mechanism involves replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemia cells, which results in a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Diagnosis is generally based on bone marrow aspiration and specific blood tests. AML has several subtypes for which treatments and outcomes may vary. The first-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by a chromosomal translocation involving the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) gene and is distinguished from other forms of AML by its responsiveness to all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA; also known as tretinoin) therapy. Acute promyelocytic leukemia was first characterized in 1957 by French and Norwegian physicians as a hyperacute fatal illness, with a median survival time of less than a week. Today, prognoses have drastically improved; 10-year survival rates are estimated to be approximately 80-90% according to one study. Signs and symptoms The symptoms tend to be similar to AML in general with the following being possible symptoms: * Anemia * Fatigue * Weakness * Chills * Depression * Difficulty breathing (dyspnea) * Low platelets (thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Aberrations
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where there is an atypical number of chromosomes, or as structural abnormalities, where one or more individual chromosomes are altered. Chromosome mutation was formerly used in a strict sense to mean a change in a chromosomal segment, involving more than one gene. Chromosome anomalies usually occur when there is an error in cell division following meiosis or mitosis. Chromosome abnormalities may be detected or confirmed by comparing an individual's karyotype, or full set of chromosomes, to a typical karyotype for the species via genetic testing. Numerical abnormality An abnormal number of chromosomes is called aneuploidy, and occurs when an individual is either missing a chromosome from a pair (resulting in monosomy) or has more than two chromosome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
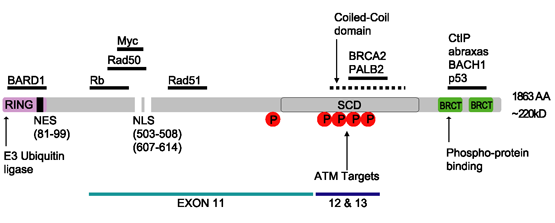
BARD1
BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BARD1'' gene. The human BARD1 protein is 777 amino acids long and contains a RING finger domain (residues 46-90), four ankyrin repeats (residues 420-555), and two tandem BRCT domains (residues 568-777). Function Most, if not all, BRCA1 heterodimerizes with BARD1 in vivo. BARD1 and BRCA1 form a heterodimer via their N-terminal RING finger domains. The BARD1-BRCA1 interaction is observed in vivo and in vitro and is essential for BRCA1 stability. BARD1 shares homology with the two most conserved regions of BRCA1: the N-terminal RING motif and the C-terminal BRCT domain. The RING motif is a cysteine-rich sequence found in a variety of proteins that regulate cell growth, including the products of tumor suppressor genes and dominant protooncogenes, and developmentally important genes such as the polycomb group of genes. The BARD1 protein also contains three tandem ankyrin repeats. The BARD1/BRCA1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AKT1
RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''AKT1'' gene. This enzyme belongs to the AKT subfamily of serine/threonine kinases that contain SH2 (Src homology 2-like) protein domains. It is commonly referred to as PKB, or by both names as "Akt/PKB". Function The serine-threonine protein kinase AKT1 is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may include feeling tired, shortness of breath, bleeding disorders, anemia, or frequent infections. Some types may develop into acute myeloid leukemia. Risk factors include previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy, exposure to certain chemicals such as tobacco smoke, pesticides, and benzene, and exposure to heavy metals such as mercury or lead. Problems with blood cell formation result in some combination of low red blood cell, platelet, and white blood cell counts. Some types have an increase in immature blood cells, called blasts, in the bone marrow or blood. The types of MDS are based on specific changes in the blood cells and bone marrow. Treatments may include supportive care, drug therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |