|
Nanotube
A nanotube is a nanometer-scale hollow tube-like structure. Kinds of nanotubes * BCN nanotube, composed of comparable amounts of boron, carbon, and nitrogen atoms * Boron nitride nanotube, a polymorph of boron nitride * Carbon nanotube, includes general nanotube terminology and diagrams * DNA nanotechnology#DNA nanotubes, DNA nanotube, a two-dimensional lattice which curves back upon itself, somewhat similar in size and shape to a carbon nanotube * Gallium nitride nanotube, a nanotube of gallium nitride * Silicon nanotube, made of silicon atoms * Non-carbon nanotube, especially Tungsten(IV) sulfide#Nanotubes, tungsten(IV) sulfide nanotubes * Tunneling nanotube, a tubular membrane connection between cells * Titanium dioxide#Nanotubes, Titanium nanotubes, created by the conversion of the mineral anatase by hydrothermal synthesis References {{chemistry index ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
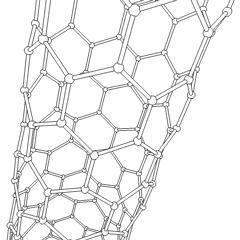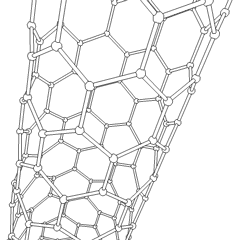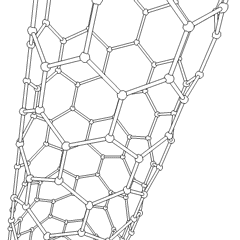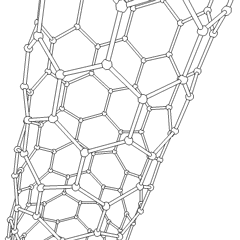
Carbon Nanotube
A scanning tunneling microscopy image of a single-walled carbon nanotube Rotating single-walled zigzag carbon nanotube A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with diameters typically measured in nanometers. ''Single-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') are one of the allotropes of carbon, intermediate between fullerene cages and flat graphene, with diameters in the range of a nanometre. Although not made this way, single-wall carbon nanotubes can be idealized as cutouts from a two-dimensional Hexagonal tiling, hexagonal lattice of carbon atoms rolled up along one of the Bravais lattice vectors of the hexagonal lattice to form a hollow cylinder. In this construction, periodic boundary conditions are imposed over the length of this roll-up vector to yield a helical lattice of seamlessly bonded carbon atoms on the cylinder surface. ''Multi-wall carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consisting of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes weakly bound together by van der Waals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-carbon Nanotube
A non-carbon nanotube is a cylindrical molecule often composed of metal oxides, or group III-Nitrides and morphologically similar to a carbon nanotube. Non-carbon nanotubes have been observed to occur naturally in some mineral deposits. A few years after Linus Pauling mentioned the possibility of curved layers in minerals as early as 1930, some minerals such as white asbestos (or chrysotile) and imogolite were actually shown to have a tubular structure. However, the first synthetic non-carbon nanotubes did not appear until Reshef Tenne ''et al.'' reported the synthesis of nanotubes composed of tungsten disulfide (WS2) in 1992. In the intervening years, nanotubes have been synthesised of many non-carbon materials, such as vanadium oxide and manganese oxide, and are being researched for such applications as redox catalysts and cathode materials for batteries. History and occurrence Non-carbon nanotubes are morphologically similar to carbon nanotubes and are observed in some minera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunneling Nanotube
A tunneling nanotube (TNT) or membrane nanotube is a term that has been applied to protrusions that extend from the plasma membrane which enable different animal cells to touch over long distances, sometimes over 100 μm between T cells. Two types of structures have been called nanotubes. The first type are less than 0.7 micrometers in diameter, contain actin and carry portions of plasma membrane between cells in both directions. The second type are larger (>0.7 μm), contain both actin and microtubules, and can carry components of the cytoplasm such as vesicles and organelles between cells, including whole mitochondria. The diameter of TNTs ranges from 50 to 200 nm and they can reach lengths of several cell diameters. These structures may be involved in cell-to-cell communication, transfer of nucleic acids such as mRNA and miRNA between cells in culture or in a tissue, and the spread of pathogens or toxins such as HIV and prions. TNTs have observed lifetimes ranging from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Nitride Nanotube
Boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) are a polymorph of boron nitride. They were predicted in 1994 and experimentally discovered in 1995. Structurally they are similar to carbon nanotubes, which are cylinders with sub-micrometer diameters and micrometer lengths, except that carbon atoms are alternately substituted by nitrogen and boron atoms. However, the properties of BN nanotubes are very different: whereas carbon nanotubes can be metallic or semiconducting depending on the rolling direction and radius, a BN nanotube is an electrical insulator with a bandgap of ~5.5 eV, basically independent of tube chirality and morphology. In addition, a layered BN structure is much more thermally and chemically stable than a graphitic carbon structure. BNNTs have unique physical and chemical properties, when compared to Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) providing a very wide range of commercial and scientific applications. Although BNNTs and CNTs share similar tensile strength properties of circa 100 times s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten(IV) Sulfide
Tungsten disulfide is an inorganic chemical compound composed of tungsten and sulfur with the chemical formula WS2. This compound is part of the group of materials called the transition metal dichalcogenides. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral tungstenite. This material is a component of certain catalysts used for hydrodesulfurization and hydrodenitrification. WS2 adopts a layered structure similar, or isotypic with MoS2, instead with W atoms situated in trigonal prismatic coordination sphere (in place of Mo atoms). Owing to this layered structure, WS2 forms non-carbon nanotubes, which were discovered after heating a thin sample of WS2 in 1992. Structure and physical properties Bulk WS2 forms dark gray hexagonal crystals with a layered structure. Like the closely related MoS2, it exhibits properties of a dry lubricant. Although it has long been thought that WS2 is relatively stable in ambient air, recent reports on the ambient air oxidation of monolayer WS2 have found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Nanotechnology
DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, and functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins to determine structures. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated. The conceptual foundation for DNA nanotechnology was first laid out by Nadrian Seeman in the early 1980s, and the field began to attract widespread int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCN Nanotube
BCN nanotubes are tubular structures with a sub-micrometer diameter and a length much longer than diameter. They are composed of comparable amounts of boron, carbon and nitrogen atoms. First made in 1994, synthesis methods have included: arc-discharge, laser ablation, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), template route, and pyrolysis techniques. Single-walled B–C–N nanotubes have been made with a hot-filament method. Solvothermal synthesis Vertically aligned arrays of ~BC2N nanotubes can be produced by solvothermal synthesis in a stainless steel autoclave An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilizati ... from a mixture of sodium azide (NaN3), ammonium fluoroborate (NH4BF4) and methyl cyanide (CH3CN). The mixture, together with the solvent and other additives is heated to 400&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Nitride Nanotube
Gallium is a chemical element with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Discovered by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in 1875, Gallium is in group 13 of the periodic table and is similar to the other metals of the group (aluminium, indium, and thallium). Elemental gallium is a soft, silvery metal in standard temperature and pressure. In its liquid state, it becomes silvery white. If too much force is applied, the gallium may fracture conchoidally. Since its discovery in 1875, gallium has widely been used to make alloys with low melting points. It is also used in semiconductors, as a dopant in semiconductor substrates. The melting point of gallium is used as a temperature reference point. Gallium alloys are used in thermometers as a non-toxic and environmentally friendly alternative to mercury, and can withstand higher temperatures than mercury. An even lower melting point of , well below the freezing point of water, is claimed for the alloy galinstan (62–� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Nanotube
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |