|
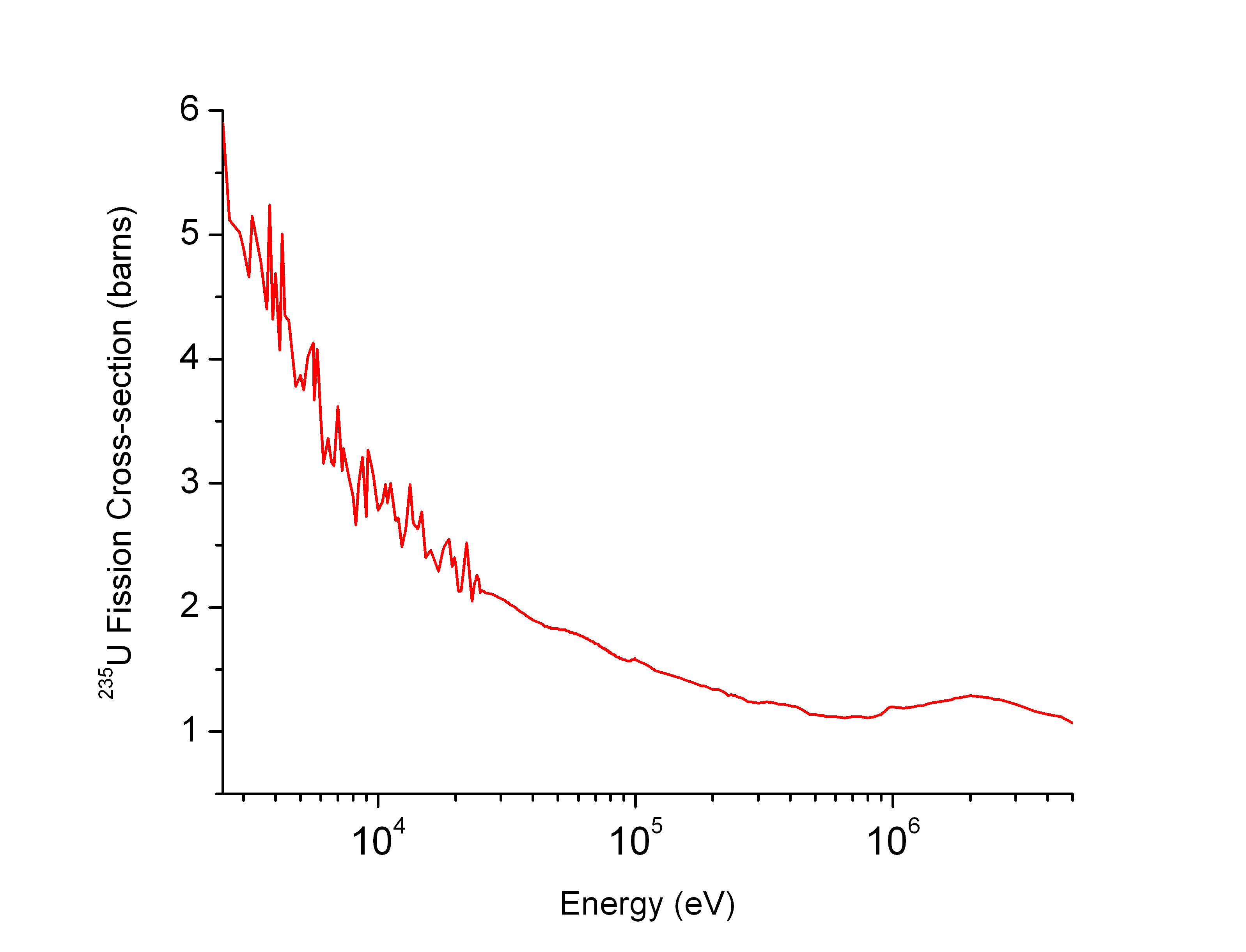
Nuclear Cross Section
The nuclear cross section of a nucleus is used to describe the probability that a nuclear reaction will occur. The concept of a nuclear cross section can be quantified physically in terms of "characteristic area" where a larger area means a larger probability of interaction. The standard unit for measuring a nuclear cross section (denoted as σ) is the barn, which is equal to , or . Cross sections can be measured for all possible interaction processes together, in which case they are called total cross sections, or for specific processes, distinguishing elastic scattering and inelastic scattering; of the latter, amongst neutron cross sections the absorption cross sections are of particular interest. In nuclear physics it is conventional to consider the impinging particles as point particles having negligible diameter. Cross sections can be computed for any nuclear process, such as capture scattering, production of neutrons, or nuclear fusion. In many cases, the number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (physics)
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place in a collision of two particles. For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted (sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. When two discrete particles interact in classical physics, their mutual cross section is the area transverse to their relative motion within which they must meet in order to scatter from each other. If the particles are hard inelastic sphere A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon-135
Xenon-135 (135Xe) is an Isotope#Radioactive, primordial, and stable isotopes, unstable isotope of xenon with a half-life of about 9.2 hours. 135Xe is a fission product of uranium and it is the most powerful known neutron-absorbing nuclear poison (2 million Barn (unit), barns; up to 3 million barn (unit), barns under reactor conditions), with a significant effect on nuclear reactor operation. The ultimate yield of xenon-135 from fission is 6.3%, though most of this is from fission-produced tellurium-135 and iodine-135. 135Xe effects on reactor restart In a typical nuclear reactor fueled with uranium-235, the presence of 135Xe as a fission product presents designers and operators with problems due to its large neutron cross section for absorption. Because absorbing neutrons can impair a nuclear reactor's ability to increase power, reactors are designed to mitigate this effect and operators are trained to anticipate and react to these transients. This practice dates to the Chicago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis J
Louis may refer to: People * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer Other uses * Louis (coin), a French coin * HMS Louis, HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also * Derived terms * King Louis (other) * Saint Louis (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig (other), Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik, names sometimes translated to English as "Louis" {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James J
James may refer to: People * James (given name) * James (surname) * James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician * James, brother of Jesus * King James (other), various kings named James * Prince James (other) * Saint James (other) Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, York, James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Film and television * James (2005 film), ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * James (2008 film), ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * James (2022 film), ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * "James", a television Adventure Time (season 5)#ep42, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering Cross-section
In physics, the cross section is a measure of the probability that a specific process will take place in a collision of two particles. For example, the Rutherford cross-section is a measure of probability that an alpha particle will be deflected by a given angle during an interaction with an atomic nucleus. Cross section is typically denoted (sigma) and is expressed in units of area, more specifically in barns. In a way, it can be thought of as the size of the object that the excitation must hit in order for the process to occur, but more exactly, it is a parameter of a stochastic process. When two discrete particles interact in classical physics, their mutual cross section is the area transverse to their relative motion within which they must meet in order to scatter from each other. If the particles are hard inelastic spheres that interact only upon contact, their scattering cross section is related to their geometric size. If the particles interact through some action-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Cross-section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), but different nucleon numbers (mass numbers) due to different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. While all isotopes of a given element have similar chemical properties, they have different atomic masses and physical properties. The term isotope is derived from the Greek roots isos (wikt:ἴσος, ἴσος "equal") and topos (wikt:τόπος, τόπος "place"), meaning "the same place"; thus, the meaning behind the name is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. It was coined by Scottish doctor and writer Margaret Todd (doctor), Margaret Todd in a 1913 suggestion to the British chemist Frederick Soddy, who popularized the term. The number of protons within the atomic nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle, they then separate without changing the nature of any nuclide, the process is simply referred to as a type of nuclear scattering, rather than a nuclear reaction. In principle, a reaction can involve more than two particles collision, colliding, but because the probability of three or more nuclei to meet at the same time at the same place is much less than for two nuclei, such an event is exceptionally rare (see triple alpha process for an example very close to a three-body nuclear reaction). The term "nuclear reaction" may refer either to a change in a nuclide induced by collision with another particle or to a spontaneous change of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from high energy interactions like the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei or astronomical events like solar flares. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz () and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (), gamma ray photons have the highest photon energy of any form of electromagnetic radiation. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900, he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or an isotope into another chemical element. Nuclear transmutation occurs in any process where the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is changed. A transmutation can be achieved either by nuclear reactions (in which an outside particle reacts with a nucleus) or by radioactive decay, where no outside cause is needed. Natural transmutation by stellar nucleosynthesis in the past created most of the heavier chemical elements in the known existing universe, and continues to take place to this day, creating the vast majority of the most common elements in the universe, including helium, oxygen and carbon. Most stars carry out transmutation through fusion reactions involving hydrogen and helium, while much larger stars are also capable of fusing heavier elements up to iron late in their evolution. Elements heavier than iron, such as gold or lead, are created through elemental transmutations that can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Neutron
The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term ''temperature'' is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is then adapted to the Maxwell distribution known for thermal motion. Qualitatively, the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the free neutrons. The momentum and wavelength of the neutron are related through the de Broglie relation. The long wavelength of slow neutrons allows for the large cross section. Neutron energy distribution ranges The precise boundaries of neutron energy ranges are not well defined, and differ between sources, but some common names and limits are given in the following table. The following is a detailed classification: Thermal A thermal neutron is a free neutron with a kinetic energy of about 0.025 eV (about 4.0×10−21 J or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th ed., (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', vol. 1, 3rd ed., (1968), Wiley, . This number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |