|
Neuroinformatics
Neuroinformatics is the emergent field that combines informatics and neuroscience. Neuroinformatics is related with neuroscience data and information processing by artificial neural networks. There are three main directions where neuroinformatics has to be applied: * the development of computational models of the nervous system and neural processes; * the development of tools for analyzing and modeling neuroscience data; and * the development of tools and databases for management and sharing of neuroscience data at all levels of analysis. Neuroinformatics encompasses philosophy (computational theory of mind), psychology (information processing theory), computer science (natural computing, bio-inspired computing), among others disciplines. Neuroinformatics doesn't deal with matter or energy, so it can be seen as a branch of neurobiology that studies various aspects of nervous systems. The term ''neuroinformatics'' seems to be used synonymously with cognitive informatics, described b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Brain
The Blue Brain Project was a Swiss brain research initiative that aimed to create a Artificial brain, digital reconstruction of the mouse brain. The project was founded in May 2005 by the Brain Mind Institute of ''École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne'' (EPFL) in Switzerland. The project ended in December 2024. Its mission was to use biologically-detailed digital reconstructions and brain simulation, simulations of the mammalian brain to identify the fundamental principles of brain structure and function. The project was headed by the founding director Henry Markram—who also launched the European Human Brain Project—and was co-directed by Felix Schürmann, Adriana Salvatore and Sean Hill (scientist), Sean Hill. Using a Blue Gene supercomputer running Michael Hines's Neuron (software), NEURON, the simulation involved a biologically realistic model of neurons and an empirically reconstructed model connectome. There were a number of collaborations, including the Cajal Blue B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Informatics
Informatics is the study of computational systems. According to the Association for Computing Machinery, ACM Europe Council and Informatics Europe, informatics is synonymous with computer science and computing as a profession, in which the central notion is Data processing, transformation of information. In some cases, the term "informatics" may also be used with different meanings, e.g., in the context of social computing or library science. Different meanings In some countries, depending on local interpretations and contexts, the term "informatics" is used synonymously to mean information systems, information science, information theory, information engineering, information technology, information processing, or other theoretical or practical fields. In Germany, the term ''informatics'' closely corresponds to modern computer science. Accordingly, universities in continental Europe usually translate "informatics" as computer science, or sometimes information and computer sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurobiology
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and Mathematical Modeling, mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the Biology, biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cell biology, cellular studies of individual neurons to neuroimaging, imaging of Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurocomputing
Computational neuroscience (also known as theoretical neuroscience or mathematical neuroscience) is a branch of neuroscience which employs mathematics, computer science, theoretical analysis and abstractions of the brain to understand the principles that govern the development, structure, physiology and cognitive abilities of the nervous system. Computational neuroscience employs computational simulations to validate and solve mathematical models, and so can be seen as a sub-field of theoretical neuroscience; however, the two fields are often synonymous. The term mathematical neuroscience is also used sometimes, to stress the quantitative nature of the field. Computational neuroscience focuses on the description of biologically plausible neurons (and neural systems) and their physiology and dynamics, and it is therefore not directly concerned with biologically unrealistic models used in connectionism, control theory, cybernetics, quantitative psychology, machine lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind Uploading
