|
Nilpotent Lie Algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra \mathfrak is nilpotent if its lower central series terminates in the zero subalgebra. The ''lower central series'' is the sequence of subalgebras : \mathfrak \geq mathfrak,\mathfrak\geq mathfrak,[\mathfrak,\mathfrak \geq [\mathfrak, mathfrak,[\mathfrak,\mathfrak] \geq ... We write \mathfrak_0 = \mathfrak, and \mathfrak_n = [\mathfrak,\mathfrak_] for all n > 0. If the lower central series eventually arrives at the zero subalgebra, then the Lie algebra is called nilpotent. The lower central series for Lie algebras is analogous to the lower central series in group theory, and nilpotent Lie algebras are analogs of nilpotent groups. The nilpotent Lie algebras are precisely those that can be obtained from abelian Lie algebras, by successive central extensions. Note that the definition means that, viewed as a non-associative non-unital algebra, a Lie algebra \mathfrak is nilpotent if it is nilpotent as an ideal. Definition Let \mathfrak be a Lie alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lie Algebra
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identity. The Lie bracket of two vectors x and y is denoted ,y/math>. The vector space \mathfrak g together with this operation is a non-associative algebra, meaning that the Lie bracket is not necessarily associative. Lie algebras are closely related to Lie groups, which are groups that are also smooth manifolds: any Lie group gives rise to a Lie algebra, which is its tangent space at the identity. Conversely, to any finite-dimensional Lie algebra over real or complex numbers, there is a corresponding connected Lie group unique up to finite coverings ( Lie's third theorem). This correspondence allows one to study the structure and classification of Lie groups in terms of Lie algebras. In physics, Lie groups appear as symmetry grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
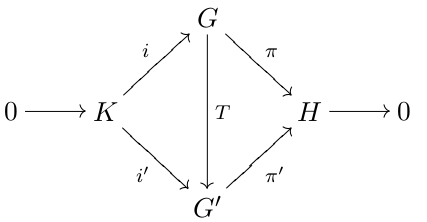
Lower Central Series
In mathematics, especially in the fields of group theory and Lie theory, a central series is a kind of normal series of subgroups or Lie subalgebras, expressing the idea that the commutator is nearly trivial. For groups, the existence of a central series means it is a nilpotent group; for matrix rings (considered as Lie algrebras), it means that in some basis the ring consists entirely of upper triangular matrices with constant diagonal. This article uses the language of group theory; analogous terms are used for Lie algebras. A general group possesses a lower central series and upper central series (also called the descending central series and ascending central series, respectively), but these are central series in the strict sense (terminating in the trivial subgroup) if and only if the group is nilpotent. A related but distinct construction is the derived series, which terminates in the trivial subgroup whenever the group is solvable. Definition A central series is a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Theory
In abstract algebra, group theory studies the algebraic structures known as group (mathematics), groups. The concept of a group is central to abstract algebra: other well-known algebraic structures, such as ring (mathematics), rings, field (mathematics), fields, and vector spaces, can all be seen as groups endowed with additional operation (mathematics), operations and axioms. Groups recur throughout mathematics, and the methods of group theory have influenced many parts of algebra. Linear algebraic groups and Lie groups are two branches of group theory that have experienced advances and have become subject areas in their own right. Various physical systems, such as crystals and the hydrogen atom, and Standard Model, three of the four known fundamental forces in the universe, may be modelled by symmetry groups. Thus group theory and the closely related representation theory have many important applications in physics, chemistry, and materials science. Group theory is also ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilpotent Group
In mathematics, specifically group theory, a nilpotent group ''G'' is a group that has an upper central series that terminates with ''G''. Equivalently, its central series is of finite length or its lower central series terminates with . Intuitively, a nilpotent group is a group that is "almost abelian". This idea is motivated by the fact that nilpotent groups are solvable, and for finite nilpotent groups, two elements having relatively prime orders must commute. It is also true that finite nilpotent groups are supersolvable. The concept is credited to work in the 1930s by Russian mathematician Sergei Chernikov. Nilpotent groups arise in Galois theory, as well as in the classification of groups. They also appear prominently in the classification of Lie groups. Analogous terms are used for Lie algebras (using the Lie bracket) including nilpotent, lower central series, and upper central series. Definition The definition uses the idea of a central series for a group. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Extension (mathematics)
In mathematics, a group extension is a general means of describing a group in terms of a particular normal subgroup and quotient group. If Q and N are two groups, then G is an extension of Q by N if there is a short exact sequence :1\to N\;\overset\;G\;\overset\;Q \to 1. If G is an extension of Q by N, then G is a group, \iota(N) is a normal subgroup of G and the quotient group G/\iota(N) is isomorphic to the group Q. Group extensions arise in the context of the extension problem, where the groups Q and N are known and the properties of G are to be determined. Note that the phrasing "G is an extension of N by Q" is also used by some. Since any finite group G possesses a maximal normal subgroup N with simple factor group G/N, all finite groups may be constructed as a series of extensions with finite simple groups. This fact was a motivation for completing the classification of finite simple groups. An extension is called a central extension if the subgroup N lies in the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilpotent
In mathematics, an element x of a ring R is called nilpotent if there exists some positive integer n, called the index (or sometimes the degree), such that x^n=0. The term was introduced by Benjamin Peirce in the context of his work on the classification of algebras. Examples *This definition can be applied in particular to square matrices. The matrix :: A = \begin 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end :is nilpotent because A^3=0. See nilpotent matrix for more. * In the factor ring \Z/9\Z, the equivalence class of 3 is nilpotent because 32 is congruent to 0 modulo 9. * Assume that two elements a and b in a ring R satisfy ab=0. Then the element c=ba is nilpotent as \beginc^2&=(ba)^2\\ &=b(ab)a\\ &=0.\\ \end An example with matrices (for ''a'', ''b''):A = \begin 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 \end, \;\; B =\begin 0 & 1\\ 0 & 0 \end. Here AB=0 and BA=B. *By definition, any element of a nilsemigroup is nilpotent. Properties No nilpotent el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engel's Theorem
In representation theory, a branch of mathematics, Engel's theorem states that a finite-dimensional Lie algebra \mathfrak g is a nilpotent Lie algebra if and only if for each X \in \mathfrak g, the adjoint representation of a Lie algebra">adjoint map :\operatorname(X)\colon \mathfrak \to \mathfrak, given by \operatorname(X)(Y) = [X, Y], is a nilpotent endomorphism on \mathfrak; i.e., \operatorname(X)^k = 0 for some ''k''. It is a consequence of the theorem, also called Engel's theorem, which says that if a Lie algebra of matrices consists of nilpotent matrices, then the matrices can all be simultaneously brought to a strictly upper triangular form. Note that if we merely have a Lie algebra of matrices which is nilpotent ''as a Lie algebra'', then this conclusion does ''not'' follow (i.e. the naïve replacement in Lie's theorem of "solvable" with "nilpotent", and "upper triangular" with "strictly upper triangular", is false; this already fails for the one-dimensional Lie subalgebra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |