|
Nautiloid
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods ( Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species. They flourished during the early Paleozoic era, when they constituted the main predatory animals. Early in their evolution, nautiloids developed an extraordinary diversity of shell shapes, including coiled morphologies and giant straight-shelled forms ( orthocones). Only a handful of rare coiled species, the nautiluses, survive to the present day. In a broad sense, "nautiloid" refers to a major cephalopod subclass or collection of subclasses (Nautiloidea ''sensu lato''). Nautiloids are typically considered one of three main groups of cephalopods, along with the extinct ammonoids (ammonites) and living coleoids (such as squid, octopus, and kin). While ammonoids and coleoids are monophyletic clades with exclusive ancestor-descendant rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
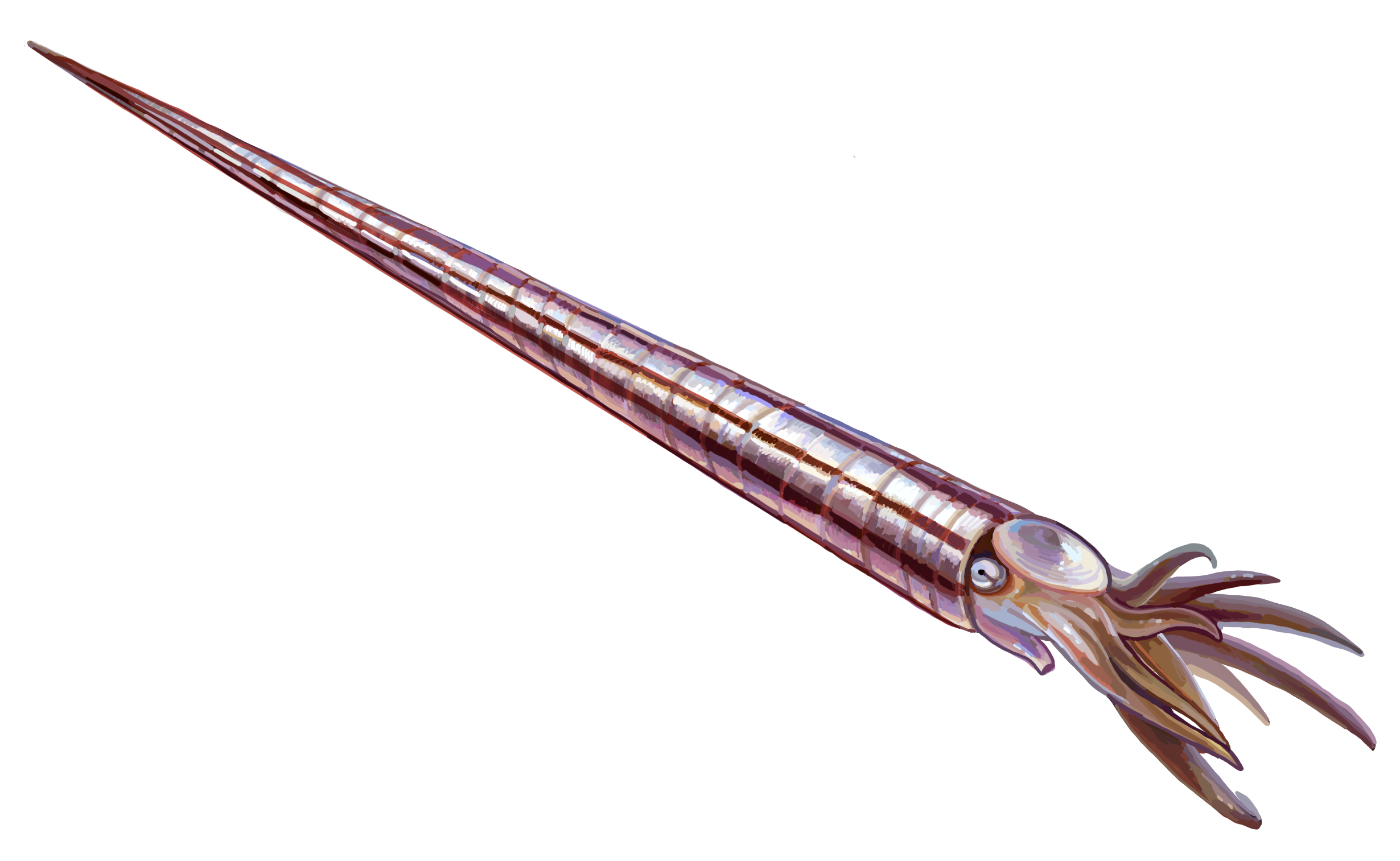
Orthoceratoidea
Orthoceratoidea is a major subclass of nautiloid cephalopods. Members of this subclass usually have orthoconic (straight) to slightly cyrtoconic (curved) shells, and central to subcentral siphuncles which may bear internal deposits. Orthoceratoids are also characterized by dorsomyarian muscle scars (a small number of large scars concentrated at the top of the body chamber), extensive cameral deposits, and calciosiphonate connecting rings with a porous and calcitic inner layer. Currently, Orthoceratoidea comprises the orders Riocerida, Dissidocerida, Actinocerida, Pseudorthocerida, Lituitida and Orthocerida. Orthocerida is a noteworthy paraphyletic order which is ancestral to the major cephalopod groups such as the extinct ammonoids and living coleoids (cephalopods without external shells, including squids, octopus, cuttlefish, etc.). Taxonomy As a superorder, Orthoceratiodea was one of six superorders within the Nautiloidea, the others being the Plectronoceratoidea (= Ellesm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellesmerocerida
The Ellesmerocerida is an order of primitive cephalopods belonging to the subclass Nautiloidea with a widespread distribution that lived during the Late Cambrian and Ordovician. Morphology The Ellesmerocerida are characterized by shells that are typically small, some even tiny, with close-spaced septa and relatively large ventral siphuncles. In some genera (e.g. '' Paleoceras''), the septa are uniformly spaced. Shells of ellesmerocerids are typically smooth and compressed and vary in form. They may be breviconic (short) or longiconic (elongate), straight (orthoconic) or curved (cyrtoconic). Cyrtoconic forms are usually endogastric, with longitudinally convex ventral margins. The apeces of straight forms typically have an endogastric curvature. Some may have grown to as much as 15 cm. Siphuncle segments are tubular or concave. Septal necks are short. Connecting rings which may appear layered are thick and typically wedge shaped with their maximum width at or near where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoceratoidea
Endocerida is an extinct nautiloid order, a group of cephalopods from the Lower Paleozoic with cone-like deposits in their siphuncle. Endocerida was a diverse group of cephalopods that lived from the Early Ordovician possibly to the Late Silurian. Their shells were variable in form. Some were straight (orthoconic), others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like ''Endoceras'' attained shell lengths close to . The related ''Cameroceras'' is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching , but these claims are problematic. The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long when fully grown. Morphology Endocerids had a relatively small body chamber as well as a proportionally large siphuncle, which in some genera reached nearly half the shell diameter. This suggests that much of the visceral mass may have been housed within the siphuncle itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocerida
Endocerida is an extinct nautiloid order, a group of cephalopods from the Lower Paleozoic with cone-like deposits in their siphuncle. Endocerida was a diverse group of cephalopods that lived from the Early Ordovician possibly to the Late Silurian. Their shells were variable in form. Some were straight (orthoconic), others curved (cyrtoconic); some were long (longiconic), others short (breviconic). Some long-shelled forms like '' Endoceras'' attained shell lengths close to . The related ''Cameroceras'' is anecdotally reported to have reached lengths approaching , but these claims are problematic. The overwhelming majority of endocerids and nautiloids in general are much smaller, usually less than a meter long when fully grown. Morphology Endocerids had a relatively small body chamber as well as a proportionally large siphuncle, which in some genera reached nearly half the shell diameter. This suggests that much of the visceral mass may have been housed within the siphuncle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilus
The nautilus (, ) is a pelagic marine mollusc of the cephalopod family Nautilidae. The nautilus is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and of its smaller but near equal suborder, Nautilina. It comprises six living species in two genera, the type of which is the genus ''Nautilus''. Though it more specifically refers to species ''Nautilus pompilius'', the name chambered nautilus is also used for any of the Nautilidae. All are protected under CITES Appendix II. Depending on species, adult shell diameter is between 4 and 10 inches. Nautilidae, both extant and extinct, are characterized by involute or more or less convolute shells that are generally smooth, with compressed or depressed whorl sections, straight to sinuous sutures, and a tubular, generally central siphuncle.Kümmel, B. 1964. Nautiloidae-Nautilida, in the Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology, Geological Society of America and Univ of Kansas Press, Teichert and Moore eds. Having survived relatively u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarphycerida
The Tarphycerida were the first of the coiled cephalopods, found in marine sediments from the Lower Ordovician (middle and upper Canad) to the Middle Devonian. Some, such as '' Aphetoceras'' and '' Estonioceras'', are loosely coiled and gyroconic; others, such as '' Campbelloceras'', '' Tarphyceras'', and '' Trocholites'', are tightly coiled, but evolute with all whorls showing. The body chamber of tarphycerids is typically long and tubular,Furnish and Glenister 1964; Nautiloidea - Tarphycerida; In the ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' Vol K; Teichert and Moore, (eds) GSA and U of Kansas Press 1964 as much as half the length of the containing whorl in most, greater than in the Silurian Ophidioceratidae. The Tarphycerida evolved from the elongated, compressed, exogastric Bassleroceratidae, probably ''Bassleroceras'', around the end of the Gasconadian through forms like ''Aphetoceras''. Close coiling developed rather quickly, and both gyroconic and evolute forms are fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilida
The Nautilida constitute a large and diverse order of generally coiled nautiloid cephalopods that began in the mid Paleozoic and continues to the present with a single family, the Nautilidae which includes two genera, ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus'', with six species. All told, between 22 and 34 families and 165 to 184 genera have been recognised, making this the largest order of the subclass Nautiloidea. Classification and phylogeny Current classification The current classification of the Nautilida, in prevalent use, is that of Bernhard Kummel (Kummel 1964) in the Treatise which divides the Nautilida into five superfamilies, the Aipocerataceae, Clydonautilaceae, Tainocerataceae, and Trigonocerataceae, mostly of the Paleozoic, and the later Nautilaceae. These include 22 families and some 165 or so genera (Teichert and Moore 1964) Other concepts Shimansky 1962 (in Kummel 1964) divided the Nautilida into five suborders, the mostly Paleozoic Centroceratina, Liroceratina, Rutoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plectronoceratoidea
Plectronoceratoidea is a superorder or subclass containing primitive nautiloids from the Late Cambrian and Early Ordovician. This group is best considered a paraphyletic grade of early cephalopods, as it contains the ancestors of subsequent post-Cambrian cephalopod orders. Plectronoceratoidea contains several exclusively Cambrian cephalopod orders: Plectronocerida, Protactinocerida, and Yanhecerida. Under some classification schemes, the plectronoceratoid grade may also contain the paraphyletic Cambro-Ordovician Ellesmerocerida. A few older studies consider Plectronocerida to be descended from Ellesmerocerida (rather than ancestral), but this is no longer believed to be the case. The Plectronocerida is the earliest group of the four, and may have given rise to the other three. Of these four orders, only the Ellesmerocerida crossed (barely) into the Ordovician, with two genera, '' Ectenolites'' and ''Clarkoceras''. Ordovician ellesmerocerids in turn likely gave rise to several new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautilus (genus)
''Nautilus'' is a genus of cephalopods in the family Nautilidae. Species in this genus differ significantly in terms of morphology from those placed in the sister taxon ''Allonautilus''. The oldest fossils of the genus are known from the Late Eocene Hoko River Formation, in Washington State and from Late-Eocene to Early Oligocene sediments in Kazakhstan. The oldest fossils of the modern species ''Nautilus pompilius'' are from Early Pleistocene sediments off the coast of Luzon in the Philippines. The commonly used term 'nautilus' usually refers to any of the surviving members of ''Nautilidae'', and more specifically to the ''Nautilus pompilius'' species. The entire family of ''Nautilidae'', including all species in the genera ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus'', is listed on Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). The current consensus is that the genus consists of four valid species, although this remains the sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiceratoidea
Multiceratoidea is a major subclass or superorder of Paleozoic nautiloid cephalopods. Members of this group can be characterized by nautilosiphonate connecting rings, with an organic inner layer and outer layer of calcitic spherules and blades, similar to the modern nautilus. The earliest-diverging multiceratoids have oncomyarian muscle scars (with numerous small muscle attachments ringing the body chamber), though several orders trend towards a ventromyarian condition (with muscle scar area concentrated at the bottom of the body chamber). Multiceratoid shells are generally short and curled, with a relatively small aperture (opening). Cameral deposits are never found among the multiceratoids, though several orders are known to bear endosiphuncular deposits within their siphuncles. When originally defined in 2013, Multiceratoidea included four nautiloid orders: Ellesmerocerida, Oncocerida, Discosorida, and Ascocerida. The order Tarphycerida was considered a potential member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoidea
Subclass (biology), Subclass Coleoidea, or Dibranchiata, is the grouping of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group, Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal cuttlebone, gladius (cephalopod), gladius, or shell that is used for buoyancy or support. Some species have lost their cuttlebone altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure. A unique trait of the group is the ability to edit their own RNA. The major divisions of Coleoidea are based upon the number of cephalopod limb, arms or tentacles and their structure. The extinct and most primitive form, the Belemnoidea, presumably had ten equally-sized arms in five pairs numbered Dorsum (biology), dorsal to ventral as I, II, III, IV and V. More modern species either modified or lost a pair of arms. The superor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)