Mind uploading is a speculative process of whole brain emulation in which a brain scan is used to completely emulate the mental state of the individual in a digital computer. The computer would then run a simulation of the brain's information processing, such that it would respond in essentially the same way as the original brain and experience having a sentient conscious mind. Substantial mainstream research in related areas is being conducted in neuroscience and computer science, including animal brain mapping and simulation, development of faster supercomputers, virtual reality, brain–computer interfaces, connectomics, and information extraction from dynamically functioning brains. According to supporters, many of the tools and ideas needed to achieve mind uploading already exist or are under active development; however, they will admit that others are, as yet, very speculative, but say they are still in the realm of engineering possibility. Mind uploading may potentiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Emulation
Mind uploading is a speculative process of whole brain emulation in which a brain scan is used to completely emulate the mental state of the individual in a digital computer. The computer would then run a simulation of the brain's information processing, such that it would respond in essentially the same way as the original brain and experience having a sentient conscious mind. Substantial mainstream research in related areas is being conducted in neuroscience and computer science, including animal brain mapping and simulation, development of faster supercomputers, virtual reality, brain–computer interfaces, connectomics, and information extraction from dynamically functioning brains. According to supporters, many of the tools and ideas needed to achieve mind uploading already exist or are under active development; however, they will admit that others are, as yet, very speculative, but say they are still in the realm of engineering possibility. Mind uploading may potentially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service has over 5,500 journalists working across its output including in 50 foreign news bureaus where more than 250 foreign correspondents are stationed. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Gene
Blue Gene was an IBM project aimed at designing supercomputers that can reach operating speeds in the petaFLOPS (PFLOPS) range, with relatively low power consumption. The project created three generations of supercomputers, Blue Gene/L, Blue Gene/P, and Blue Gene/Q. During their deployment, Blue Gene systems often led the TOP500 and Green500 rankings of the most powerful and most power-efficient supercomputers, respectively. Blue Gene systems have also consistently scored top positions in the Graph500 list. The project was awarded the 2009 National Medal of Technology and Innovation. After Blue Gene/Q, IBM focused its supercomputer efforts on the OpenPower platform, using accelerators such as FPGAs and GPUs to address the diminishing returns of Moore's law. History A video presentation of the history and technology of the Blue Gene project was given at the Supercomputing 2020 conference. In December 1999, IBM announced a US$100 million research initiative for a five-year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
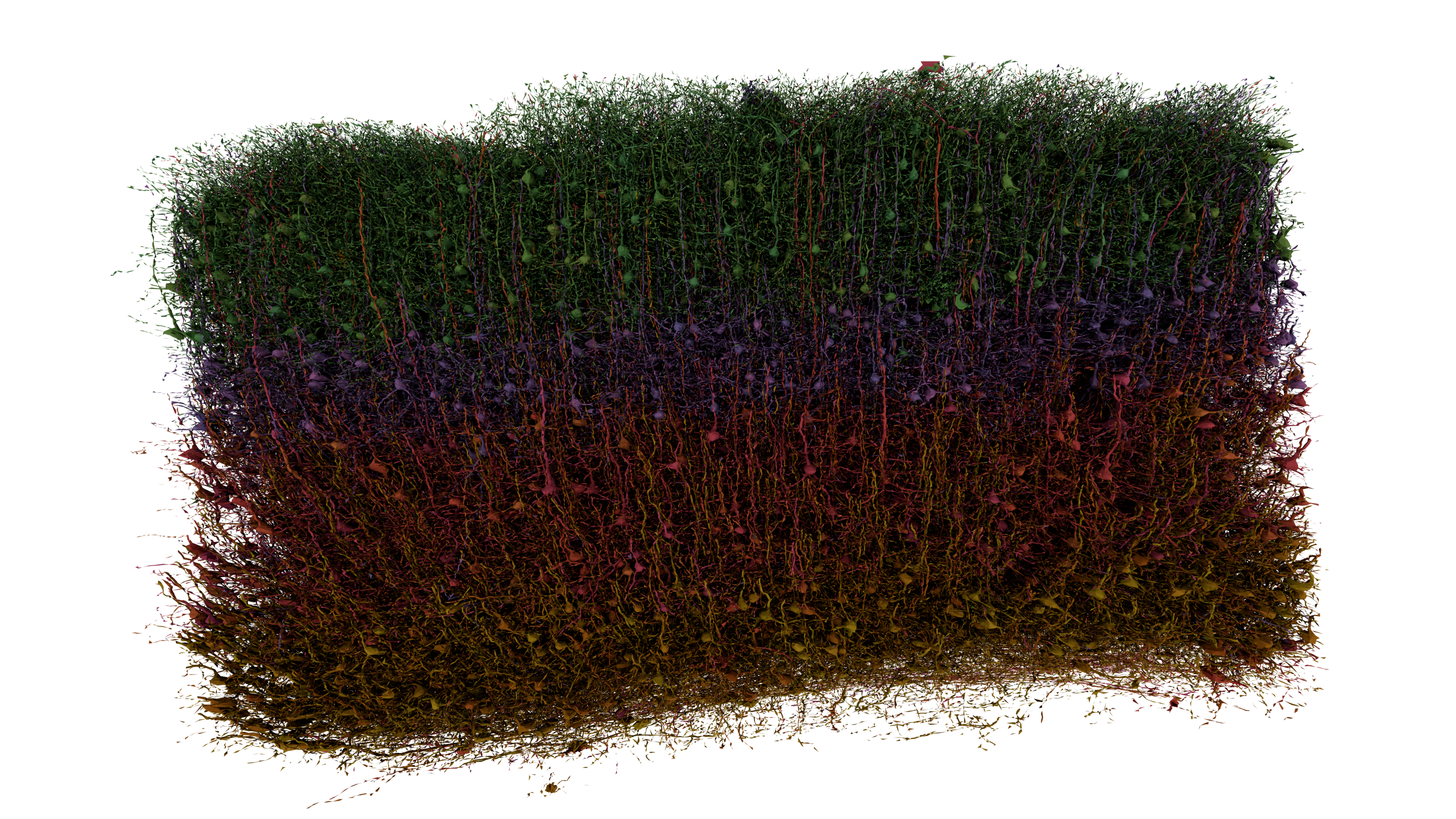
Neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, spatial reasoning, and language. The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex. In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%. The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI. Etymology The term is from ''cortex'', Latin, " bark" or "rind", combined with ''neo-'', Greek, "new". ''Neopallium'' is a similar hybrid, from Latin ''pallium'', "cloak". ''Isocortex'' and ''allocortex'' are hybrids with Greek ''isos'', "same", and ''allos'', "other". Anatomy The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues. The neocortex cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |