|
Non-syllabic
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel, glide or semiconsonant is a sound that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary, rather than as the nucleus of a syllable. Examples of semivowels in English are the consonants ''y'' and ''w'', in ''yes'' and ''west'', respectively. Written in IPA, ''y'' and ''w'' are near to the vowels ''ee'' and ''oo'' in ''seen'' and ''moon,'' written in IPA. The term ''glide'' may alternatively refer to any type of transitional sound, not necessarily a semivowel. Classification Semivowels form a subclass of approximants. Although "semivowel" and "approximant" are sometimes treated as synonymous, most authors use the term "semivowel" for a more restricted set; there is no universally agreed-upon definition, and the exact details may vary from author to author. For example, do not consider the labiodental approximant to be a semivowel, while proposes that it should be considered one. In the International Phonet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphthong
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech organ, speech apparatus) moves during the pronunciation of the vowel. In most International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects, varieties of English language, English, the phrase "no highway cowboy" () has five distinct diphthongs, one in every syllable. Diphthongs contrast with monophthongs, where the tongue or other speech organs do not move and the syllable contains only a single vowel sound. For instance, in English, the word ''ah'' is spoken as a monophthong (), while the word ''ow'' is spoken as a diphthong in most varieties (). Where two adjacent vowel sounds occur in different syllables (e.g. in the English word ''re-elect'') the result is described as hiatus (linguistics), hiatus, not as a diphthong. (The English word ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphthong
A diphthong ( ; , ), also known as a gliding vowel, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of the speech organ, speech apparatus) moves during the pronunciation of the vowel. In most International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects, varieties of English language, English, the phrase "no highway cowboy" () has five distinct diphthongs, one in every syllable. Diphthongs contrast with monophthongs, where the tongue or other speech organs do not move and the syllable contains only a single vowel sound. For instance, in English, the word ''ah'' is spoken as a monophthong (), while the word ''ow'' is spoken as a diphthong in most varieties (). Where two adjacent vowel sounds occur in different syllables (e.g. in the English word ''re-elect'') the result is described as hiatus (linguistics), hiatus, not as a diphthong. (The English word ''h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximant Consonant
Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough nor with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no turbulence. This class is composed of sounds like (as in ''rest'') and semivowels like and (as in ''yes'' and ''west'', respectively), as well as lateral approximants like (as in ''less''). Terminology Before Peter Ladefoged coined the term "approximant" in the 1960s, the terms "frictionless continuant" and "semivowel" were used to refer to non-lateral approximants. In phonology, "approximant" is also a distinctive feature that encompasses all sonorants except nasals, including vowels, taps and trills. Semivowels Some approximants resemble vowels in acoustic and articulatory properties and the terms ''semivowel'' and ''glide'' are often used for these non-syllabic vowel-like segme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhotic Consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthography, orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek alphabet, Greek letter Rho (letter), rho, including R, , in the Latin script and Er (Cyrillic), , in the Cyrillic script. They are transcribed in the International Phonetic Alphabet by upper- or lower-case variants of Roman , : , , , , , , , and as well as by the lower-case turned Roman (the symbol for the near-open central vowel) combined with the "non-syllabic" diacritic, that is . This class of sounds is difficult to characterise phonetically; from a phonetic standpoint, there is no single articulatory correlate (manner of articulation, manner or place of articulation, place) common to rhotic consonants. Rhotics have instead been found to carry out similar phonological functions or to have certain similar phonological features across different languages. Being "R-like" is an elusive and ambiguous con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverted Breve
Inverted breve or arch is a diacritical mark, shaped like the top half of a circle ( ̑ ), that is, like an upside-down breve (˘). It looks similar to the circumflex (ˆ), which has a sharp tip (''Â â Ê ê Î î Ô ô Û û''), while the inverted breve is rounded: (''Ȃ ȃ Ȇ ȇ Ȋ ȋ Ȏ ȏ Ȗ ȗ''). Inverted breve can occur above or below the letter. It is not used in any natural language alphabet, but as a phonetic indicator. It is identical in form to the Ancient Greek circumflex. Uses Serbo-Croatian The inverted breve above is used in traditional Slavicist notation of Serbo-Croatian phonology to indicate long falling accent. It is placed above the syllable nucleus, which can be one of five vowels (ȃ ȇ ȋ ȏ ȗ) or syllabic ȓ. This use of the inverted breve is derived from the Ancient Greek circumflex, which was preserved in the polytonic orthography of Modern Greek and influenced early Serbian Cyrillic printing through religious literature. In the early 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Back Unrounded Vowel
The open back unrounded vowel, or low back unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is A. The letter is called ''script a'' because it lacks the extra hook on top of a printed letter ''a'', which corresponds to a different vowel, the open front unrounded vowel. ''Script a'', which has its linear stroke on the bottom right, should not be confused with ''turned script a'', , which has its linear stroke on the top left and corresponds to a rounded version of this vowel, the open back rounded vowel. The open back unrounded vowel is the vocalic equivalent of the pharyngeal approximant . with the non-syllabic diacritic and are used in different transcription systems to represent the same sound. In some languages (such as Azerbaijani, Estonian, Luxembourgish and Toda) there is the near-open back unrounded vowel (a sound between car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extra-shortness
The International Phonetic Alphabet uses a breve to indicate a speech sound (usually a vowel) with extra-short duration. That is, is a very short vowel with the quality of . An example from English is the short schwa of the word ''police'' . This is typical of vowel reduction. Before the 1989 Kiel Convention, the breve was used for a Semi-vowel, non-syllabic vowel (that is, part of a diphthong), which is now indicated by an breve placed under the vowel letter, as in ''eye'' . It is also sometimes used for any flap consonants missing dedicated symbols in the IPA, since a flap is in effect a very brief stop consonant, stop. References Phonetics {{Phonetics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (length). They are usually voiced and are closely involved in prosodic variation such as tone, intonation and stress. The word ''vowel'' comes from the Latin word , meaning "vocal" (i.e. relating to the voice). In English, the word ''vowel'' is commonly used to refer both to vowel sounds and to the written symbols that represent them (a, e, i, o, u, and sometimes y). Definition There are two complementary definitions of vowel, one phonetic and the other phonological. *In the phonetic definition, a vowel is a sound, such as the English "ah" or "oh" , produced with an open vocal tract; it is median (the air escapes along the middle of the tongue), oral (at least some of the airflow must escape through the mouth), frictionless and continuant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic transcription, phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standardized representation of speech sounds in written form.International Phonetic Association (IPA), ''Handbook''. The IPA is used by lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, linguistics, linguists, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of wiktionary:lexical, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, phonemes, Intonation (linguistics), intonation, and the separation of words and syllables. To represent additional qualities of speech—such as tooth wiktionary:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation (also point of articulation) of a consonant is a location along the vocal tract where its production occurs. It is a point where a constriction is made between an active and a passive articulator. Active articulators are organs capable of voluntary movement which create the constriction, while passive articulators are so called because they are normally fixed and are the parts with which an active articulator makes contact. Along with the manner of articulation and phonation, the place of articulation gives the consonant its distinctive sound. Since vowels are produced with an open vocal tract, the point where their production occurs cannot be easily determined. Therefore, they are not described in terms of a place of articulation but by the relative positions in vowel space. This is mostly dependent on their formant frequencies and less on the specific tongue position and lip rounding. The terminology used in describing place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds typically made up of a syllable nucleus (most often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (typically, consonants). Syllables are often considered the phonological "building blocks" of words. They can influence the rhythm of a language, its prosody, its poetic metre and its stress patterns. Speech can usually be divided up into a whole number of syllables: for example, the word ''ignite'' is made of two syllables: ''ig'' and ''nite''. Syllabic writing began several hundred years before the first letters. The earliest recorded syllables are on tablets written around 2800 BC in the Sumerian city of Ur. This shift from pictograms to syllables has been called "the most important advance in the history of writing". A word that consists of a single syllable (like English ''dog'') is called a monosyllable (and is said to be ''monosyllabic''). Similar terms include disyllable (and ''disyllabic''; also ''bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
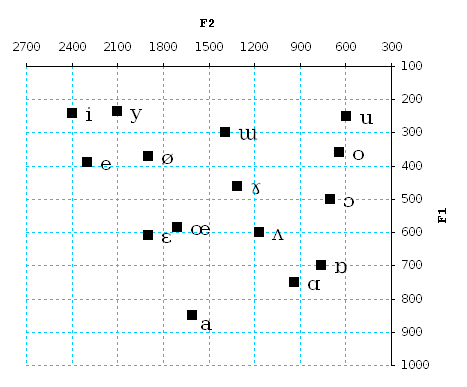
Formant
In speech science and phonetics, a formant is the broad spectral maximum that results from an acoustic resonance of the human vocal tract. In acoustics, a formant is usually defined as a broad peak, or local maximum, in the spectrum. For harmonic sounds, with this definition, the formant frequency is sometimes taken as that of the harmonic that is most augmented by a resonance. The difference between these two definitions resides in whether "formants" characterise the production mechanisms of a sound or the produced sound itself. In practice, the frequency of a spectral peak differs slightly from the associated resonance frequency, except when, by luck, harmonics are aligned with the resonance frequency. A room can be said to have formants characteristic of that particular room, due to its resonances, i.e., to the way sound reflects from its walls and objects. Room formants of this nature reinforce themselves by emphasizing specific frequencies and absorbing others, as exploited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |